Sperm express a Ca2+-regulated NAADP synthase
- PMID: 18215126
- PMCID: PMC2518628
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20071616
Sperm express a Ca2+-regulated NAADP synthase
Abstract
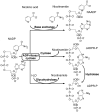
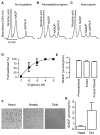
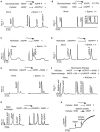
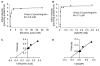
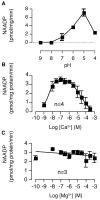
NAADP (nicotinic acid-adenine dinucleotide phosphate), the most potent Ca2+-mobilizing second messenger, is active in a wide range of organisms and cell types. Until now, all NAADP-producing enzymes have been thought to be members of the ADP-ribosyl cyclase family. ADP-ribosyl cyclases exhibit promiscuous substrate selectivity, synthesize a variety of products and are regulated in a limited manner, which may be non-physiological. In the present paper, we report the presence of an enzyme on the surface of sea urchin sperm that exhibits bell-shaped regulation by Ca2+ over a range (EC(50) of 10 nM and IC(50) of 50 microM) that is physiologically relevant. Uniquely, this surface enzyme possesses complete selectivity for nucleotides with a 2'-phosphate group and exhibits only base-exchange activity without any detectable cyclase activity. Taken together, these findings indicate that this novel enzyme should be considered as the first true NAADP synthase.
Figures
Comment in
-
Ca2+ signalling: a new route to NAADP.Biochem J. 2008 Apr 1;411(1):e1-3. doi: 10.1042/BJ20080282. Biochem J. 2008. PMID: 18333834 Review.
Similar articles
-
Cyclic GMP-dependent and -independent effects on the synthesis of the calcium messengers cyclic ADP-ribose and nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide phosphate.J Biol Chem. 1998 Jan 2;273(1):118-25. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.1.118. J Biol Chem. 1998. PMID: 9417055
-
Fluorescent analogs of NAADP with calcium mobilizing activity.Biochim Biophys Acta. 1998 Sep 16;1425(1):263-71. doi: 10.1016/s0304-4165(98)00079-8. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1998. PMID: 9813359
-
The ecto-enzyme CD38 is a nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NAADP) synthase that couples receptor activation to Ca2+ mobilization from lysosomes in pancreatic acinar cells.J Biol Chem. 2010 Dec 3;285(49):38251-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.125864. Epub 2010 Sep 24. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20870729 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of calcium signaling by cyclic ADP-ribose and NAADP.Physiol Rev. 1997 Oct;77(4):1133-64. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1997.77.4.1133. Physiol Rev. 1997. PMID: 9354813 Review.
-
The hunt for an alternate way to generate NAADP. Focus on "NAADP as a second messenger: neither CD38 nor base-exchange reaction are necessary for in vivo generation of NAADP in myometrial cells".Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2007 Jan;292(1):C4-7. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00390.2006. Epub 2006 Aug 9. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2007. PMID: 16899546 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
A single residue in a novel ADP-ribosyl cyclase controls production of the calcium-mobilizing messengers cyclic ADP-ribose and nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide phosphate.J Biol Chem. 2010 Jun 25;285(26):19900-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.105312. Epub 2010 Apr 12. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20385553 Free PMC article.
-
TPC2-mediated Ca2+ signaling is required for the establishment of synchronized activity in developing zebrafish primary motor neurons.Dev Biol. 2018 Jun 1;438(1):57-68. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2018.02.011. Epub 2018 Mar 23. Dev Biol. 2018. PMID: 29577882 Free PMC article.
-
The importance of NAD in multiple sclerosis.Curr Pharm Des. 2009;15(1):64-99. doi: 10.2174/138161209787185751. Curr Pharm Des. 2009. PMID: 19149604 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Two-Pore Channels: Lessons from Mutant Mouse Models.Messenger (Los Angel). 2015 Jun;4(1):4-22. doi: 10.1166/msr.2015.1041. Messenger (Los Angel). 2015. PMID: 27330869 Free PMC article.
-
Preferential Coupling of the NAADP Pathway to Exocytosis in T-Cells.Messenger (Los Angel). 2015 Jun;4(1):53-66. doi: 10.1166/msr.2015.1040. Messenger (Los Angel). 2015. PMID: 27330870 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Streb H, Irvine RF, Berridge MJ, Schulz I. Release of Ca2+ from a nonmitochondrial intracellular store in pancreatic acinar cells by inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate. Nature. 1983;306:67–9. - PubMed
-
- Lee HC, Walseth TF, Bratt GT, Hayes RN, Clapper DL. Structural determination of a cyclic metabolite of NAD+ with intracellular Ca2+-mobilizing activity. J. Biol. Chem. 1989;264:1608–15. - PubMed
-
- Young KW, Nahorski SR. Sphingosine 1-phosphate: a Ca2+ release mediator in the balance. Cell Calcium. 2002;32:335–41. - PubMed
-
- Lee HC, Aarhus R. A derivative of NADP mobilizes calcium stores insensitive to inositol trisphosphate and cyclic ADP-ribose. J. Biol. Chem. 1995;270:2152–7. - PubMed
-
- Churchill GC, Okada Y, Thomas JM, Genazzani AA, Patel S, Galione A. NAADP mobilizes Ca2+ from reserve granules, lysosome-related organelles, in sea urchin eggs. Cell. 2002;111:703–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

