Interstrand DNA cross-links induced by alpha,beta-unsaturated aldehydes derived from lipid peroxidation and environmental sources
- PMID: 18500830
- PMCID: PMC2785109
- DOI: 10.1021/ar700246x
Interstrand DNA cross-links induced by alpha,beta-unsaturated aldehydes derived from lipid peroxidation and environmental sources
Abstract
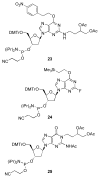
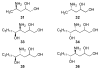
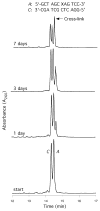
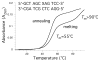
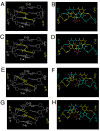
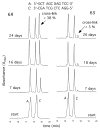
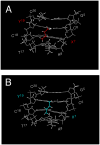
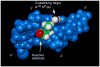
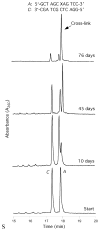
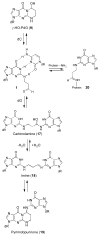
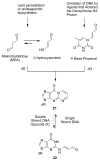
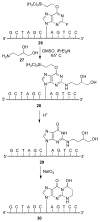
Significant levels of the 1, N(2)-gamma-hydroxypropano-dG adducts of the alpha,beta-unsaturated aldehydes acrolein, crotonaldehyde, and 4-hydroxy-2E-nonenal (HNE) have been identified in human DNA, arising from both exogenous and endogenous exposures. They yield interstrand DNA cross-links between guanines in the neighboring C.G and G.C base pairs located in 5'-CpG-3' sequences, as a result of opening of the 1,N(2)-gamma-hydroxypropano-dG adducts to form reactive aldehydes that are positioned within the minor groove of duplex DNA. Using a combination of chemical, spectroscopic, and computational methods, we have elucidated the chemistry of cross-link formation in duplex DNA. NMR spectroscopy revealed that, at equilibrium, the acrolein and crotonaldehyde cross-links consist primarily of interstrand carbinolamine linkages between the exocyclic amines of the two guanines located in the neighboring C.G and G.C base pairs located in 5'-CpG-3' sequences, that maintain the Watson-Crick hydrogen bonding of the cross-linked base pairs. The ability of crotonaldehyde and HNE to form interstrand cross-links depends upon their common relative stereochemistry at the C6 position of the 1,N(2)-gamma-hydroxypropano-dG adduct. The stereochemistry at this center modulates the orientation of the reactive aldehyde within the minor groove of the double-stranded DNA, either facilitating or hindering the cross-linking reactions; it also affects the stabilities of the resulting diastereoisomeric cross-links. The presence of these cross-links in vivo is anticipated to interfere with DNA replication and transcription, thereby contributing to the etiology of human disease. Reduced derivatives of these cross-links are useful tools for studying their biological processing.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Chemistry and biology of DNA containing 1,N(2)-deoxyguanosine adducts of the alpha,beta-unsaturated aldehydes acrolein, crotonaldehyde, and 4-hydroxynonenal.Chem Res Toxicol. 2009 May;22(5):759-78. doi: 10.1021/tx9000489. Chem Res Toxicol. 2009. PMID: 19397281 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stereospecific formation of interstrand carbinolamine DNA cross-links by crotonaldehyde- and acetaldehyde-derived alpha-CH3-gamma-OH-1,N2-propano-2'-deoxyguanosine adducts in the 5'-CpG-3' sequence.Chem Res Toxicol. 2006 Feb;19(2):195-208. doi: 10.1021/tx050239z. Chem Res Toxicol. 2006. PMID: 16485895 Free PMC article.
-
Spectroscopic characterization of interstrand carbinolamine cross-links formed in the 5'-CpG-3' sequence by the acrolein-derived gamma-OH-1,N2-propano-2'-deoxyguanosine DNA adduct.J Am Chem Soc. 2005 Dec 21;127(50):17686-96. doi: 10.1021/ja053897e. J Am Chem Soc. 2005. PMID: 16351098 Free PMC article.
-
Rearrangement of the (6S,8R,11S) and (6R,8S,11R) exocyclic 1,N2-deoxyguanosine adducts of trans-4-hydroxynonenal to N2-deoxyguanosine cyclic hemiacetal adducts when placed complementary to cytosine in duplex DNA.J Am Chem Soc. 2008 Aug 20;130(33):10898-906. doi: 10.1021/ja801824b. Epub 2008 Jul 29. J Am Chem Soc. 2008. PMID: 18661996 Free PMC article.
-
DNA cross-link induced by trans-4-hydroxynonenal.Environ Mol Mutagen. 2010 Jul;51(6):625-34. doi: 10.1002/em.20599. Environ Mol Mutagen. 2010. PMID: 20577992 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Fanconi anaemia pathway: new players and new functions.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2016 Jun;17(6):337-49. doi: 10.1038/nrm.2016.48. Epub 2016 May 5. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 27145721 Review.
-
The Fanconi anemia pathway and ICL repair: implications for cancer therapy.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2010 Oct;45(5):424-39. doi: 10.3109/10409238.2010.502166. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 20807115 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chemistry and biology of DNA containing 1,N(2)-deoxyguanosine adducts of the alpha,beta-unsaturated aldehydes acrolein, crotonaldehyde, and 4-hydroxynonenal.Chem Res Toxicol. 2009 May;22(5):759-78. doi: 10.1021/tx9000489. Chem Res Toxicol. 2009. PMID: 19397281 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Formation and Repair of an Interstrand DNA Cross-Link Arising from a Common Endogenous Lesion.J Am Chem Soc. 2021 Sep 22;143(37):15344-15357. doi: 10.1021/jacs.1c06926. Epub 2021 Sep 13. J Am Chem Soc. 2021. PMID: 34516735 Free PMC article.
-
Nucleotide excision repair of chemically stabilized analogues of DNA interstrand cross-links produced from oxidized abasic sites.Biochemistry. 2014 Sep 23;53(37):5958-65. doi: 10.1021/bi500914d. Epub 2014 Sep 10. Biochemistry. 2014. PMID: 25208227 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Burcham PC. Genotoxic lipid peroxidation products: Their DNA damaging properties and role in formation of endogenous DNA adducts. Mutagenesis. 1998;13:287–305. - PubMed
-
- Chung FL, Nath RG, Nagao M, Nishikawa A, Zhou GD, Randerath K. Endogenous formation and significance of 1,N2-propanodeoxyguanosine adducts. Mutat Res. 1999;424:71–81. - PubMed
-
- Chung FL, Zhang L, Ocando JE, Nath RG. Role of 1,N2-propanodeoxyguanosine adducts as endogenous DNA lesions in rodents and humans. IARC Sci Pub. 1999;150:45–54. - PubMed
-
- Nair U, Bartsch H, Nair J. Lipid peroxidation-induced DNA damage in cancer-prone inflammatory diseases: A review of published adduct types and levels in humans. Free Radic Biol Med. 2007;43:1109–1120. - PubMed
-
- Hecht SS, Upadhyaya P, Wang M. Reactions of α-acetoxy-N-nitrosopyrrolidine and crotonaldehyde with DNA. IARC Sci Pub. 1999;150:147–154. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

