NMD resulting from encephalomyocarditis virus IRES-directed translation initiation seems to be restricted to CBP80/20-bound mRNA
- PMID: 18369367
- PMCID: PMC2373368
- DOI: 10.1038/embor.2008.36
NMD resulting from encephalomyocarditis virus IRES-directed translation initiation seems to be restricted to CBP80/20-bound mRNA
Abstract
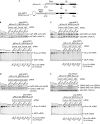
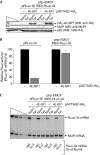
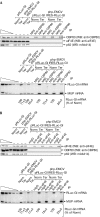
Nonsense-mediated messenger RNA decay (NMD) generally degrades mRNAs that prematurely terminate translation as a means of quality control. NMD in mammalian cells targets newly spliced mRNA that is bound by the cap-binding protein heterodimer CBP80/20 and one or more post-splicing exon junction complexes during a pioneer round of translation. NMD targets mRNA that initiates translation using the encephalomyocarditis virus (EMCV) internal ribosome entry site (IRES), therefore NMD might target not only CBP80/20-bound mRNA but also its remodelled product, eIF4E-bound mRNA. Here, we provide evidence that NMD triggered by translation initiation at the EMCV IRES, similar to NMD triggered by translation initiation at an mRNA cap, targets CBP80/20-bound mRNA but does not detectably target eIF4E-bound mRNA. We show that EMCV IRES-initiated translation undergoes a CBP80/20-associated pioneer round of translation that results in CBP80/20-dependent and Upf factor-dependent NMD when translation terminates prematurely.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Failsafe nonsense-mediated mRNA decay does not detectably target eIF4E-bound mRNA.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2007 Oct;14(10):974-9. doi: 10.1038/nsmb1297. Epub 2007 Sep 16. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17873884
-
CBP80 promotes interaction of Upf1 with Upf2 during nonsense-mediated mRNA decay in mammalian cells.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2005 Oct;12(10):893-901. doi: 10.1038/nsmb995. Epub 2005 Sep 25. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2005. PMID: 16186820
-
The pioneer translation initiation complex is functionally distinct from but structurally overlaps with the steady-state translation initiation complex.Genes Dev. 2004 Apr 1;18(7):745-54. doi: 10.1101/gad.1170204. Epub 2004 Apr 1. Genes Dev. 2004. PMID: 15059963 Free PMC article.
-
CBP80-promoted mRNP rearrangements during the pioneer round of translation, nonsense-mediated mRNA decay, and thereafter.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2010;75:127-34. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2010.75.028. Epub 2011 Mar 29. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2010. PMID: 21447822 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Translation initiation mediated by nuclear cap-binding protein complex.BMB Rep. 2017 Apr;50(4):186-193. doi: 10.5483/bmbrep.2017.50.4.007. BMB Rep. 2017. PMID: 28088948 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Nonsense-mediated RNA decay regulation by cellular stress: implications for tumorigenesis.Mol Cancer Res. 2010 Mar;8(3):295-308. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-09-0502. Epub 2010 Feb 23. Mol Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20179151 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diverse Roles of the Exon Junction Complex Factors in the Cell Cycle, Cancer, and Neurodevelopmental Disorders-Potential for Therapeutic Targeting.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 8;23(18):10375. doi: 10.3390/ijms231810375. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36142288 Free PMC article. Review.
-
UPF1 association with the cap-binding protein, CBP80, promotes nonsense-mediated mRNA decay at two distinct steps.Mol Cell. 2010 Aug 13;39(3):396-409. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2010.07.004. Epub 2010 Aug 5. Mol Cell. 2010. PMID: 20691628 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of gene expression by translation factor eIF5A: Hypusine-modified eIF5A enhances nonsense-mediated mRNA decay in human cells.Translation (Austin). 2017 Aug 14;5(2):e1366294. doi: 10.1080/21690731.2017.1366294. eCollection 2017. Translation (Austin). 2017. PMID: 29034140 Free PMC article.
-
The multiple lives of NMD factors: balancing roles in gene and genome regulation.Nat Rev Genet. 2008 Sep;9(9):699-712. doi: 10.1038/nrg2402. Nat Rev Genet. 2008. PMID: 18679436 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Behm-Ansmant I, Kashima I, Rehwinkel J, Sauliere J, Wittkopp N, Izaurralde E (2007) mRNA quality control: an ancient machinery recognizes and degrades mRNAs with nonsense codons. FEBS Lett 581: 2845–2853 - PubMed
-
- Brocke KS, Neu-Yilik G, Gehring NH, Hentze MW, Kulozik AE (2002) The human intronless melanocortin 4-receptor gene is NMD insensitive. Hum Mol Genet 11: 331–335 - PubMed
-
- Bühler M, Steiner S, Mohn F, Paillusson A, Mühlemann O (2006) EJC-independent degradation of nonsense immunoglobulin-μ mRNA depends on 3′ UTR length. Nat Struct Mol Biol 13: 462–464 - PubMed
-
- Calero G, Wilson KF, Ly T, Rios-Steiner JL, Clardy JC, Cerione RA (2002) Structural basis of m7GpppG binding to the nuclear cap-binding protein complex. Nat Struct Biol 9: 912–917 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

