Rice yellow mottle virus, an RNA plant virus, evolves as rapidly as most RNA animal viruses
- PMID: 18199644
- PMCID: PMC2268501
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02506-07
Rice yellow mottle virus, an RNA plant virus, evolves as rapidly as most RNA animal viruses
Abstract
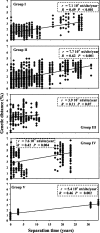
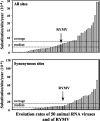
The rate of evolution of an RNA plant virus has never been estimated using temporally spaced sequence data, by contrast to the information available on an increasing range of animal viruses. Accordingly, the evolution rate of Rice yellow mottle virus (RYMV) was calculated from sequences of the coat protein gene of isolates collected from rice over a 40-year period in different parts of Africa. The evolution rate of RYMV was estimated by pairwise distance linear regression on five phylogeographically defined groups comprising a total of 135 isolates. It was further assessed from 253 isolates collected all over Africa by Bayesian coalescent methods under strict and relaxed molecular clock models and under constant size and skyline population genetic models. Consistent estimates of the evolution rate between 4 x 10(-4) and 8 x 10(-4) nucleotides (nt)/site/year were obtained whatever method and model were applied. The synonymous evolution rate was between 8 x 10(-4) and 11 x 10(-4) nt/site/year. The overall and synonymous evolution rates of RYMV were within the range of the rates of 50 RNA animal viruses, below the average but above the distribution median. Experimentally, in host change studies, substitutions accumulated at an even higher rate. The results show that an RNA plant virus such as RYMV evolves as rapidly as most RNA animal viruses. Knowledge of the molecular clock of plant viruses provides methods for testing a wide range of biological hypotheses.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Diversification of rice yellow mottle virus and related viruses spans the history of agriculture from the neolithic to the present.PLoS Pathog. 2008 Aug 15;4(8):e1000125. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000125. PLoS Pathog. 2008. PMID: 18704169 Free PMC article.
-
Recombination, selection and clock-like evolution of Rice yellow mottle virus.Virology. 2009 Nov 10;394(1):164-72. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2009.08.008. Epub 2009 Sep 9. Virology. 2009. PMID: 19740507
-
A reassessment of the epidemiology of Rice yellow mottle virus following recent advances in field and molecular studies.Virus Res. 2009 May;141(2):258-67. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2009.01.011. Epub 2009 Feb 3. Virus Res. 2009. PMID: 19195488
-
The biogeography of viral emergence: rice yellow mottle virus as a case study.Curr Opin Virol. 2015 Feb;10:7-13. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2014.12.002. Epub 2014 Dec 26. Curr Opin Virol. 2015. PMID: 25544357 Review.
-
A Review of Vector-Borne Rice Viruses.Viruses. 2022 Oct 14;14(10):2258. doi: 10.3390/v14102258. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 36298813 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Fine mapping of RYMV3: a new resistance gene to Rice yellow mottle virus from Oryza glaberrima.Theor Appl Genet. 2017 Apr;130(4):807-818. doi: 10.1007/s00122-017-2853-0. Epub 2017 Jan 31. Theor Appl Genet. 2017. PMID: 28144699
-
Evolution of a wild-plant tobamovirus passaged through an exotic host: Fixation of mutations and increased replication.Virus Evol. 2017 Mar 2;3(1):vex001. doi: 10.1093/ve/vex001. eCollection 2017 Jan. Virus Evol. 2017. PMID: 28458912 Free PMC article.
-
On the importance of negative controls in viral landscape phylogeography.Virus Evol. 2018 Aug 16;4(2):vey023. doi: 10.1093/ve/vey023. eCollection 2018 Jul. Virus Evol. 2018. PMID: 30151241 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid turnover of intra-host genetic diversity in Zucchini yellow mosaic virus.Virus Res. 2011 Feb;155(2):389-96. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2010.11.007. Epub 2010 Dec 4. Virus Res. 2011. PMID: 21138748 Free PMC article.
-
Comparing patterns and scales of plant virus phylogeography: Rice yellow mottle virus in Madagascar and in continental Africa.Virus Evol. 2019 Aug 1;5(2):vez023. doi: 10.1093/ve/vez023. eCollection 2019 Jul. Virus Evol. 2019. PMID: 31384483 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abubakar, Z., F. Ali, A. Pinel, O. Traoré, P. N′Guessan, J. Notteghem, F. Kimmins, G. Konaté, and D. Fargette. 2003. Phylogeography of Rice yellow mottle virus in Africa. J. Gen. Virol. 84733-743. - PubMed
-
- Allarangaye, M. D., O. Traoré, E. V. S. Traoré, R. J. Millogo, S. Guinko, and G. Konaté. 2007. Host range of Rice yellow mottle virus in Sudano-Sahelian savannahs. Pakistan J. Biol. Sci. 101414-1421. - PubMed
-
- Bakker, W. 1974. Characterization and ecological aspects of rice yellow mottle virus in Kenya. Agricultural research report no. 829. Wageningen Agricultural University, Wageningen, The Netherlands.
-
- Blok, J., A. Mackenzie, P. Guy, and A. Gibbs. 1987. Nucleotide sequence comparisons of turnip yellow mosaic virus isolates from Australia and Europe. Arch. Virol. 97283-295. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

