A combinatorial library of lipid-like materials for delivery of RNAi therapeutics
- PMID: 18438401
- PMCID: PMC3014085
- DOI: 10.1038/nbt1402
A combinatorial library of lipid-like materials for delivery of RNAi therapeutics
Abstract
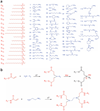
The safe and effective delivery of RNA interference (RNAi) therapeutics remains an important challenge for clinical development. The diversity of current delivery materials remains limited, in part because of their slow, multi-step syntheses. Here we describe a new class of lipid-like delivery molecules, termed lipidoids, as delivery agents for RNAi therapeutics. Chemical methods were developed to allow the rapid synthesis of a large library of over 1,200 structurally diverse lipidoids. From this library, we identified lipidoids that facilitate high levels of specific silencing of endogenous gene transcripts when formulated with either double-stranded small interfering RNA (siRNA) or single-stranded antisense 2'-O-methyl (2'-OMe) oligoribonucleotides targeting microRNA (miRNA). The safety and efficacy of lipidoids were evaluated in three animal models: mice, rats and nonhuman primates. The studies reported here suggest that these materials may have broad utility for both local and systemic delivery of RNA therapeutics.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Lipid-Based Nanocarriers for RNA Delivery.Curr Pharm Des. 2015;21(22):3140-7. doi: 10.2174/1381612821666150531164540. Curr Pharm Des. 2015. PMID: 26027572 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combinatorial library strategies for synthesis of cationic lipid-like nanoparticles and their potential medical applications.Nanomedicine (Lond). 2015 Mar;10(4):643-57. doi: 10.2217/nnm.14.192. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2015. PMID: 25723096 Review.
-
Combinatorial Synthesis of a Lipidoid Library by Thiolactone Chemistry: In Vitro Screening and In Vivo Validation for siRNA Delivery.Bioconjug Chem. 2020 Mar 18;31(3):852-860. doi: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.0c00013. Epub 2020 Feb 28. Bioconjug Chem. 2020. PMID: 32068393
-
Single-Tailed Lipidoids Enhance the Transfection Activity of Their Double-Tailed Counterparts.ACS Comb Sci. 2016 Jan 11;18(1):43-50. doi: 10.1021/acscombsci.5b00117. Epub 2015 Dec 24. ACS Comb Sci. 2016. PMID: 26651853
-
One-Pot Parallel Synthesis of Lipid Library via Thiolactone Ring Opening and Screening for Gene Delivery.Bioconjug Chem. 2018 Apr 18;29(4):992-999. doi: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.8b00007. Epub 2018 Mar 20. Bioconjug Chem. 2018. PMID: 29558113
Cited by
-
Lipid nanoparticle technology for therapeutic gene regulation in the liver.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2020;159:344-363. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2020.06.026. Epub 2020 Jul 2. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2020. PMID: 32622021 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inorganic coatings for optimized non-viral transfection of stem cells.Sci Rep. 2013;3:1567. doi: 10.1038/srep01567. Sci Rep. 2013. PMID: 23535735 Free PMC article.
-
Preclinical and clinical development of siRNA-based therapeutics.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2015 Jun 29;87:108-19. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2015.01.007. Epub 2015 Feb 7. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2015. PMID: 25666164 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pyruvate kinase M2-specific siRNA induces apoptosis and tumor regression.J Exp Med. 2012 Feb 13;209(2):217-24. doi: 10.1084/jem.20111487. Epub 2012 Jan 23. J Exp Med. 2012. PMID: 22271574 Free PMC article.
-
Topical delivery of siRNA-based spherical nucleic acid nanoparticle conjugates for gene regulation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Jul 24;109(30):11975-80. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1118425109. Epub 2012 Jul 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22773805 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Novina CD, Sharp PA. The RNAi revolution. Nature. 2004;430:161–164. - PubMed
-
- Soutschek J, et al. Therapeutic silencing of an endogenous gene by systemic administration of modified siRNAs. Nature. 2004;432:173–178. - PubMed
-
- Krutzfeldt J, et al. Silencing of microRNAs in vivo with ‘antagomirs’. Nature. 2005;438:685–689. - PubMed
-
- Bitko V, Musiyenko A, Shulyayeva O, Barik S. Inhibition of respiratory viruses by nasally administered siRNA. Nat. Med. 2005;11:50–55. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

