Cullin-RING ubiquitin ligases: global regulation and activation cycles
- PMID: 18282298
- PMCID: PMC2266742
- DOI: 10.1186/1747-1028-3-7
Cullin-RING ubiquitin ligases: global regulation and activation cycles
Abstract
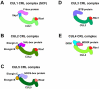
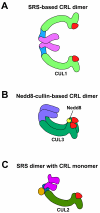
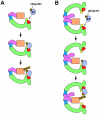
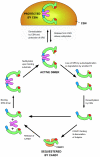
Cullin-RING ubiquitin ligases (CRLs) comprise the largest known category of ubiquitin ligases. CRLs regulate an extensive number of dynamic cellular processes, including multiple aspects of the cell cycle, transcription, signal transduction, and development. CRLs are multisubunit complexes composed of a cullin, RING H2 finger protein, a variable substrate-recognition subunit (SRS), and for most CRLs, an adaptor that links the SRS to the complex. Eukaryotic species contain multiple cullins, with five major types in metazoa. Each cullin forms a distinct class of CRL complex, with distinct adaptors and/or substrate-recognition subunits. Despite this diversity, each of the classes of CRL complexes is subject to similar regulatory mechanisms. This review focuses on the global regulation of CRL complexes, encompassing: neddylation, deneddylation by the COP9 Signalosome (CSN), inhibitory binding by CAND1, and the dimerization of CRL complexes. We also address the role of cycles of activation and inactivation in regulating CRL activity and switching between substrate-recognition subunits.
Figures
Similar articles
-
CSN- and CAND1-dependent remodelling of the budding yeast SCF complex.Nat Commun. 2013;4:1641. doi: 10.1038/ncomms2628. Nat Commun. 2013. PMID: 23535662
-
Deregulation of the COP9 signalosome-cullin-RING ubiquitin-ligase pathway: mechanisms and roles in urological cancers.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2013 Jul;45(7):1327-37. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2013.03.023. Epub 2013 Apr 10. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23583660 Review.
-
Characterization of the role of COP9 signalosome in regulating cullin E3 ubiquitin ligase activity.Mol Biol Cell. 2011 Dec;22(24):4706-15. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E11-03-0251. Epub 2011 Oct 19. Mol Biol Cell. 2011. PMID: 22013077 Free PMC article.
-
Cullin-RING Ligase Regulation by the COP9 Signalosome: Structural Mechanisms and New Physiologic Players.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1217:47-60. doi: 10.1007/978-981-15-1025-0_4. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 31898221 Review.
-
Are Inositol Polyphosphates the Missing Link in Dynamic Cullin RING Ligase Regulation by the COP9 Signalosome?Biomolecules. 2019 Aug 7;9(8):349. doi: 10.3390/biom9080349. Biomolecules. 2019. PMID: 31394817 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ubiquitin and Not Only Unfolded Domains Drives Toscana Virus Non-Structural NSs Protein Degradation.Viruses. 2020 Oct 12;12(10):1153. doi: 10.3390/v12101153. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 33053780 Free PMC article.
-
COP9-Signalosome deneddylase activity is enhanced by simultaneous neddylation: insights into the regulation of an enzymatic protein complex.Cell Div. 2015 Aug 11;10:5. doi: 10.1186/s13008-015-0011-0. eCollection 2015. Cell Div. 2015. PMID: 26265931 Free PMC article.
-
Cullin-3 protein expression levels correlate with breast cancer progression.Cancer Biol Ther. 2012 Sep;13(11):1042-6. doi: 10.4161/cbt.21046. Epub 2012 Jul 24. Cancer Biol Ther. 2012. PMID: 22825334 Free PMC article.
-
Biophysical and functional study of CRL5Ozz, a muscle specific ubiquitin ligase complex.Sci Rep. 2022 May 12;12(1):7820. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-10955-w. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35551201 Free PMC article.
-
AUXIN UP-REGULATED F-BOX PROTEIN1 regulates the cross talk between auxin transport and cytokinin signaling during plant root growth.Plant Physiol. 2011 Aug;156(4):1878-93. doi: 10.1104/pp.111.179812. Epub 2011 Jun 8. Plant Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21653785 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Glickman MH, Ciechanover A. The ubiquitin-proteasome proteolytic pathway: destruction for the sake of construction. Physiol Rev. 2002;82:373–428. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

