Molecular basis for the unique deubiquitinating activity of the NF-kappaB inhibitor A20
- PMID: 18164316
- PMCID: PMC2346432
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2007.11.092
Molecular basis for the unique deubiquitinating activity of the NF-kappaB inhibitor A20
Abstract
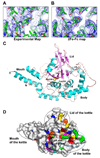
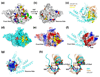
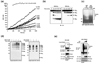
Nuclear factor kappaB (NF-kappaB) activation in tumor necrosis factor, interleukin-1, and Toll-like receptor pathways requires Lys63-linked nondegradative polyubiquitination. A20 is a specific feedback inhibitor of NF-kappaB activation in these pathways that possesses dual ubiquitin-editing functions. While the N-terminal domain of A20 is a deubiquitinating enzyme (DUB) for Lys63-linked polyubiquitinated signaling mediators such as TRAF6 and RIP, its C-terminal domain is a ubiquitin ligase (E3) for Lys48-linked degradative polyubiquitination of the same substrates. To elucidate the molecular basis for the DUB activity of A20, we determined its crystal structure and performed a series of biochemical and cell biological studies. The structure reveals the potential catalytic mechanism of A20, which may be significantly different from papain-like cysteine proteases. Ubiquitin can be docked onto a conserved A20 surface; this interaction exhibits charge complementarity and no steric clash. Surprisingly, A20 does not have specificity for Lys63-linked polyubiquitin chains. Instead, it effectively removes Lys63-linked polyubiquitin chains from TRAF6 without dissembling the chains themselves. Our studies suggest that A20 does not act as a general DUB but has the specificity for particular polyubiquitinated substrates to assure its fidelity in regulating NF-kappaB activation in the tumor necrosis factor, interleukin-1, and Toll-like receptor pathways.
Figures

Similar articles
-
De-ubiquitination and ubiquitin ligase domains of A20 downregulate NF-kappaB signalling.Nature. 2004 Aug 5;430(7000):694-9. doi: 10.1038/nature02794. Epub 2004 Jul 18. Nature. 2004. PMID: 15258597
-
The K48-K63 Branched Ubiquitin Chain Regulates NF-κB Signaling.Mol Cell. 2016 Oct 20;64(2):251-266. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2016.09.014. Epub 2016 Oct 13. Mol Cell. 2016. PMID: 27746020
-
The seventh zinc finger motif of A20 is required for the suppression of TNF-α-induced apoptosis.FEBS Lett. 2015 May 22;589(12):1369-75. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2015.04.022. Epub 2015 Apr 22. FEBS Lett. 2015. PMID: 25911380
-
ABINs: A20 binding inhibitors of NF-kappa B and apoptosis signaling.Biochem Pharmacol. 2009 Jul 15;78(2):105-14. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2009.02.009. Epub 2009 Feb 27. Biochem Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19464428 Review.
-
Expression, biological activities and mechanisms of action of A20 (TNFAIP3).Biochem Pharmacol. 2010 Dec 15;80(12):2009-20. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2010.06.044. Epub 2010 Jul 3. Biochem Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20599425 Review.
Cited by
-
Dimerization and ubiquitin mediated recruitment of A20, a complex deubiquitinating enzyme.Immunity. 2013 May 23;38(5):896-905. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2013.03.008. Epub 2013 Apr 18. Immunity. 2013. PMID: 23602765 Free PMC article.
-
Non-catalytic ubiquitin binding by A20 prevents psoriatic arthritis-like disease and inflammation.Nat Immunol. 2020 Apr;21(4):422-433. doi: 10.1038/s41590-020-0634-4. Epub 2020 Mar 16. Nat Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32205880 Free PMC article.
-
Protein ubiquitination in lymphoid malignancies.Immunol Rev. 2015 Jan;263(1):240-56. doi: 10.1111/imr.12247. Immunol Rev. 2015. PMID: 25510281 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phosphorylation-dependent activity of the deubiquitinase DUBA.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2012 Jan 15;19(2):171-5. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2206. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22245969
-
The ubiquitin-modifying enzyme A20 restricts ubiquitination of the kinase RIPK3 and protects cells from necroptosis.Nat Immunol. 2015 Jun;16(6):618-27. doi: 10.1038/ni.3172. Epub 2015 May 4. Nat Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25939025 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jaattela M, Mouritzen H, Elling F, Bastholm L. A20 zinc finger protein inhibits TNF and IL-1 signaling. J Immunol. 1996;156:1166–1173. - PubMed
-
- Cooper JT, Stroka DM, Brostjan C, Palmetshofer A, Bach FH, Ferran C. A20 blocks endothelial cell activation through a NF-kappaB-dependent mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:18068–18073. - PubMed
-
- Ferran C, Stroka DM, Badrichani AZ, Cooper JT, Bach FH. Adenovirus-mediated gene transfer of A20 renders endothelial cells resistant to activation: a means of evaluating the role of endothelial cell activation in xenograft rejection. Transplant Proc. 1997;29:879–880. - PubMed
-
- Beyaert R, Heyninck K, Van Huffel S. A20 and A20-binding proteins as cellular inhibitors of nuclear factor-kappa B-dependent gene expression and apoptosis. Biochem Pharmacol. 2000;60:1143–1151. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

