Localization and translocation of RhoA protein in the human gastric cancer cell line SGC-7901
- PMID: 18300342
- PMCID: PMC2690664
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.14.1175
Localization and translocation of RhoA protein in the human gastric cancer cell line SGC-7901
Abstract
Aim: To elucidate the localization of RhoA in gastric SGC-7901 cancer cells and its translocation by lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) and/or 8-chlorophenylthio-cAMP (CPT-cAMP).
Methods: Immunofluorescence microscopy was used to determine the localization of RhoA. Western blotting was used to detect both endogenous and exogenous RhoA in different cellular compartments (membrane, cytosol, nucleus) and the translocation of RhoA following treatment with LPA, CPT-cAMP, or CPT-cAMP + LPA.
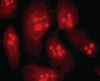
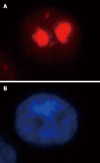
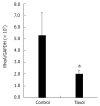
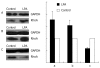
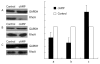
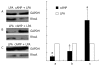
Results: Immunofluorescence staining revealed endogenous RhoA to be localized in the membrane, the cytosol, and the nucleus, and its precise localization within the nucleus to be the nucleolus. Western blotting identified both endogenous and exogenous RhoA within different cellular compartments (membrane, cytosol, nucleus, nucleolus). After stimulation with LPA, the amount of RhoA within membrane and nuclear extracts increased, while it decreased in the cytosol fractions. After treatment with CPT-cAMP the amount of RhoA within the membrane and the nuclear extracts decreased, while it increased within the cytosol fraction. Treatment with a combination of both substances led to a decrease in RhoA in the membrane and the nucleus but to an increase in the cytosol.
Conclusion: In SGC-7901 cells RhoA was found to be localized within the membrane, the cytosol, and the nucleus. Within the nucleus its precise localization could be demonstrated to be the nucleolus. Stimulation with LPA caused a translocation of RhoA from the cytosol towards the membrane and the nucleus; treatment with CPT-cAMP caused the opposite effect. Furthermore, pre-treatment with CPT-cAMP was found to block the effect of LPA.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The cross talk between protein kinase A- and RhoA-mediated signaling in cancer cells.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2005 Nov;230(10):731-41. doi: 10.1177/153537020523001006. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2005. PMID: 16246900
-
Factors influencing RhoA protein distribution in the nucleus.Mol Med Rep. 2011 Nov-Dec;4(6):1115-9. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2011.556. Epub 2011 Aug 16. Mol Med Rep. 2011. PMID: 21850373
-
RhoA protein is generally distributed in the nuclei of cancer cells.Oncol Rep. 2010 Oct;24(4):1005-9. doi: 10.3892/or.2010.1005. Oncol Rep. 2010. PMID: 20811682
-
Nuclear translocation of small G protein RhoA via active transportation in gastric cancer cells.Oncol Rep. 2013 Oct;30(4):1878-82. doi: 10.3892/or.2013.2638. Epub 2013 Jul 25. Oncol Rep. 2013. PMID: 23900609
-
Inhibition of lysophosphatidic acid-induced RhoA activation and tumor cell invasion by 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase inhibitors.Int J Oncol. 2003 Oct;23(4):1173-8. Int J Oncol. 2003. PMID: 12964001
Cited by
-
Requirement of Osteopontin in the migration and protection against Taxol-induced apoptosis via the ATX-LPA axis in SGC7901 cells.BMC Cell Biol. 2011 Mar 16;12:11. doi: 10.1186/1471-2121-12-11. BMC Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21406114 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation and Activation of RhoA by ERK in Response to Epidermal Growth Factor Stimulation.PLoS One. 2016 Jan 27;11(1):e0147103. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0147103. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26816343 Free PMC article.
-
Ran promotes membrane targeting and stabilization of RhoA to orchestrate ovarian cancer cell invasion.Nat Commun. 2019 Jun 17;10(1):2666. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-10570-w. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31209254 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of RhoA gene silencing on proliferation and migration of gastric MGC-803 cells.Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015 Aug 15;8(8):14410-5. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015. PMID: 26550428 Free PMC article.
-
The long journey of actin and actin-associated proteins from genes to polysomes.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2009 Jul;66(13):2151-65. doi: 10.1007/s00018-009-0012-8. Epub 2009 Mar 20. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2009. PMID: 19300907 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ridley AJ, Hall A. The small GTP-binding protein rho regulates the assembly of focal adhesions and actin stress fibers in response to growth factors. Cell. 1992;70:389–399. - PubMed
-
- McCormick F. ras GTPase activating protein: signal transmitter and signal terminator. Cell. 1989;56:5–8. - PubMed
-
- Bourne HR, Sanders DA, McCormick F. The GTPase superfamily: a conserved switch for diverse cell functions. Nature. 1990;348:125–132. - PubMed
-
- Hall A. The cellular functions of small GTP-binding proteins. Science. 1990;249:635–640. - PubMed
-
- Takai Y, Kaibuchi K, Kikuchi A, Kawata M. Small GTP-binding proteins. Int Rev Cytol. 1992;133:187–230. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

