Altered TAB1:I kappaB kinase interaction promotes transforming growth factor beta-mediated nuclear factor-kappaB activation during breast cancer progression
- PMID: 18316610
- PMCID: PMC2615489
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-3094
Altered TAB1:I kappaB kinase interaction promotes transforming growth factor beta-mediated nuclear factor-kappaB activation during breast cancer progression
Abstract
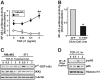
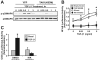
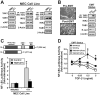
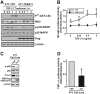
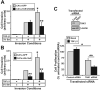
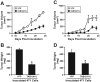
The conversion of transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta) from a tumor suppressor to a tumor promoter occurs frequently during mammary tumorigenesis, yet the molecular mechanisms underlying this phenomenon remain undefined. We show herein that TGF-beta repressed nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) activity in normal NMuMG cells, but activated this transcription factor in their malignant counterparts, 4T1 cells, by inducing assembly of TGF-beta-activated kinase 1 (TAK1)-binding protein 1 (TAB1):I kappaB kinase beta (IKK beta) complexes, which led to the stimulation of a TAK1:IKK beta:p65 pathway. TAB1:IKK beta complexes could only be detected in NMuMG cells following their induction of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), which, on TGF-beta treatment, activated NF-kappaB. Expression of a truncated TAB1 mutant [i.e., TAB1(411)] reduced basal and TGF-beta-mediated NF-kappaB activation in NMuMG cells driven to undergo EMT by TGF-beta and in 4T1 cells stimulated by TGF-beta. TAB1(411) expression also inhibited TGF-beta-stimulated tumor necrosis factor-alpha and cyclooxygenase-2 expression in 4T1 cells. Additionally, the ability of human MCF10A-CA1a breast cancer cells to undergo invasion in response to TGF-beta absolutely required the activities of TAK1 and NF-kappaB. Moreover, small interfering RNA-mediated TAK1 deficiency restored the cytostatic activity of TGF-beta in MCF10A-CA1a cells. Finally, expression of truncated TAB1(411) dramatically reduced the growth of 4T1 breast cancers in syngeneic BALB/c, as well as in nude mice, suggesting a potentially important role of NF-kappaB in regulating innate immunity by TGF-beta. Collectively, our findings have defined a novel TAB1:TAK1:IKK beta:NF-kappaB signaling axis that forms aberrantly in breast cancer cells and, consequently, enables oncogenic signaling by TGF-beta.
Figures
Similar articles
-
X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein and its E3 ligase activity promote transforming growth factor-{beta}-mediated nuclear factor-{kappa}B activation during breast cancer progression.J Biol Chem. 2009 Aug 7;284(32):21209-17. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.018374. Epub 2009 Jun 15. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19531477 Free PMC article.
-
Functional interactions of transforming growth factor beta-activated kinase 1 with IkappaB kinases to stimulate NF-kappaB activation.J Biol Chem. 1999 Apr 9;274(15):10641-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.15.10641. J Biol Chem. 1999. PMID: 10187861
-
The interaction of TAK1 and TAB1 enhances LPS-induced cytokine release via modulating NF-κB activation (Larimichthys crocea).Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018 Mar;74:450-458. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2018.01.005. Epub 2018 Jan 8. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29325713
-
TAK1 regulates hepatic cell survival and carcinogenesis.J Gastroenterol. 2014 Feb;49(2):185-94. doi: 10.1007/s00535-013-0931-x. Epub 2014 Jan 21. J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 24443058 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NF-κB as a regulator of cancer metastasis and therapy response: A focus on epithelial-mesenchymal transition.J Cell Physiol. 2022 Jul;237(7):2770-2795. doi: 10.1002/jcp.30759. Epub 2022 May 13. J Cell Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35561232 Review.
Cited by
-
TGF-β induces miR-182 to sustain NF-κB activation in glioma subsets.J Clin Invest. 2012 Oct;122(10):3563-78. doi: 10.1172/JCI62339. Epub 2012 Sep 24. J Clin Invest. 2012. PMID: 23006329 Free PMC article.
-
Transforming growth factor-β and the hallmarks of cancer.Cell Signal. 2011 Jun;23(6):951-62. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2010.10.015. Epub 2010 Nov 6. Cell Signal. 2011. PMID: 20940046 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The pathophysiology of epithelial-mesenchymal transition induced by transforming growth factor-beta in normal and malignant mammary epithelial cells.J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2010 Jun;15(2):169-90. doi: 10.1007/s10911-010-9181-1. Epub 2010 May 15. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2010. PMID: 20467795 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Procarcinogenic effects of cyclosporine A are mediated through the activation of TAK1/TAB1 signaling pathway.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011 May 13;408(3):363-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.02.039. Epub 2011 Feb 17. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011. PMID: 21333626 Free PMC article.
-
Activated Abl kinase inhibits oncogenic transforming growth factor-beta signaling and tumorigenesis in mammary tumors.FASEB J. 2009 Dec;23(12):4231-43. doi: 10.1096/fj.09-138412. Epub 2009 Aug 18. FASEB J. 2009. PMID: 19690215 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Galliher AJ, Neil JR, Schiemann WP. Role of TGF-β in cancer progression. Future Oncology. 2006;2:743–63. - PubMed
-
- Blobe GC, Schiemann WP, Lodish HF. Role of TGF-β in human disease. N Engl J Med. 2000;342:1350–8. - PubMed
-
- Shi Y, Massague J. Mechanisms of TGF-β signaling from cell membrane to the nucleus. Cell. 2003;113:685–700. - PubMed
-
- Kamaraju AK, Roberts AB. Role of Rho/ROCK and p38 MAP kinase pathways in TGF-β-mediated Smad-dependent growth inhibition of human breast carcinoma cells in vivo. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:1024–36. - PubMed
-
- Hartsough MT, Mulder KM. TGF-β activation of p44MAPK in proliferating cultures of epithelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:7117–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

