A glycoconjugate antigen based on the recognition motif of a broadly neutralizing human immunodeficiency virus antibody, 2G12, is immunogenic but elicits antibodies unable to bind to the self glycans of gp120
- PMID: 18434393
- PMCID: PMC2447108
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00293-08
A glycoconjugate antigen based on the recognition motif of a broadly neutralizing human immunodeficiency virus antibody, 2G12, is immunogenic but elicits antibodies unable to bind to the self glycans of gp120
Abstract
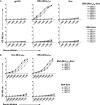
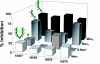
The glycan shield of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) gp120 contributes to viral evasion from humoral immune responses. However, the shield is recognized by the HIV-1 broadly neutralizing antibody (Ab), 2G12, at a relatively conserved cluster of oligomannose glycans. The discovery of 2G12 raises the possibility that a carbohydrate immunogen may be developed that could elicit 2G12-like neutralizing Abs and contribute to an AIDS vaccine. We have previously dissected the fine specificity of 2G12 and reported that the synthetic tetramannoside (Man(4)) that corresponds to the D1 arm of Man(9)GlcNAc(2) inhibits 2G12 binding to gp120 as efficiently as Man(9)GlcNAc(2) itself, indicating the potential use of Man(4) as a building block for creating immunogens. Here, we describe the development of neoglycoconjugates displaying variable copy numbers of Man(4) on bovine serum albumin (BSA) molecules by conjugation to Lys residues. The increased valency enhances the apparent affinity of 2G12 for Man(4) up to a limit which is achieved at approximately 10 copies per BSA molecule, beyond which no further enhancement is observed. Immunization of rabbits with BSA-(Man(4))(14) elicits significant serum Ab titers to Man(4). However, these Abs are unable to bind gp120. Further analysis reveals that the elicited Abs bind a variety of unbranched and, to a lesser extent, branched Man(9) derivatives but not natural N-linked oligomannose containing the chitobiose core. These results suggest that Abs can be readily elicited against the D1 arm; however, potential differences in the presentation of Man(4) on neoglycoconjugates, compared to glycoproteins, poses challenges for eliciting anti-mannose Abs capable of cross-reacting with gp120 and HIV-1.
Figures

Similar articles
-
An engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain binds the broadly neutralizing human immunodeficiency virus type 1 antibody 2G12 and elicits mannose-specific gp120-binding antibodies.J Virol. 2008 Jul;82(13):6447-57. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00412-08. Epub 2008 Apr 23. J Virol. 2008. PMID: 18434410 Free PMC article.
-
A yeast glycoprotein shows high-affinity binding to the broadly neutralizing human immunodeficiency virus antibody 2G12 and inhibits gp120 interactions with 2G12 and DC-SIGN.J Virol. 2009 May;83(10):4861-70. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02537-08. Epub 2009 Mar 4. J Virol. 2009. PMID: 19264785 Free PMC article.
-
Antibody 2G12 recognizes di-mannose equivalently in domain- and nondomain-exchanged forms but only binds the HIV-1 glycan shield if domain exchanged.J Virol. 2010 Oct;84(20):10690-9. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01110-10. Epub 2010 Aug 11. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20702629 Free PMC article.
-
Antibody responses to the HIV-1 envelope high mannose patch.Adv Immunol. 2019;143:11-73. doi: 10.1016/bs.ai.2019.08.002. Epub 2019 Sep 11. Adv Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31607367 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glycosylation of HIV-1 gp120 V3 loop: towards the rational design of a synthetic carbohydrate vaccine.Curr Med Chem. 2007;14(30):3232-42. doi: 10.2174/092986707782793826. Curr Med Chem. 2007. PMID: 18220757 Review.
Cited by
-
Recent advances on smart glycoconjugate vaccines in infections and cancer.FEBS J. 2022 Jul;289(14):4251-4303. doi: 10.1111/febs.15909. Epub 2021 Jun 1. FEBS J. 2022. PMID: 33934527 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural insights into key sites of vulnerability on HIV-1 Env and influenza HA.Immunol Rev. 2012 Nov;250(1):180-98. doi: 10.1111/imr.12005. Immunol Rev. 2012. PMID: 23046130 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prime-boost immunization of rabbits with HIV-1 gp120 elicits potent neutralization activity against a primary viral isolate.PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e52732. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0052732. Epub 2013 Jan 9. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23326351 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Antiretroviral Structures from Marine Organisms.Molecules. 2019 Sep 26;24(19):3486. doi: 10.3390/molecules24193486. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31561445 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preventive and therapeutic applications of neutralizing antibodies to Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 (HIV-1).Ther Adv Vaccines. 2013 Jul;1(2):67-80. doi: 10.1177/2051013613494534. Ther Adv Vaccines. 2013. PMID: 24757516 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baba, T. W., V. Liska, R. Hofmann-Lehmann, J. Vlasak, W. Xu, S. Ayehunie, L. A. Cavacini, M. R. Posner, H. Katinger, G. Stiegler, B. J. Bernacky, T. A. Rizvi, R. Schmidt, L. R. Hill, M. E. Keeling, Y. Lu, J. E. Wright, T. C. Chou, and R. M. Ruprecht. 2000. Human neutralizing monoclonal antibodies of the IgG1 subtype protect against mucosal simian-human immunodeficiency virus infection. Nat. Med. 6200-206. - PubMed
-
- Barbas, C. F., III, T. A. Collet, W. Amberg, P. Roben, J. M. Binley, D. Hoekstra, D. Cababa, T. M. Jones, R. A. Williamson, G. R. Pilkington, et al. 1993. Molecular profile of an antibody response to HIV-1 as probed by combinatorial libraries. J. Mol. Biol. 230812-823. - PubMed
-
- Beirnaert, E., S. De Zutter, W. Janssens, and G. van der Groen. 2001. Potent broad cross-neutralizing sera inhibit attachment of primary HIV-1 isolates (groups M and O) to peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Virology 281305-314. - PubMed
-
- Binley, J. M., T. Wrin, B. Korber, M. B. Zwick, M. Wang, C. Chappey, G. Stiegler, R. Kunert, S. Zolla-Pazner, H. Katinger, C. J. Petropoulos, and D. R. Burton. 2004. Comprehensive cross-clade neutralization analysis of a panel of anti-human immunodeficiency virus type 1 monoclonal antibodies. J. Virol. 7813232-13252. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Blixt, O., S. Head, T. Mondala, C. Scanlan, M. E. Huflejt, R. Alvarez, M. C. Bryan, F. Fazio, D. Calarese, J. Stevens, N. Razi, D. J. Stevens, J. J. Skehel, I. van Die, D. R. Burton, I. A. Wilson, R. Cummings, N. Bovin, C. H. Wong, and J. C. Paulson. 2004. Printed covalent glycan array for ligand profiling of diverse glycan binding proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 10117033-17038. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

