Recruitment of calcium-permeable AMPA receptors during synaptic potentiation is regulated by CaM-kinase I
- PMID: 18524905
- PMCID: PMC2671029
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0384-08.2008
Recruitment of calcium-permeable AMPA receptors during synaptic potentiation is regulated by CaM-kinase I
Abstract
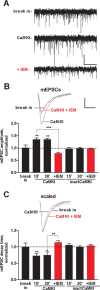
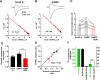
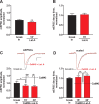
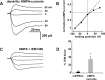
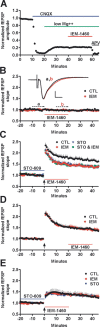
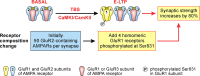
Ca(2+)-permeable AMPA receptors (CP-AMPARs) at central glutamatergic synapses are of special interest because of their unique biophysical and signaling properties that contribute to synaptic plasticity and their roles in multiple neuropathologies. However, intracellular signaling pathways that recruit synaptic CP-AMPARs are unknown, and involvement of CP-AMPARs in hippocampal region CA1 synaptic plasticity is controversial. Here, we report that intracellular infusion of active CaM-kinase I (CaMKI) into cultured hippocampal neurons enhances miniature EPSC amplitude because of recruitment of CP-AMPARs, likely from an extrasynaptic pool. The ability of CaMKI, which regulates the actin cytoskeleton, to recruit synaptic CP-AMPARs was blocked by inhibiting actin polymerization with latrunculin A. CaMK regulation of CP-AMPARs was also confirmed in hippocampal slices. CA1 long-term potentiation (LTP) after theta bursts, but not high-frequency tetani, produced a rapid, transient expression of synaptic CP-AMPARs that facilitated LTP. This component of TBS LTP was blocked by inhibition of CaM-kinase kinase (CaMKK), the upstream activator of CaMKI. Our calculations show that adding CP-AMPARs numbering <5% of existing synaptic AMPARs is sufficient to account for the potentiation observed in LTP. Thus, synaptic expression of CP-AMPARs is a very efficient mechanism for rapid enhancement of synaptic strength that depends on CaMKK/CaMKI signaling, actin dynamics, and the pattern of synaptic activity used to induce CA1 LTP.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Long-term potentiation-dependent spine enlargement requires synaptic Ca2+-permeable AMPA receptors recruited by CaM-kinase I.J Neurosci. 2010 Sep 1;30(35):11565-75. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1746-10.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20810878 Free PMC article.
-
Ca(2+) permeable AMPA receptor induced long-term potentiation requires PI3/MAP kinases but not Ca/CaM-dependent kinase II.PLoS One. 2009;4(2):e4339. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0004339. Epub 2009 Feb 3. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19190753 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium-Permeable AMPA Receptors Mediate the Induction of the Protein Kinase A-Dependent Component of Long-Term Potentiation in the Hippocampus.J Neurosci. 2016 Jan 13;36(2):622-31. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3625-15.2016. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 26758849 Free PMC article.
-
How Ca2+-permeable AMPA receptors, the kinase PKA, and the phosphatase PP2B are intertwined in synaptic LTP and LTD.Sci Signal. 2016 Apr 26;9(425):e2. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aaf7067. Sci Signal. 2016. PMID: 27117250 Review.
-
The Role of Calcium-Permeable AMPARs in Long-Term Potentiation at Principal Neurons in the Rodent Hippocampus.Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2018 Nov 22;10:42. doi: 10.3389/fnsyn.2018.00042. eCollection 2018. Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30524263 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Alcohol Exposure Induces Depressive and Anxiety-like Behaviors via Activating Ferroptosis in Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 10;23(22):13828. doi: 10.3390/ijms232213828. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36430312 Free PMC article.
-
CaMKII binding to GluN2B is critical during memory consolidation.EMBO J. 2012 Mar 7;31(5):1203-16. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2011.482. Epub 2012 Jan 10. EMBO J. 2012. PMID: 22234183 Free PMC article.
-
Calmodulin-kinases: modulators of neuronal development and plasticity.Neuron. 2008 Sep 25;59(6):914-31. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2008.08.021. Neuron. 2008. PMID: 18817731 Free PMC article. Review.
-
AMPA-Type Glutamate Receptor Conductance Changes and Plasticity: Still a Lot of Noise.Neurochem Res. 2019 Mar;44(3):539-548. doi: 10.1007/s11064-018-2491-1. Epub 2018 Feb 23. Neurochem Res. 2019. PMID: 29476449 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spinal AMPA receptors: Amenable players in central sensitization for chronic pain therapy?Channels (Austin). 2021 Dec;15(1):284-297. doi: 10.1080/19336950.2021.1885836. Channels (Austin). 2021. PMID: 33565904 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Barria A, Derkach V, Soderling T. Identification of the Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II regulatory phosphorylation site in the alpha-amino-3-hydroxyl-5-methyl-4-isoxazole-propionate-type glutamate receptor. J Biol Chem. 1997a;272:32727–32730. - PubMed
-
- Barria A, Muller D, Derkach V, Griffith LC, Soderling TR. Regulatory phosphorylation of AMPA-type glutamate receptors by CaM-KII during long-term potentiation. Science. 1997b;276:2042–2045. - PubMed
-
- Benke TA, Luthi A, Isaac JT, Collingridge GL. Modulation of AMPA receptor unitary conductance by synaptic activity. Nature. 1998;393:793–797. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
