Purinergic receptors and synaptic transmission in enteric neurons
- PMID: 18368519
- PMCID: PMC2486344
- DOI: 10.1007/s11302-007-9088-5
Purinergic receptors and synaptic transmission in enteric neurons
Abstract
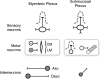
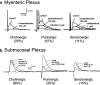
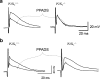
Purines such as ATP and adenosine participate in synaptic transmission in the enteric nervous system as neurotransmitters or neuromodulators. Purinergic receptors are localized on the cell bodies or nerve terminals of different functional classes of enteric neurons and, with other receptors, form unique receptor complements. Activation of purinergic receptors can regulate neuronal activity by depolarization, by regulating intracellular calcium, or by modulating second messenger pathways. Purinergic signaling between enteric neurons plays an important role in regulating specific enteric reflexes and overall gastrointestinal function. In the present article, we review evidence for purine receptors in the enteric nervous system, including P1 (adenosine) receptors and P2 (ATP) receptors. We will explore the role they play in mediating fast and slow synaptic transmission and in presynaptic inhibition of transmission. Finally, we will examine the molecular properties of the native receptors, their signaling mechanisms, and their role in gastrointestinal pathology.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Neuropharmacology of purinergic receptors in human submucous plexus: Involvement of P2X₁, P2X₂, P2X₃ channels, P2Y and A₃ metabotropic receptors in neurotransmission.Neuropharmacology. 2015 Aug;95:83-99. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2015.02.014. Epub 2015 Feb 24. Neuropharmacology. 2015. PMID: 25724083 Free PMC article.
-
Purinergic neuron-to-glia signaling in the enteric nervous system.Gastroenterology. 2009 Apr;136(4):1349-58. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2008.12.058. Epub 2009 Jan 1. Gastroenterology. 2009. PMID: 19250649
-
Role of purines in brain development, from neuronal proliferation to synaptic refinement.Neuropharmacology. 2023 Oct 1;237:109640. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2023.109640. Epub 2023 Jun 20. Neuropharmacology. 2023. PMID: 37348675 Review.
-
Plasticity of mouse enteric synapses mediated through endocannabinoid and purinergic signaling.Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2012 Mar;24(3):e113-24. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2982.2011.01860.x. Epub 2012 Jan 11. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2012. PMID: 22235973 Free PMC article.
-
The purinergic neurotransmitter revisited: a single substance or multiple players?Pharmacol Ther. 2014 Nov;144(2):162-91. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2014.05.012. Epub 2014 Jun 2. Pharmacol Ther. 2014. PMID: 24887688 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Neuropharmacology of purinergic receptors in human submucous plexus: Involvement of P2X₁, P2X₂, P2X₃ channels, P2Y and A₃ metabotropic receptors in neurotransmission.Neuropharmacology. 2015 Aug;95:83-99. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2015.02.014. Epub 2015 Feb 24. Neuropharmacology. 2015. PMID: 25724083 Free PMC article.
-
Purinergic mechanisms in the control of gastrointestinal motility.Purinergic Signal. 2008 Sep;4(3):197-212. doi: 10.1007/s11302-007-9081-z. Epub 2007 Oct 6. Purinergic Signal. 2008. PMID: 18368521 Free PMC article.
-
Optogenetic analysis of neuromuscular transmission in the colon of ChAT-ChR2-YFP BAC transgenic mice.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2019 Nov 1;317(5):G569-G579. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00089.2019. Epub 2019 Aug 14. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31411893 Free PMC article.
-
In situ Ca2+ imaging of the enteric nervous system.J Vis Exp. 2015 Jan 29;(95):52506. doi: 10.3791/52506. J Vis Exp. 2015. PMID: 25741967 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced Electrical Field Stimulated Nitrergic and Purinergic Vasoreactivity in Distal vs Proximal Internal Pudendal Arteries.J Sex Med. 2017 Nov;14(11):1285-1296. doi: 10.1016/j.jsxm.2017.09.013. J Sex Med. 2017. PMID: 29110801 Free PMC article.
References
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '12482722', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12482722/'}]}
- Furness JB, Sanger GJ (2002) Intrinsic nerve circuits of the gastrointestinal tract: identification of drug targets. Curr Opin Pharmacol 2(6):612–622 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '12464083', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12464083/'}]}
- Galligan JJ (2002) Ligand-gated ion channels in the enteric nervous system. Neurogastroenterol Motil 14(6):611–623 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '15066009', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15066009/'}]}
- Wood JD, Kirchgessner A (2004) Slow excitatory metabotropic signal transmission in the enteric nervous system. Neurogastroenterol Motil 16(Suppl 1):71–80 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

