The interferon signaling network and transcription factor C/EBP-beta
- PMID: 18163952
- PMCID: PMC2782719
The interferon signaling network and transcription factor C/EBP-beta
Abstract
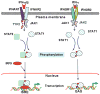
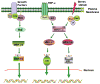
Cytokines like interferons (IFNs) play a central role in regulating innate and specific immunities against the pathogens and neoplastic cells. A number of signaling pathways are induced in response to IFN in various cells. One classic mechanism employed by IFNs is the JAK-STAT signaling pathway for inducing cellular responses. Here we describe the non-STAT pathways that participate in IFN-induced responses. In particular, we will focus on the role played by transcription factor C/EBP-beta in mediating these responses.
Figures
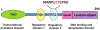
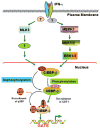
Similar articles
-
CCAAT/enhancer binding proteins and interferon signaling pathways.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2005 Dec;25(12):757-69. doi: 10.1089/jir.2005.25.757. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2005. PMID: 16375604 Review.
-
Modeling regulatory mechanisms in IL-6 signal transduction in hepatocytes.Biotechnol Bioeng. 2006 Dec 5;95(5):850-62. doi: 10.1002/bit.21026. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2006. PMID: 16752369
-
Interference without interferon: interferon-independent induction of interferon-stimulated genes and its role in cellular innate immunity.mBio. 2024 Oct 16;15(10):e0258224. doi: 10.1128/mbio.02582-24. Epub 2024 Sep 20. mBio. 2024. PMID: 39302126 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Critical role for transcription factor C/EBP-beta in regulating the expression of death-associated protein kinase 1.Mol Cell Biol. 2008 Apr;28(8):2528-48. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00784-07. Epub 2008 Feb 4. Mol Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18250155 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the JAK/STAT signaling pathway in regulation of innate immunity in neuroinflammatory diseases.Clin Immunol. 2018 Apr;189:4-13. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2016.09.014. Epub 2016 Oct 3. Clin Immunol. 2018. PMID: 27713030 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
miR-155 promotes FLT3-ITD-induced myeloproliferative disease through inhibition of the interferon response.Blood. 2017 Jun 8;129(23):3074-3086. doi: 10.1182/blood-2016-09-740209. Epub 2017 Apr 21. Blood. 2017. PMID: 28432220 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a protective microglial state mediated by miR-155 and interferon-γ signaling in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.Nat Neurosci. 2023 Jul;26(7):1196-1207. doi: 10.1038/s41593-023-01355-y. Epub 2023 Jun 8. Nat Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37291336 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclic regulation of transcription factor C/EBP beta in human endometrium.Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2009 Feb 17;7:15. doi: 10.1186/1477-7827-7-15. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2009. PMID: 19222842 Free PMC article.
-
Immune and non-immune mediators in the fibrosis pathogenesis of salivary gland in Sjögren's syndrome.Front Immunol. 2024 Oct 14;15:1421436. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1421436. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39469708 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxidative stress induced interleukin-32 mRNA expression in human bronchial epithelial cells.Respir Res. 2012 Mar 14;13(1):19. doi: 10.1186/1465-9921-13-19. Respir Res. 2012. PMID: 22413812 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kalvakolanu DV, Borden EC. Interferons: cellular and molecular biology of their actions. In: Bertion JR, editor. Encyclopedia Cancer. Vol. 2. 2002. pp. 511–521.
-
- Stark GR, Kerr IM, Williams BR, Silverman RH, Schreiber RD. How cells respond to Interferons. Annu Rev Biochem. 1998;67:227–264. - PubMed
-
- Biron CA. Initial and innate responses to viral infections-pattern setting in immunity or disease. Curr Opin Microbiol. 1999;2:374–381. - PubMed
-
- Williams BR. Signal integration via PKR. Sci STKE. 2001;2001:RE2. - PubMed
-
- Silverman R. 2-5A Dependent RNase L: a regulated endoribonuclease in the interferon system. In: D'Alessio GRJ, editor. Rionucleases: Structure and Functions. 1997. pp. 515–551.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
