Deficiency of zonula occludens-1 causes embryonic lethal phenotype associated with defected yolk sac angiogenesis and apoptosis of embryonic cells
- PMID: 18353970
- PMCID: PMC2397322
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e07-12-1215
Deficiency of zonula occludens-1 causes embryonic lethal phenotype associated with defected yolk sac angiogenesis and apoptosis of embryonic cells
Abstract
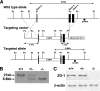
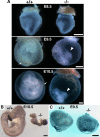
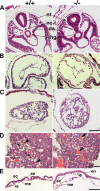
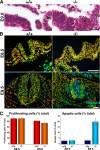
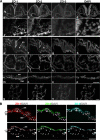
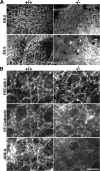
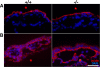
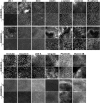
Zonula occludens (ZO)-1/2/3 are the members of the TJ-MAGUK family of membrane-associated guanylate kinases associated with tight junctions. To investigate the role of ZO-1 (encoded by Tjp1) in vivo, ZO-1 knockout (Tjp1(-/-)) mice were generated by gene targeting. Although heterozygous mice showed normal development and fertility, delayed growth and development were evident from E8.5 onward in Tjp1(-/-) embryos, and no viable Tjp1(-/-) embryos were observed beyond E11.5. Tjp1(-/-) embryos exhibited massive apoptosis in the notochord, neural tube area, and allantois at embryonic day (E)9.5. In the yolk sac, the ZO-1 deficiency induced defects in vascular development, with impaired formation of vascular trees, along with defective chorioallantoic fusion. Immunostaining of wild-type embryos at E8.5 for ZO-1/2/3 revealed that ZO-1/2 were expressed in almost all embryonic cells, showing tight junction-localizing patterns, with or without ZO-3, which was confined to the epithelial cells. ZO-1 deficiency depleted ZO-1-expression without influence on ZO-2/3 expression. In Tjp1(+/+) yolk sac extraembryonic mesoderm, ZO-1 was dominant without ZO-2/3 expression. Thus, ZO-1 deficiency resulted in mesoderms with no ZO-1/2/3, associated with mislocalization of endothelial junctional adhesion molecules. As a result, angiogenesis was defected in Tjp1(-/-) yolk sac, although differentiation of endothelial cells seemed to be normal. In conclusion, ZO-1 may be functionally important for cell remodeling and tissue organization in both the embryonic and extraembryonic regions, thus playing an essential role in embryonic development.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Early embryonic lethality of mice lacking ZO-2, but Not ZO-3, reveals critical and nonredundant roles for individual zonula occludens proteins in mammalian development.Mol Cell Biol. 2008 Mar;28(5):1669-78. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00891-07. Epub 2008 Jan 2. Mol Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18172007 Free PMC article.
-
Defects in yolk sac vasculogenesis, chorioallantoic fusion, and embryonic axis elongation in mice with targeted disruption of Yap65.Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Jan;26(1):77-87. doi: 10.1128/MCB.26.1.77-87.2006. Mol Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16354681 Free PMC article.
-
Expression and distribution of ZO-3, a tight junction MAGUK protein, in mouse tissues.Genes Cells. 2003 Nov;8(11):837-45. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2443.2003.00681.x. Genes Cells. 2003. PMID: 14622136
-
MAGUK proteins: structure and role in the tight junction.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2000 Aug;11(4):315-24. doi: 10.1006/scdb.2000.0178. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2000. PMID: 10966866 Review.
-
Analysis of homozygous TGF beta 1 null mouse embryos demonstrates defects in yolk sac vasculogenesis and hematopoiesis.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1995 Mar 27;752:300-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1995.tb17439.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1995. PMID: 7755275 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Tight junctions: from simple barriers to multifunctional molecular gates.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2016 Sep;17(9):564-80. doi: 10.1038/nrm.2016.80. Epub 2016 Jun 29. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 27353478 Review.
-
Cilostazol prevents retinal ischemic damage partly via inhibition of tumor necrosis factor-α-induced nuclear factor-kappa B/activator protein-1 signaling pathway.Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2013 Oct;1(1):e00006. doi: 10.1002/prp2.6. Epub 2013 Oct 1. Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2013. PMID: 25505560 Free PMC article.
-
Protein Interactions at Endothelial Junctions and Signaling Mechanisms Regulating Endothelial Permeability.Circ Res. 2017 Jan 6;120(1):179-206. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.306534. Circ Res. 2017. PMID: 28057793 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plakophilin-1, a Novel Wnt Signaling Regulator, Is Critical for Tooth Development and Ameloblast Differentiation.PLoS One. 2016 Mar 24;11(3):e0152206. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0152206. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27015268 Free PMC article.
-
Cell adhesion in epidermal development and barrier formation.Curr Top Dev Biol. 2015;112:383-414. doi: 10.1016/bs.ctdb.2014.11.027. Epub 2015 Feb 11. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2015. PMID: 25733147 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Argraves W. S., Drake C. J. Genes critical to vasculogenesis as defined by systematic analysis of vascular defects in knockout mice. Anat. Rec. A Discov. Mol. Cell Evol. Biol. 2005;286:875–884. - PubMed
-
- Baumer S., Keller L., Holtmann A., Funke R., August B., Gamp A., Wolburg H., Wolburg-Buchholz K., Deutsch U., Vestweber D. Vascular endothelial cell–specific phosphotyrosine phosphatase (VE-PTP) activity is required for blood vessel development. Blood. 2006;107:4754–4762. - PubMed
-
- Bazzoni G., Martinez-Estrada O. M., Orsenigo F., Cordenonsi M., Citi S., Dejana E. Interaction of junctional adhesion molecule with the tight junction components ZO-1, cingulin, and occludin. J. Biol. Chem. 2000;275:20520–20526. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

