Inhibition of p38 MAPK suppresses inflammatory cytokine induction by etoposide, 5-fluorouracil, and doxorubicin without affecting tumoricidal activity
- PMID: 18523641
- PMCID: PMC2396285
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0002355
Inhibition of p38 MAPK suppresses inflammatory cytokine induction by etoposide, 5-fluorouracil, and doxorubicin without affecting tumoricidal activity
Abstract
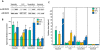
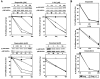
Cancer patients undergoing treatment with systemic cancer chemotherapy drugs often experience debilitating fatigue similar to sickness behavior, a normal response to infection or tissue damage caused by the production of the inflammatory cytokines IL-1beta, TNF-alpha, and IL-6. The p38 mitogen activated protein kinase (p38 MAPK) plays a central role in the production of these cytokines and consequently the development of sickness behavior. Targeted inhibitors of p38 MAPK can reduce systemic inflammatory cytokine production and the development of sickness behavior. Several systemic cancer chemotherapy drugs have been shown to stimulate inflammatory cytokine production, yet whether this response is related to a common ability to activate p38 MAPK is not known and is the focus of this study. This understanding may present the possibility of using p38 MAPK inhibitors to reduce chemotherapy-induced inflammatory cytokine production and consequently treatment-related fatigue. One caveat of this approach is a potential reduction in chemotherapeutic efficacy as some believe that p38 MAPK activity is required for chemotherapy-induced cytotoxicity of tumor cells. The purpose of this study was to demonstrate proof of principal that p38 MAPK inhibition can block chemotherapy-induced inflammatory cytokine production without inhibiting drug-induced cytotoxicity using murine peritoneal macrophages and Lewis Lung Carcinoma (LLC1) cells as model cell systems. Using these cells we assessed the requirement of etoposide, doxorubicin, 5-fluorouracil, and docetaxel for p38 MAPK in inflammatory cytokine production and cytotoxicity. Study findings demonstrate that clinically relevant doses of etoposide, doxorubicin, and 5-FU activated p38 MAPK in both macrophages and LLC1 cells. In contrast, docetaxel failed to activate p38 MAPK in either cell type. Activation of p38 MAPK mediated the drug's effects on inflammatory cytokine production in macrophages but not LLC1 cytotoxicity and this was confirmed with inhibitor studies.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
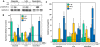
Similar articles
-
The cancer chemotherapy drug etoposide (VP-16) induces proinflammatory cytokine production and sickness behavior-like symptoms in a mouse model of cancer chemotherapy-related symptoms.Biol Res Nurs. 2006 Oct;8(2):157-69. doi: 10.1177/1099800406290932. Biol Res Nurs. 2006. PMID: 17003255
-
Strong inhibition of TNF-alpha production and inhibition of IL-8 and COX-2 mRNA expression in monocyte-derived macrophages by RWJ 67657, a p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) inhibitor.Arthritis Res Ther. 2004;6(4):R384-92. doi: 10.1186/ar1204. Epub 2004 Jun 21. Arthritis Res Ther. 2004. PMID: 15225374 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of p38 MAPK-dependent excision repair cross-complementing 1 expression decreases the DNA repair capacity to sensitize lung cancer cells to etoposide.Mol Cancer Ther. 2012 Mar;11(3):561-71. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-11-0684. Epub 2011 Nov 3. Mol Cancer Ther. 2012. PMID: 22053010
-
The potential of p38 MAPK inhibitors to modulate periodontal infections.Curr Drug Metab. 2009 Jan;10(1):55-67. doi: 10.2174/138920009787048347. Curr Drug Metab. 2009. PMID: 19149513 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic potential of p38 MAP kinase inhibition in the management of cardiovascular disease.Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2014 Jun;14(3):155-65. doi: 10.1007/s40256-014-0063-6. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2014. PMID: 24504769 Review.
Cited by
-
Losmapimod ameliorates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity through attenuating senescence and inflammatory pathways.Biomed Pharmacother. 2024 Oct;179:117288. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.117288. Epub 2024 Aug 14. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024. PMID: 39146767 Free PMC article.
-
The Analysis of Differentially Expressed circRNAs Under the Antiproliferative Effect From 5-Fluorouracil on Osteosarcoma Cells.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2020 Jan-Dec;19:1533033820964215. doi: 10.1177/1533033820964215. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2020. PMID: 33308021 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of plasma complement by the initial dose of epirubicin/docetaxel therapy in breast cancer and its predictive value.Br J Cancer. 2010 Oct 12;103(8):1201-8. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6605909. Epub 2010 Sep 28. Br J Cancer. 2010. PMID: 20877360 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
ZAK is required for doxorubicin, a novel ribotoxic stressor, to induce SAPK activation and apoptosis in HaCaT cells.Cancer Biol Ther. 2010 Aug 1;10(3):258-66. doi: 10.4161/cbt.10.3.12367. Epub 2010 Aug 13. Cancer Biol Ther. 2010. PMID: 20559024 Free PMC article.
-
Small molecule kinase inhibitors block the ZAK-dependent inflammatory effects of doxorubicin.Cancer Biol Ther. 2013 Jan;14(1):56-63. doi: 10.4161/cbt.22628. Epub 2012 Oct 31. Cancer Biol Ther. 2013. PMID: 23114643 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vollmer-Conna U, Fazou C, Cameron B, Li H, Brennan C, et al. Production of pro-inflammatory cytokines correlates with the symptoms of acute sickness behaviour in humans. Psychol Med. 2004;34:1289–1297. - PubMed
-
- Teeling JL, Felton LM, Deacon RM, Cunningham C, Rawlins JN, et al. Sub-pyrogenic systemic inflammation impacts on brain and behavior, independent of cytokines. Brain Behav Immun 2007 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

