IL-22 mediates mucosal host defense against Gram-negative bacterial pneumonia
- PMID: 18264110
- PMCID: PMC2901867
- DOI: 10.1038/nm1710
IL-22 mediates mucosal host defense against Gram-negative bacterial pneumonia
Abstract
Emerging evidence supports the concept that T helper type 17 (T(H)17) cells, in addition to mediating autoimmunity, have key roles in mucosal immunity against extracellular pathogens. Interleukin-22 (IL-22) and IL-17A are both effector cytokines produced by the T(H)17 lineage, and both were crucial for maintaining local control of the Gram-negative pulmonary pathogen, Klebsiella pneumoniae. Although both cytokines regulated CXC chemokines and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor production in the lung, only IL-22 increased lung epithelial cell proliferation and increased transepithelial resistance to injury. These data support the concept that the T(H)17 cell lineage and its effector molecules have evolved to effect host defense against extracellular pathogens at mucosal sites.
Figures
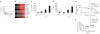
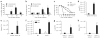
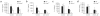
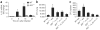
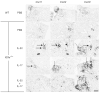
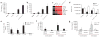
Comment in
-
Interleukin-22: a sheep in wolf's clothing.Nat Med. 2008 Mar;14(3):247-9. doi: 10.1038/nm0308-247. Nat Med. 2008. PMID: 18323844 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Requirement of interleukin 17 receptor signaling for lung CXC chemokine and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor expression, neutrophil recruitment, and host defense.J Exp Med. 2001 Aug 20;194(4):519-27. doi: 10.1084/jem.194.4.519. J Exp Med. 2001. PMID: 11514607 Free PMC article.
-
Divergent roles of IL-23 and IL-12 in host defense against Klebsiella pneumoniae.J Exp Med. 2005 Sep 19;202(6):761-9. doi: 10.1084/jem.20050193. Epub 2005 Sep 12. J Exp Med. 2005. PMID: 16157683 Free PMC article.
-
IL-17 Receptor Signaling in the Lung Epithelium Is Required for Mucosal Chemokine Gradients and Pulmonary Host Defense against K. pneumoniae.Cell Host Microbe. 2016 Nov 9;20(5):596-605. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2016.10.003. Epub 2016 Oct 27. Cell Host Microbe. 2016. PMID: 27923703 Free PMC article.
-
Th17 cells and mucosal host defense.Semin Immunol. 2007 Dec;19(6):377-82. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2007.10.009. Epub 2007 Nov 28. Semin Immunol. 2007. PMID: 18054248 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Th17 cytokines and mucosal immunity.Immunol Rev. 2008 Dec;226:160-71. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2008.00703.x. Immunol Rev. 2008. PMID: 19161423 Review.
Cited by
-
Vitamin D regulates cytokine patterns secreted by dendritic cells to promote differentiation of IL-22-producing T cells.PLoS One. 2015 Jun 24;10(6):e0130395. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0130395. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26107738 Free PMC article.
-
IL-17 and IL-22 in cerebrospinal fluid and plasma are elevated in Guillain-Barré syndrome.Mediators Inflamm. 2012;2012:260473. doi: 10.1155/2012/260473. Epub 2012 Oct 2. Mediators Inflamm. 2012. PMID: 23091305 Free PMC article.
-
An update on the hyper-IgE syndromes.Arthritis Res Ther. 2012 Nov 30;14(6):228. doi: 10.1186/ar4069. Arthritis Res Ther. 2012. PMID: 23210525 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interleukin-22 protects against non-typeable Haemophilus influenzae infection: alteration during chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Mucosal Immunol. 2017 Jan;10(1):139-149. doi: 10.1038/mi.2016.40. Epub 2016 May 4. Mucosal Immunol. 2017. PMID: 27143304
-
The role of IL-22 in intestinal health and disease.J Exp Med. 2020 Feb 13;217(3):e20192195. doi: 10.1084/jem.20192195. Print 2020 Mar 2. J Exp Med. 2020. PMID: 32997932 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Weaver CT, Hatton RD, Mangan PR, Harrington LE. IL-17 family cytokines and the expanding diversity of effector T cell lineages. Annu Rev Immunol. 2007;25:821–852. - PubMed
-
- Kolls JK, Linden A. Interleukin-17 family members and inflammation. Immunity. 2004;21:467–476. - PubMed
-
- Lubberts E. The role of IL-17 and family members in the pathogenesis of arthritis. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2003;4:572–577. - PubMed
-
- Harrington LE, et al. Interleukin 17–producing CD4+ effector T cells develop via a lineage distinct from the T helper type 1 and 2 lineages. Nat Immunol. 2005;6:1123–1132. - PubMed
-
- Mangan PR, et al. Transforming growth factor-β induces development of the TH17 lineage. Nature. 2006;441:231–234. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

