An amphiphilic region in the cytoplasmic domain of KdpD is recognized by the signal recognition particle and targeted to the Escherichia coli membrane
- PMID: 18433452
- PMCID: PMC2440551
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2008.06246.x
An amphiphilic region in the cytoplasmic domain of KdpD is recognized by the signal recognition particle and targeted to the Escherichia coli membrane
Abstract
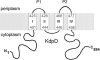
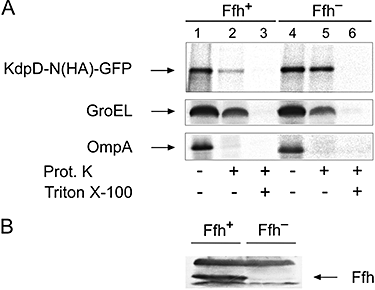
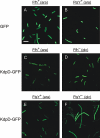
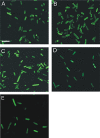
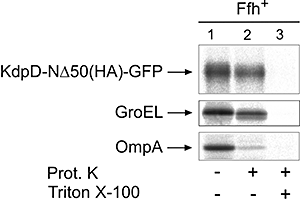
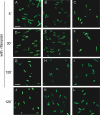
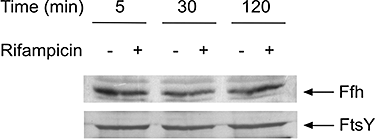
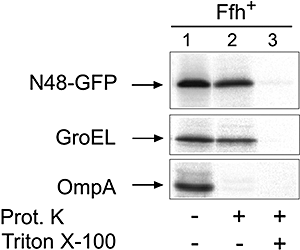
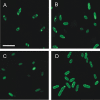
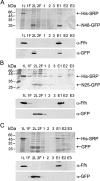
The sensor protein KdpD of Escherichia coli is composed of a large N-terminal hydrophilic region (aa 1-400), four transmembrane regions (aa 401-498) and a large hydrophilic region (aa 499-894) at the C-terminus. KdpD requires the signal recognition particle (SRP) for its targeting to the membrane. Deletions within KdpD show that the first 50 residues are required for SRP-driven membrane insertion. A fusion protein of the green fluorescent protein (GFP) with KdpD is found localized at the membrane only when SRP is present. The membrane targeting of GFP was not observed when the first 50 KdpD residues were deleted. A truncated mutant of KdpD containing only the first 25 amino acids fused to GFP lost its ability to specifically interact with SRP, whereas a specific interaction between SRP and the first 48 amino acids of KdpD fused to GFP was confirmed by pull-down experiments. Conclusively, a small amphiphilic region of 27 residues within the amino-terminal domain of KdpD (aa 22-48) is recognized by SRP and targets the protein to the membrane. This shows that membrane proteins with a large N-terminal region in the cytoplasm can be membrane-targeted early on to allow co-translational membrane insertion of their distant transmembrane regions.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The SRP signal sequence of KdpD.Sci Rep. 2019 Jun 18;9(1):8717. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-45233-9. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31213649 Free PMC article.
-
The sensor protein KdpD inserts into the Escherichia coli membrane independent of the Sec translocase and YidC.Eur J Biochem. 2003 Apr;270(8):1724-34. doi: 10.1046/j.1432-1033.2003.03531.x. Eur J Biochem. 2003. PMID: 12694185
-
The transmembrane domains of the sensor kinase KdpD of Escherichia coli are not essential for sensing K+ limitation.Mol Microbiol. 2003 Feb;47(3):839-48. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2003.03348.x. Mol Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 12535080
-
Signal recognition particle mediated protein targeting in Escherichia coli.Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2001 Jan;79(1):17-31. doi: 10.1023/a:1010256109582. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2001. PMID: 11392480 Review.
-
Dynamics of co-translational protein targeting.Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2015 Dec;29:79-86. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2015.09.016. Epub 2015 Oct 30. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2015. PMID: 26517565 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Polar localization of a tripartite complex of the two-component system DcuS/DcuR and the transporter DctA in Escherichia coli depends on the sensor kinase DcuS.PLoS One. 2014 Dec 30;9(12):e115534. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0115534. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25549248 Free PMC article.
-
SecA drives transmembrane insertion of RodZ, an unusual single-span membrane protein.J Mol Biol. 2015 Mar 13;427(5):1023-37. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2014.05.005. Epub 2014 May 15. J Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 24846669 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting and Insertion of Membrane Proteins.EcoSal Plus. 2017 Mar;7(2):10.1128/ecosalplus.ESP-0012-2016. doi: 10.1128/ecosalplus.ESP-0012-2016. EcoSal Plus. 2017. PMID: 28276312 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of integral membrane protein insertion and folding.J Mol Biol. 2015 Mar 13;427(5):999-1022. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2014.09.014. Epub 2014 Sep 30. J Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25277655 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biogenesis of bacterial inner-membrane proteins.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2010 Jul;67(14):2343-62. doi: 10.1007/s00018-010-0303-0. Epub 2010 Mar 5. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2010. PMID: 20204450 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alami M, Luke I, Deitermann S, Eisner G, Koch H-G, Brunner J, Müller M. Differential interactions between a twin-arginine signal peptide and its translocase in Escherichia coli. Mol Cell. 2003;12:937–946. - PubMed
-
- Batey RT, Rambo RP, Lucast L, Rha B, Doudna JA. Crystal structure of the ribonucleoprotein core of the signal recognition particle. Science. 2000;287:1232–1239. - PubMed
-
- Cormack B, Valdivia R, Falkow S. FACS-optimized mutants of the green fluorescent protein (GFP) Gene. 1996;173:33–38. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

