BMP signaling dynamics in embryonic orofacial tissue
- PMID: 18446813
- PMCID: PMC2746655
- DOI: 10.1002/jcp.21455
BMP signaling dynamics in embryonic orofacial tissue
Abstract
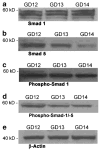
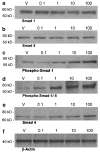
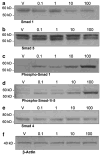
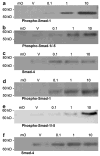
The bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) family represents a class of signaling molecules, that plays key roles in morphogenesis, cell proliferation, survival and differentiation during normal development. Members of this family are essential for the development of the mammalian orofacial region where they regulate cell proliferation, extracellular matrix synthesis, and cellular differentiation. Perturbation of any of these processes results in orofacial clefting. Embryonic orofacial tissue expresses BMP mRNAs, their cognate proteins, and BMP-specific receptors in unique temporo-spatial patterns, suggesting functional roles in orofacial development. However, specific genes that function as downstream mediators of BMP action during orofacial ontogenesis have not been well defined. In the current study, elements of the Smad component of the BMP intracellular signaling system were identified and characterized in embryonic orofacial tissue and functional activation of the Smad pathway by BMP2 and BMP4 was demonstrated. BMP2 and BMP4-initiated Smad signaling in cells derived from embryonic orofacial tissue was found to result in: (1) phosphorylation of Smads 1 and 5; (2) nuclear translocation of Smads 1, 4, and 5; (3) binding of Smads 1, 4, and 5 to a consensus Smad binding element (SBE)-containing oligonucleotide; (4) transactivation of transfected reporter constructs, containing BMP-inducible Smad response elements; and (5) increased expression at transcriptional as well as translational levels of Id3 (endogenous gene containing BMP receptor-specific Smad response elements). Collectively, these data document the existence of a functional Smad-mediated BMP signaling system in cells of the developing murine orofacial region.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Intracellular dynamics of Smad-mediated TGFbeta signaling.J Cell Physiol. 2003 Nov;197(2):261-71. doi: 10.1002/jcp.10355. J Cell Physiol. 2003. PMID: 14502566
-
DRAGON, a bone morphogenetic protein co-receptor.J Biol Chem. 2005 Apr 8;280(14):14122-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M410034200. Epub 2005 Jan 25. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15671031
-
Temporal regulation of mRNAs for select bone morphogenetic proteins (BMP), BMP receptors and their associated SMAD proteins during bovine early embryonic development: effects of exogenous BMP2 on embryo developmental progression.Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2014 Jul 15;12:67. doi: 10.1186/1477-7827-12-67. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2014. PMID: 25027287 Free PMC article.
-
Bone morphogenetic protein receptor signal transduction in human disease.J Pathol. 2019 Jan;247(1):9-20. doi: 10.1002/path.5170. Epub 2018 Nov 27. J Pathol. 2019. PMID: 30246251 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bone morphogenetic proteins.Growth Factors. 2004 Dec;22(4):233-41. doi: 10.1080/08977190412331279890. Growth Factors. 2004. PMID: 15621726 Review.
Cited by
-
Alcohol modulates expression of DNA methyltranferases and methyl CpG-/CpG domain-binding proteins in murine embryonic fibroblasts.Reprod Toxicol. 2013 Jun;37:40-8. doi: 10.1016/j.reprotox.2013.01.003. Epub 2013 Feb 6. Reprod Toxicol. 2013. PMID: 23395981 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic regulation of Sox4 during palate development.Epigenomics. 2013 Apr;5(2):131-46. doi: 10.2217/epi.13.1. Epigenomics. 2013. PMID: 23566091 Free PMC article.
-
Palate morphogenesis: current understanding and future directions.Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today. 2010 Jun;90(2):133-54. doi: 10.1002/bdrc.20180. Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today. 2010. PMID: 20544696 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Suppression of chondrogenesis by Id helix-loop-helix proteins in murine embryonic orofacial tissue.Differentiation. 2009 Jun;77(5):462-72. doi: 10.1016/j.diff.2009.02.002. Epub 2009 Apr 5. Differentiation. 2009. PMID: 19349107 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway mediates bone morphogenetic protein 2-induced invasion of pancreatic cancer cells Panc-1.Pathol Oncol Res. 2011 Jun;17(2):257-61. doi: 10.1007/s12253-010-9307-1. Epub 2010 Sep 17. Pathol Oncol Res. 2011. PMID: 20848249
References
-
- Abramoff MD, Magelhaes PJ, Ram SJ. Image processing with image. J Biophotons Int. 2004;11:36–42.
-
- Anderson RM, Lawrence AR, Stottmann RW, Bachiller D, Klingensmith J. Chordin and noggin promote organizing centers of forebrain development in the mouse. Development. 2002;129:4975–4987. - PubMed
-
- Barlow AJ, Francis-West PH. Ectopic application of recombinant BMP-2 and BMP-4 can change patterning of developing chick facial primordia. Development. 1997;124:391–398. - PubMed
-
- Bennett JH, Hunt P, Thorogood P. Bone morphogenetic protein-2 and -4 expression during murine orofacial development. Arch Oral Biol. 1995;40:847–854. - PubMed
-
- Chaudhary J, Johnson J, Kim G, Skinner MK. Hormonal regulation and differential actions of the helix-loop-helix transcriptional inhibitors of differentiation (Id1, Id2, Id3, and Id4) in Sertoli cells. Endocrinology. 2001;142:1727–1736. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

