Rearrangement of mouse immunoglobulin kappa deleting element recombining sequence promotes immune tolerance and lambda B cell production
- PMID: 18261939
- PMCID: PMC2351955
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2007.12.011
Rearrangement of mouse immunoglobulin kappa deleting element recombining sequence promotes immune tolerance and lambda B cell production
Abstract
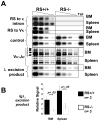
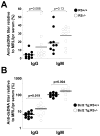
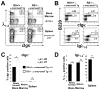
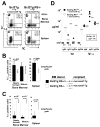
The recombining sequence (RS) of mouse and its human equivalent, the immunoglobulin (Ig) kappa deleting element (IGKDE), are sequences found at the 3' end of the Ig kappa locus (Igk) that rearrange to inactivate Igk in developing B cells. RS recombination correlates with Ig lambda (Iglambda) light (L) chain expression and likely plays a role in receptor editing by eliminating Igk genes encoding autoantibodies. A mouse strain was generated in which the recombination signal of RS was removed, blocking RS-mediated Igk inactivation. In RS mutant mice, receptor editing and self-tolerance were impaired, in some cases leading to autoantibody formation. Surprisingly, mutant mice also made fewer B cells expressing lambda chain, whereas lambda versus kappa isotype exclusion was only modestly affected. These results provide insight into the mechanism of L chain isotype exclusion and indicate that RS has a physiological role in promoting the formation of lambda L chain-expressing B cells.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Gene targeting in the Ig kappa locus: efficient generation of lambda chain-expressing B cells, independent of gene rearrangements in Ig kappa.EMBO J. 1993 Mar;12(3):811-20. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05721.x. EMBO J. 1993. PMID: 8458339 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of immunoglobulin gene rearrangement by the expression of a lambda 2 transgene.J Exp Med. 1989 Jun 1;169(6):1911-29. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.6.1911. J Exp Med. 1989. PMID: 2499652 Free PMC article.
-
Light chain editing in kappa-deficient animals: a potential mechanism of B cell tolerance.J Exp Med. 1994 Nov 1;180(5):1805-15. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.5.1805. J Exp Med. 1994. PMID: 7964462 Free PMC article.
-
Dual surface immunoglobulin light-chain expression in B-cell lymphoproliferative disorders.Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2006 Jun;130(6):853-6. doi: 10.5858/2006-130-853-DSILEI. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2006. PMID: 16740039 Review.
-
Comparative Aspects of Immunoglobulin Gene Rearrangement Arrays in Different Species.Front Immunol. 2022 Feb 11;13:823145. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.823145. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35222402 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Allelic exclusion of immunoglobulin genes: models and mechanisms.Immunol Rev. 2010 Sep;237(1):22-42. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2010.00935.x. Immunol Rev. 2010. PMID: 20727027 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oncogenic transformation in the absence of Xrcc4 targets peripheral B cells that have undergone editing and switching.J Exp Med. 2008 Dec 22;205(13):3079-90. doi: 10.1084/jem.20082271. Epub 2008 Dec 8. J Exp Med. 2008. PMID: 19064702 Free PMC article.
-
miRNAs Are Essential for the Regulation of the PI3K/AKT/FOXO Pathway and Receptor Editing during B Cell Maturation.Cell Rep. 2016 Nov 22;17(9):2271-2285. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.11.006. Cell Rep. 2016. PMID: 27880903 Free PMC article.
-
Allelic polymorphism controls autoreactivity and vaccine elicitation of human broadly neutralizing antibodies against influenza virus.Immunity. 2022 Sep 13;55(9):1693-1709.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2022.07.006. Epub 2022 Aug 10. Immunity. 2022. PMID: 35952670 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of central tolerance for B cells.Nat Rev Immunol. 2017 May;17(5):281-294. doi: 10.1038/nri.2017.19. Epub 2017 Apr 3. Nat Rev Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28368006 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Apel TW, Scherer A, Adachi T, Auch D, Ayane M, Reth M. The ribose 5-phosphate isomerase-encoding gene is located immediately downstream from that encoding murine immunoglobulin kappa. Gene. 1995;156:191–197. - PubMed
-
- Brauninger A, Goossens T, Rajewsky K, Kuppers R. Regulation of immunoglobulin light chain gene rearrangements during early B cell development in the human. Eur J Immunol. 2001;31:3631–3637. - PubMed
-
- Casellas R, Shih TA, Kleinewietfeld M, Rakonjac J, Nemazee D, Rajewsky K, Nussenzweig MC. Contribution of receptor editing to the antibody repertoire. Science. 2001;291:1541–1544. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- F31 AI052484-01/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI007606-03/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI 33608/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI 059714/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI007606/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- F31 AI052484/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI033608-13/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI007606-05/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI 052484/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- F31 AI052484-02/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI007606-04/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI007606-06/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI033608-13S1/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI033608-11/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- F31 AI052484-03/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI033608-14/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI059714/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI033608-12/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI033608/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI033608-15/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI 007606/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

