MicroRNAs (miRNAs) in neurodegenerative diseases
- PMID: 18226108
- PMCID: PMC2859437
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.2007.00120.x
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) in neurodegenerative diseases
Abstract
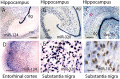
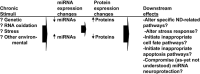
Aging-related neurodegenerative diseases (NDs) are the culmination of many different genetic and environmental influences. Prior studies have shown that RNAs are pathologically altered during the inexorable course of some NDs. Recent evidence suggests that microRNAs (miRNAs) may be a contributing factor in neurodegeneration. miRNAs are brain-enriched, small ( approximately 22 nucleotides) non-coding RNAs that participate in mRNA translational regulation. Although discovered in the framework of worm development, miRNAs are now appreciated to play a dynamic role in many mammalian brain-related biochemical pathways, including neuroplasticity and stress responses. Research about miRNAs in the context of neurodegeneration is accumulating rapidly, and the goal of this review is to provide perspective for these new data that may be helpful to specialists in either field. An overview is provided about the normal functions for miRNAs, including some of the newer concepts related to the human brain. Recently published studies pertaining to the roles of miRNAs in NDs--including Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease and triplet repeat disorders-are described. Finally, a discussion is included with theoretical syntheses and possible future directions in exploring the nexus between miRNA and ND research.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Causes and Consequences of MicroRNA Dysregulation in Neurodegenerative Diseases.Mol Neurobiol. 2015;51(3):1249-62. doi: 10.1007/s12035-014-8803-9. Epub 2014 Jun 29. Mol Neurobiol. 2015. PMID: 24973986 Review.
-
MicroRNAs in glaucoma and neurodegenerative diseases.J Hum Genet. 2017 Jan;62(1):105-112. doi: 10.1038/jhg.2016.91. Epub 2016 Jul 14. J Hum Genet. 2017. PMID: 27412874 Review.
-
New insights into the role of microRNAs and long noncoding RNAs in most common neurodegenerative diseases.J Cell Biochem. 2019 Jun;120(6):8908-8918. doi: 10.1002/jcb.28361. Epub 2019 Jan 20. J Cell Biochem. 2019. PMID: 30663117 Review.
-
MicroRNAs Dysregulation and Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Neurodegenerative Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 20;21(17):5986. doi: 10.3390/ijms21175986. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32825273 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting MicroRNAs in Prevention and Treatment of Neurodegenerative Disorders.Drug Dev Res. 2015 Nov;76(7):397-418. doi: 10.1002/ddr.21277. Epub 2015 Sep 11. Drug Dev Res. 2015. PMID: 26359796 Review.
Cited by
-
University of Kentucky Sanders-Brown healthy brain aging volunteers: donor characteristics, procedures and neuropathology.Curr Alzheimer Res. 2012 Jul;9(6):724-33. doi: 10.2174/156720512801322591. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2012. PMID: 22471862 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular dynamics simulations of Ago silencing complexes reveal a large repertoire of admissible 'seed-less' targets.Sci Rep. 2012;2:569. doi: 10.1038/srep00569. Epub 2012 Aug 10. Sci Rep. 2012. PMID: 22888400 Free PMC article.
-
Grouping Pentylenetetrazol-Induced Epileptic Rats According to Memory Impairment and MicroRNA Expression Profiles in the Hippocampus.PLoS One. 2015 May 11;10(5):e0126123. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0126123. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25962166 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro maturation in the presence of Leukemia Inhibitory Factor modulates gene and miRNA expression in bovine oocytes and embryos.Sci Rep. 2020 Oct 20;10(1):17777. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-74961-6. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33082423 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging urinary alpha-synuclein and miRNA biomarkers in Parkinson's disease.Metab Brain Dis. 2022 Aug;37(6):1687-1696. doi: 10.1007/s11011-021-00735-2. Epub 2021 Apr 21. Metab Brain Dis. 2022. PMID: 33881722 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

