Identification of a new site of sumoylation on Tel (ETV6) uncovers a PIAS-dependent mode of regulating Tel function
- PMID: 18212042
- PMCID: PMC2268428
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.01159-07
Identification of a new site of sumoylation on Tel (ETV6) uncovers a PIAS-dependent mode of regulating Tel function
Abstract
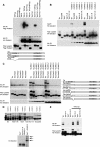
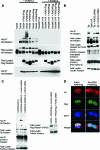
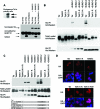
Cell proliferation and differentiation are governed by a finely controlled balance between repression and activation of gene expression. The vertebrate Ets transcriptional repressor Tel (ETV6) and its invertebrate orthologue Yan, play pivotal roles in cell fate determination although the precise mechanisms by which repression of gene expression by these factors is achieved are not clearly defined. Here, we report the identification and characterization of the primary site of sumoylation of Tel, lysine 11 (K11), which is highly conserved in vertebrates (except Danio rerio). We demonstrate that in cells PIAS3 binds to Tel and stimulates sumoylation of K11 in the nucleus. Both Tel monomers and oligomers are efficiently sumoylated on K11 in vitro; but in cells only Tel oligomers are found conjugated with SUMO, whereas sumoylation of Tel monomers is transitory and appears to sensitize them for proteasomal degradation. Mechanistically, sumoylation of K11 inhibits repression of gene expression by full-length Tel. In accordance with this observation, we found that sumoylation impedes Tel association with DNA. By contrast, a Tel isoform lacking K11 (TelM43) is strongly repressive. This isoform results from translation from an alternative initiation codon (M43) that is common to all Tel proteins that also contain the K11 sumoylation consensus site. We find that PIAS3 may have a dual, context-dependent influence on Tel; it mediates Tel sumoylation, but it also augments Tel's repressive function in a sumoylation-independent fashion. Our data support a model that suggests that PIAS-mediated sumoylation of K11 and the emergence of TelM43 in early vertebrates are linked and that this serves to refine spatiotemporal control of gene expression by Tel by establishing a pool of Tel molecules that are available either to be recycled to reinforce repression of gene expression or are degraded in a regulated fashion.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Downregulation of vertebrate Tel (ETV6) and Drosophila Yan is facilitated by an evolutionarily conserved mechanism of F-box-mediated ubiquitination.Mol Cell Biol. 2008 Jul;28(13):4394-406. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01914-07. Epub 2008 Apr 21. Mol Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18426905 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of MBD1-mediated transcriptional repression by SUMO and PIAS proteins.EMBO J. 2006 Nov 15;25(22):5317-28. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601404. Epub 2006 Oct 26. EMBO J. 2006. Retraction in: EMBO J. 2019 Oct 15;38(20):e103220. doi: 10.15252/embj.2019103220. PMID: 17066076 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Small ubiquitin-like modifier conjugation regulates nuclear export of TEL, a putative tumor suppressor.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Mar 18;100(6):3257-62. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0637114100. Epub 2003 Mar 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003. PMID: 12626745 Free PMC article.
-
PIAS proteins as regulators of small ubiquitin-related modifier (SUMO) modifications and transcription.Biochem Soc Trans. 2007 Dec;35(Pt 6):1405-8. doi: 10.1042/BST0351405. Biochem Soc Trans. 2007. PMID: 18031232 Review.
-
Proteins of the ETS family with transcriptional repressor activity.Oncogene. 2000 Dec 18;19(55):6524-32. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1204045. Oncogene. 2000. PMID: 11175368 Review.
Cited by
-
The Diverse Roles of ETV6 Alterations in B-Lymphoblastic Leukemia and Other Hematopoietic Cancers.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024;1459:291-320. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-62731-6_13. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024. PMID: 39017849 Review.
-
Autoinhibition of ETV6 (TEL) DNA binding: appended helices sterically block the ETS domain.J Mol Biol. 2012 Aug 3;421(1):67-84. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2012.05.010. Epub 2012 May 12. J Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22584210 Free PMC article.
-
ETV6 in hematopoiesis and leukemia predisposition.Semin Hematol. 2017 Apr;54(2):98-104. doi: 10.1053/j.seminhematol.2017.04.005. Epub 2017 Apr 7. Semin Hematol. 2017. PMID: 28637624 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypermethylation of miR-181b in monocytes is associated with coronary artery disease and promotes M1 polarized phenotype via PIAS1-KLF4 axis.Cardiovasc Diagn Ther. 2020 Aug;10(4):738-751. doi: 10.21037/cdt-20-407. Cardiovasc Diagn Ther. 2020. PMID: 32968630 Free PMC article.
-
Ubiquitin-Mediated Control of ETS Transcription Factors: Roles in Cancer and Development.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 12;22(10):5119. doi: 10.3390/ijms22105119. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34066106 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Baker, D. A, B. Mille-Baker, S. M. Wainwright, D. Ish-Horowicz, and N. J. Dibb. 2001. Mae mediates MAP kinase phosphorylation of Ets transcription factors in Drosophila. Nature 411330-334. - PubMed
-
- Barjesteh van Waalwijk van Doorn-Khosrovani, S. B., D. Spensberger, Y. de Knegt, M. Tang, B. Löwenberg, and R. Delwel. 2005. Somatic heterozygous mutations in ETV6 (TEL) and frequent absence of ETV6 protein in acute myeloid leukemia. Oncogene 244129-4137. - PubMed
-
- Fenrick, R., L. Wang, J. Nip, J. M. Amann, R. J. Rooney, J. Walker-Daniels, H. C. Crawford, D. L. Hulboy, M. S. Kinch, L. M. Matrisian, and S. W. Hiebert. 2000. TEL, a putative tumor suppressor, modulates cell growth and cell morphology of Ras-transformed cells while repressing the transcription of stromelysin-1. Mol. Cell. Biol. 205828-5839. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
