Reprogramming of pancreatic beta cells into induced pluripotent stem cells
- PMID: 18501604
- PMCID: PMC2819222
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2008.05.010
Reprogramming of pancreatic beta cells into induced pluripotent stem cells
Abstract
Induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells have been derived from fibroblast, stomach, and liver cultures at extremely low frequencies by ectopic expression of the transcription factors Oct4, Sox2, c-myc, and Klf4, a process coined direct or in vitro reprogramming [1-8]. iPS cells are molecularly and functionally highly similar to embryonic stem cells (ESCs), including their ability to contribute to all tissues as well as the germline in mice. The heterogeneity of the starting cell populations and the low efficiency of reprogramming suggested that a rare cell type, such as an adult stem cell, might be the cell of origin for iPS cells and that differentiated cells are refractory to reprogramming. Here, we used inducible lentiviruses [9] to express Oct4, Sox2, c-myc, and Klf4 in pancreatic beta cells to assess whether a defined terminally differentiated cell type remains amenable to reprogramming. Genetically marked beta cells gave rise to iPS cells that expressed pluripotency markers, formed teratomas, and contributed to cell types of all germ layers in chimeric animals. Our results provide genetic proof that terminally differentiated cells can be reprogrammed into pluripotent cells, suggesting that in vitro reprogramming is not restricted to certain cell types or differentiation stages.
Figures
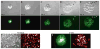
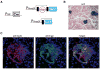
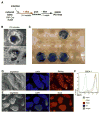
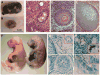
Similar articles
-
A Versatile In Vivo System to Study Myc in Cell Reprogramming.Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2318:267-279. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1476-1_14. Methods Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 34019296
-
Pluripotent stem cells induced from adult neural stem cells by reprogramming with two factors.Nature. 2008 Jul 31;454(7204):646-50. doi: 10.1038/nature07061. Epub 2008 Jun 29. Nature. 2008. PMID: 18594515
-
Generation of induced pluripotent stem cells by reprogramming mouse embryonic fibroblasts with a four transcription factor, doxycycline inducible lentiviral transduction system.J Vis Exp. 2009 Nov 13;(33):1447. doi: 10.3791/1447. J Vis Exp. 2009. PMID: 19915522 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging methods for preparing iPS cells.Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2012 Sep;42(9):773-9. doi: 10.1093/jjco/hys108. Epub 2012 Jul 23. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22826352 Review.
-
[Induced pluripotent stem cells].Genetika. 2009 Feb;45(2):160-8. Genetika. 2009. PMID: 19334609 Review. Russian.
Cited by
-
Pluripotency of human embryonic and induced pluripotent stem cells for cardiac and vascular regeneration.Thromb Haemost. 2010 Jul;104(1):23-9. doi: 10.1160/TH09-07-0507. Epub 2010 May 10. Thromb Haemost. 2010. PMID: 20458433 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Variation in mesodermal and hematopoietic potential of adult skin-derived induced pluripotent stem cell lines in mice.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2011 Nov;7(4):958-68. doi: 10.1007/s12015-011-9249-3. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2011. PMID: 21424235
-
Reprogramming of postnatal neurons into induced pluripotent stem cells by defined factors.Stem Cells. 2011 Jun;29(6):992-1000. doi: 10.1002/stem.641. Stem Cells. 2011. PMID: 21563275 Free PMC article.
-
Generation of Insulin-Expressing Cells in Mouse Small Intestine by Pdx1, MafA, and BETA2/NeuroD.Diabetes Metab J. 2017 Oct;41(5):405-416. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2017.41.5.405. Diabetes Metab J. 2017. PMID: 29086539 Free PMC article.
-
A poor imitation of a natural process: a call to reconsider the iPSC engineering technique.Cell Cycle. 2012 Dec 15;11(24):4536-44. doi: 10.4161/cc.22575. Epub 2012 Oct 31. Cell Cycle. 2012. PMID: 23114619 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Maherali N, Sridharan R, Xie W, Utikal J, Eminli S, Arnold K, Stadtfeld M, Yachechko R, Tchieu J, Jaenisch R, et al. Directly reprogrammed fibroblasts show global epigenetic reprogramming and widespread tissue contribution. Cell Stem Cell. 2007;1:55–70. - PubMed
-
- Wernig M, Meissner A, Foreman R, Brambrink T, Ku M, Hochedlinger K, Bernstein BE, Jaenisch R. In vitro reprogramming of fibroblasts into a pluripotent ES-cell-like state. Nature. 2007;448:318–324. - PubMed
-
- Okita K, Ichisaka T, Yamanaka S. Generation of germline-competent induced pluripotent stem cells. Nature. 2007;448:313–317. - PubMed
-
- Takahashi K, Tanabe K, Ohnuki M, Narita M, Ichisaka T, Tomoda K, Yamanaka S. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from adult human fibroblasts by defined factors. Cell. 2007;131:861–872. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

