Rapid isolation and identification of bacteriophage T4-encoded modifications of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase: a generic method to study bacteriophage/host interactions
- PMID: 18271525
- PMCID: PMC2612130
- DOI: 10.1021/pr070451j
Rapid isolation and identification of bacteriophage T4-encoded modifications of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase: a generic method to study bacteriophage/host interactions
Abstract
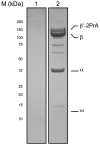
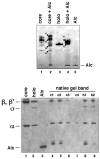
Bacteriophages are bacterial viruses that infect bacterial cells, and they have developed ingenious mechanisms to modify the bacterial RNA polymerase. Using a rapid, specific, single-step affinity isolation procedure to purify Escherichia coli RNA polymerase from bacteriophage T4-infected cells, we have identified bacteriophage T4-dependent modifications of the host RNA polymerase. We suggest that this methodology is broadly applicable for the identification of bacteriophage-dependent alterations of the host synthesis machinery.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Transcription regulation by bacteriophage T4 AsiA.Protein Expr Purif. 2005 May;41(1):1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.pep.2004.09.019. Protein Expr Purif. 2005. PMID: 15802215 Review.
-
The bacteriophage T4 late-transcription coactivator gp33 binds the flap domain of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Dec 14;101(50):17365-70. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0408028101. Epub 2004 Dec 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. PMID: 15574501 Free PMC article.
-
A mutation within the β subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase impairs transcription from bacteriophage T4 middle promoters.J Bacteriol. 2010 Nov;192(21):5580-7. doi: 10.1128/JB.00338-10. Epub 2010 Aug 20. J Bacteriol. 2010. PMID: 20729353 Free PMC article.
-
T4 early promoter strength probed in vivo with unribosylated and ADP-ribosylated Escherichia coli RNA polymerase: a mutation analysis.Microbiology (Reading). 2000 Oct;146 ( Pt 10):2643-2653. doi: 10.1099/00221287-146-10-2643. Microbiology (Reading). 2000. PMID: 11021939
-
Xenogeneic Regulation of the Bacterial Transcription Machinery.J Mol Biol. 2019 Sep 20;431(20):4078-4092. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2019.02.008. Epub 2019 Feb 15. J Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 30776429 Review.
Cited by
-
Improved methodology for the affinity isolation of human protein complexes expressed at near endogenous levels.Biotechniques. 2012 May;0(0):1-6. doi: 10.2144/000113864. Biotechniques. 2012. PMID: 22668517 Free PMC article.
-
Improved native isolation of endogenous Protein A-tagged protein complexes.Biotechniques. 2013 Apr;54(4):213-6. doi: 10.2144/000114012. Biotechniques. 2013. PMID: 23581468 Free PMC article.
-
Affinity isolation and I-DIRT mass spectrometric analysis of the Escherichia coli O157:H7 Sakai RNA polymerase complex.J Bacteriol. 2008 Feb;190(4):1284-9. doi: 10.1128/JB.01599-07. Epub 2007 Dec 14. J Bacteriol. 2008. PMID: 18083804 Free PMC article.
-
Temporal regulation of gene expression of the Thermus thermophilus bacteriophage P23-45.J Mol Biol. 2011 Jan 7;405(1):125-42. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2010.10.049. Epub 2010 Nov 2. J Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21050864 Free PMC article.
-
SepL resembles an aberrant effector in binding to a class 1 type III secretion chaperone and carrying an N-terminal secretion signal.J Bacteriol. 2010 Nov;192(22):6093-8. doi: 10.1128/JB.00760-10. Epub 2010 Sep 10. J Bacteriol. 2010. PMID: 20833800 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Matsuzaki S, Rashel M, Uchiyama J, Sakurai S, Ujihara T, Kuroda M, Ikeuchi M, Tani T, Fujieda M, Wakiguchi H, Imai S. Bacteriophage therapy: a revitalized therapy against bacterial infectious diseases. J. Infect. Chemother. 2005;11:211–9. - PubMed
-
- Nechaev S, Severinov K. Bacteriophage-induced modifications of host RNA polymerase. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2003;57:301–22. - PubMed
-
- Severinov K, Kashlev M, Severinova E, Bass I, McWilliams K, Kutter E, Nikiforov V, Snyder L, Goldfarb A. A non-essential domain of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase required for the action of the termination factor Alc. J. Biol. Chem. 1994;269:14254–9. - PubMed
-
- Kashlev M, Nudler E, Goldfarb A, White T, Kutter E. Bacteriophage T4 Alc protein: a transcription termination factor sensing local modification of DNA. Cell. 1993;75:147–54. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P41 RR000862-35/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U54 RR022220-046885/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U54 RR022220/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM059295/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM59295/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM061898/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- RR00862/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM062427/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM062427-08/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM059295-08/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P41 RR000862/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- GM61898/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM061898-08/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

