Shear stress influences spatial variations in vascular Mn-SOD expression: implication for LDL nitration
- PMID: 18434620
- PMCID: PMC3008554
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpcell.00518.2007
Shear stress influences spatial variations in vascular Mn-SOD expression: implication for LDL nitration
Abstract
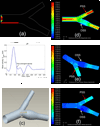
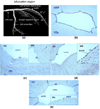
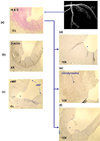
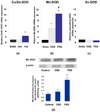
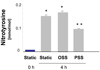
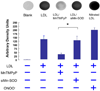
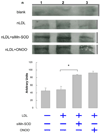
Fluid shear stress modulates vascular production of endothelial superoxide anion (O2*-) and nitric oxide (*NO). Whether the characteristics of shear stress influence the spatial variations in mitochondrial manganese superoxide dismutase (Mn-SOD) expression in vasculatures is not well defined. We constructed a three-dimensional computational fluid dynamics model simulating spatial variations in shear stress at the arterial bifurcation. In parallel, explants of arterial bifurcations were sectioned from the human left main coronary bifurcation and right coronary arteries for immunohistolocalization of Mn-SOD expression. We demonstrated that Mn-SOD staining was prominent in the pulsatile shear stress (PSS)-exposed and atheroprotective regions, but it was nearly absent in the oscillatory shear stress (OSS)-exposed regions and lateral wall of arterial bifurcation. In cultured bovine aortic endothelial cells, PSS at mean shear stress (tau ave) of 23 dyn/cm2 upregulated Mn-SOD mRNA expression at a higher level than did OSS at tau ave = 0.02 dyn/cm2 +/- 3.0 dyn.cm(-2).s(-1) and at 1 Hz (PSS by 11.3 +/- 0.4-fold vs. OSS by 5.0 +/- 0.5-fold vs. static condition; P < 0.05, n = 4). By liquid chromatography and tandem mass spectrometry, it was found that PSS decreased the extent of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) nitration, whereas OSS increased nitration (P < 0.05, n = 4). In the presence of LDL, treatment with Mn-SOD small interfering RNA increased intracellular nitrotyrosine level (P < 0.5, n = 4), a fingerprint for nitrotyrosine formation. Our findings indicate that shear stress in the atheroprone versus atheroprotective regions regulates spatial variations in mitochondrial Mn-SOD expression with an implication for modulating LDL nitration.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hemodynamics influences vascular peroxynitrite formation: Implication for low-density lipoprotein apo-B-100 nitration.Free Radic Biol Med. 2007 Feb 15;42(4):519-29. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2006.11.017. Epub 2006 Nov 21. Free Radic Biol Med. 2007. PMID: 17275684 Free PMC article.
-
Pulsatile versus oscillatory shear stress regulates NADPH oxidase subunit expression: implication for native LDL oxidation.Circ Res. 2003 Dec 12;93(12):1225-32. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000104087.29395.66. Epub 2003 Oct 30. Circ Res. 2003. PMID: 14593003 Free PMC article.
-
17beta-Estradiol reverses shear-stress-mediated low density lipoprotein modifications.Free Radic Biol Med. 2006 Aug 15;41(4):568-78. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2006.04.010. Epub 2006 Apr 26. Free Radic Biol Med. 2006. PMID: 16863990 Free PMC article.
-
Known players, new interplay in atherogenesis: Chronic shear stress and carbamylated-LDL induce and modulate expression of atherogenic LR11 in human coronary artery endothelium.Thromb Haemost. 2014 Feb;111(2):323-32. doi: 10.1160/TH12-12-0924. Epub 2013 Nov 28. Thromb Haemost. 2014. PMID: 24284991
-
Oscillatory shear stress induces mitochondrial superoxide production: implication of NADPH oxidase and c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase signaling.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2011 Sep 1;15(5):1379-88. doi: 10.1089/ars.2010.3645. Epub 2011 Apr 14. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2011. PMID: 20919940 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Stretchable electrochemical impedance sensors for intravascular detection of lipid-rich lesions in New Zealand White rabbits.Biosens Bioelectron. 2014 Apr 15;54:610-6. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2013.11.059. Epub 2013 Dec 1. Biosens Bioelectron. 2014. PMID: 24333932 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of endothelial function by mitochondrial reactive oxygen species.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2011 Sep 15;15(6):1517-30. doi: 10.1089/ars.2010.3642. Epub 2011 Apr 26. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2011. PMID: 21194353 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of endothelial mechanosensitive genes in atherosclerosis and omics approaches.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2016 Feb 1;591:111-31. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2015.11.005. Epub 2015 Dec 11. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2016. PMID: 26686737 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ambient ultrafine particles reduce endothelial nitric oxide production via S-glutathionylation of eNOS.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013 Jul 5;436(3):462-6. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.05.127. Epub 2013 Jun 7. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013. PMID: 23751346 Free PMC article.
-
A dynamic model of calcific nodule destabilization in response to monocyte- and oxidized lipid-induced matrix metalloproteinases.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2012 Feb 15;302(4):C658-65. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00313.2011. Epub 2011 Oct 26. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22031601 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ku DN, Giddens DP, Zarins CK, Glagov S. Pulsatile Flow and Atherosclerosis in the Human Carotid Bifurcation - Positive Correlation between Plaque Location and Low and Oscillating Shear-Stress. Arteriosclerosis. 1985;5:293–302. - PubMed
-
- Malek AM, Alper SL, Izumo S. Hemodynamic Shear Stress and Its Role in Atherosclerosis. Journal of American Medical Association. 1999;282:2035–2042. - PubMed
-
- Ku DN. Blood Flow in Arteries. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 1997;29:399–434.
-
- De Keulenaer GW, Chappell DC, Ishizaka N, Nerem RM, Alexander RW, Griendling KK. Oscillatory and steady laminar shear stress differentially affect human endothelial redox state: role of a superoxide-producing NADH oxidase. Circ Res. 1998;82:1094–1101. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

