Calcium signalling and calcium transport in bone disease
- PMID: 18193652
- PMCID: PMC2970924
- DOI: 10.1007/978-1-4020-6191-2_21
Calcium signalling and calcium transport in bone disease
Abstract
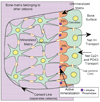
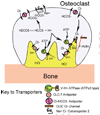
Calcium transport and calcium signalling mechanisms in bone cells have, in many cases, been discovered by study of diseases with disordered bone metabolism. Calcium matrix deposition is driven primarily by phosphate production, and disorders in bone deposition include abnormalities in membrane phosphate transport such as in chondrocalcinosis, and defects in phosphate-producing enzymes such as in hypophosphatasia. Matrix removal is driven by acidification, which dissolves the mineral. Disorders in calcium removal from bone matrix by osteoclasts cause osteopetrosis. On the other hand, although bone is central to management of extracellular calcium, bone is not a major calcium sensing organ, although calcium sensing proteins are expressed in both osteoblasts and osteoclasts. Intracellular calcium signals are involved in secondary control including cellular motility and survival, but the relationship of these findings to specific diseases is not clear. Intracellular calcium signals may regulate the balance of cell survival versus proliferation or anabolic functional response as part of signalling cascades that integrate the response to primary signals via cell stretch, estrogen, tyrosine kinase, and tumor necrosis factor receptors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Calcium-sensing receptors in bone cells.J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2004 Dec;4(4):412-3. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2004. PMID: 15758286 Review. No abstract available.
-
The transient receptor potential channel TRPV6 is dynamically expressed in bone cells but is not crucial for bone mineralization in mice.J Cell Physiol. 2012 May;227(5):1951-9. doi: 10.1002/jcp.22923. J Cell Physiol. 2012. PMID: 21732366
-
Calcium and bone disease.Biofactors. 2011 May-Jun;37(3):159-67. doi: 10.1002/biof.143. Epub 2011 Jun 14. Biofactors. 2011. PMID: 21674636 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of the calcium-sensing receptor in extracellular calcium homeostasis.Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013 Jun;27(3):333-43. doi: 10.1016/j.beem.2013.02.006. Epub 2013 Mar 13. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013. PMID: 23856263 Review.
-
Support of bone mineral deposition by regulation of pH.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2018 Oct 1;315(4):C587-C597. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00056.2018. Epub 2018 Jul 25. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2018. PMID: 30044661 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Calcium released by osteoclastic resorption stimulates autocrine/paracrine activities in local osteogenic cells to promote coupled bone formation.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2022 May 1;322(5):C977-C990. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00413.2021. Epub 2022 Apr 6. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35385325 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced osteogenic differentiation potential of Arnica montana and Bellis perennis in C3H10T1/2 multipotent mesenchymal stem cells.Mol Biol Rep. 2024 Apr 29;51(1):596. doi: 10.1007/s11033-024-09509-2. Mol Biol Rep. 2024. PMID: 38683461
-
In Vitro and In Vivo Characterization of N-Acetyl-L-Cysteine Loaded Beta-Tricalcium Phosphate Scaffolds.Int J Biomater. 2018 Jul 31;2018:9457910. doi: 10.1155/2018/9457910. eCollection 2018. Int J Biomater. 2018. PMID: 30151010 Free PMC article.
-
The Mechanotransduction Signaling Pathways in the Regulation of Osteogenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 20;24(18):14326. doi: 10.3390/ijms241814326. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37762629 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular stratification of arrhythmogenic mechanisms in the Andersen Tawil syndrome.Cardiovasc Res. 2023 May 2;119(4):919-932. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvac118. Cardiovasc Res. 2023. PMID: 35892314 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adebanjo OA, Biswas G, Moonga BS, Anandatheerthavarada HK, Sun L, Bevis PJ, Sodam BR, Lai FA, Avadhani NG, Zaidi M. Novel biochemical and functional insights into nuclear Ca2+ transport through IP3Rs and RyRs in osteoblasts. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2000;278:F784–F791. - PubMed
-
- Adebanjo OA, Anandathreethavarada HK, Koval AP, Moonga BS, Biswas G, Sun L, Sodam BR, Bevis PJR, Huang CL-H, Epstein S, Lai FA, Avadhani NG, Zaidi M. A new function for CD38/ADP-ribosyl cyclase in nuclear Ca2+ homeostasis. Nature Cell Biology. 1999;7:409–414. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
