Conserved regulation of MAP kinase expression by PUF RNA-binding proteins
- PMID: 18166083
- PMCID: PMC2323325
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.0030233
Conserved regulation of MAP kinase expression by PUF RNA-binding proteins
Abstract
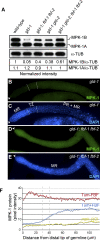
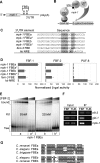
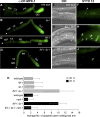
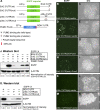
Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and PUF (for Pumilio and FBF [fem-3 binding factor]) RNA-binding proteins control many cellular processes critical for animal development and tissue homeostasis. In the present work, we report that PUF proteins act directly on MAPK/ERK-encoding mRNAs to downregulate their expression in both the Caenorhabditis elegans germline and human embryonic stem cells. In C. elegans, FBF/PUF binds regulatory elements in the mpk-1 3' untranslated region (3' UTR) and coprecipitates with mpk-1 mRNA; moreover, mpk-1 expression increases dramatically in FBF mutants. In human embryonic stem cells, PUM2/PUF binds 3'UTR elements in both Erk2 and p38alpha mRNAs, and PUM2 represses reporter constructs carrying either Erk2 or p38alpha 3' UTRs. Therefore, the PUF control of MAPK expression is conserved. Its biological function was explored in nematodes, where FBF promotes the self-renewal of germline stem cells, and MPK-1 promotes oocyte maturation and germ cell apoptosis. We found that FBF acts redundantly with LIP-1, the C. elegans homolog of MAPK phosphatase (MKP), to restrict MAPK activity and prevent apoptosis. In mammals, activated MAPK can promote apoptosis of cancer cells and restrict stem cell self-renewal, and MKP is upregulated in cancer cells. We propose that the dual negative regulation of MAPK by both PUF repression and MKP inhibition may be a conserved mechanism that influences both stem cell maintenance and tumor progression.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests. JAT owns stock, serves on the Board of Directors, and serves as Chief Scientific Officer of Cellular Dynamics International and Stem Cell Products. JAT also serves as Scientific Director of the WiCell Research Institute.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A conserved RNA-binding protein controls germline stem cells in Caenorhabditis elegans.Nature. 2002 Jun 6;417(6889):660-3. doi: 10.1038/nature754. Epub 2002 May 22. Nature. 2002. PMID: 12050669
-
The PUF binding landscape in metazoan germ cells.RNA. 2016 Jul;22(7):1026-43. doi: 10.1261/rna.055871.116. Epub 2016 May 10. RNA. 2016. PMID: 27165521 Free PMC article.
-
MPK-1/ERK regulatory network controls the number of sperm by regulating timing of sperm-oocyte switch in C. elegans germline.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017 Sep 30;491(4):1077-1082. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.08.014. Epub 2017 Aug 3. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017. PMID: 28782521 Free PMC article.
-
Role of PUF-8/PUF protein in stem cell control, sperm-oocyte decision and cell fate reprogramming.J Cell Physiol. 2014 Oct;229(10):1306-11. doi: 10.1002/jcp.24618. J Cell Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24638209 Review.
-
Diverse Roles of PUF Proteins in Germline Stem and Progenitor Cell Development in C. elegans.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Feb 6;8:29. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00029. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32117964 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
C. elegans Germline as Three Distinct Tumor Models.Biology (Basel). 2024 Jun 8;13(6):425. doi: 10.3390/biology13060425. Biology (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38927305 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Understanding and engineering RNA sequence specificity of PUF proteins.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2009 Feb;19(1):110-5. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2008.12.009. Epub 2009 Jan 29. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2009. PMID: 19186050 Free PMC article.
-
Cooperative target mRNA destabilization and translation inhibition by miR-58 microRNA family in C. elegans.Genome Res. 2015 Nov;25(11):1680-91. doi: 10.1101/gr.183160.114. Epub 2015 Jul 31. Genome Res. 2015. PMID: 26232411 Free PMC article.
-
Pumilio 1 suppresses multiple activators of p53 to safeguard spermatogenesis.Curr Biol. 2012 Mar 6;22(5):420-5. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2012.01.039. Epub 2012 Feb 16. Curr Biol. 2012. PMID: 22342750 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomics and pluripotency.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2011 Dec;46(6):493-506. doi: 10.3109/10409238.2011.624491. Epub 2011 Oct 15. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21999516 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lackner MR, Kornfeld K, Miller LM, Horvitz HR, Kim SK. A MAP kinase homolog, mpk-1, is involved in ras-mediated induction of vulval cell fates in Caenorhabditis elegans . Genes Dev. 1994;8:160–173. - PubMed
-
- Wu Y, Han M. Suppression of activated Let-60 Ras protein defines a role of Caenorhabditis elegans Sur-1 MAP kinase in vulval differentiation. Genes Dev. 1994;8:147–159. - PubMed
-
- Marshall CJ. MAP kinase kinase kinase, MAP kinase kinase and MAP kinase. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1994;4:82–89. - PubMed
-
- Camps M, Nichols A, Arkinstall S. Dual specificity phosphatases: a gene family for control of MAP kinase function. FASEB J. 2000;14:6–16. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

