The inhibitory HVEM-BTLA pathway counter regulates lymphotoxin receptor signaling to achieve homeostasis of dendritic cells
- PMID: 18097025
- PMCID: PMC2711003
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.180.1.238
The inhibitory HVEM-BTLA pathway counter regulates lymphotoxin receptor signaling to achieve homeostasis of dendritic cells
Abstract
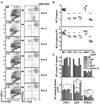
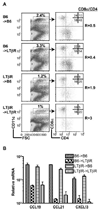
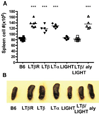
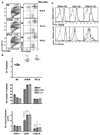
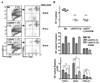
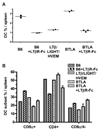
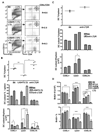
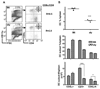
Proliferation of dendritic cells (DC) in the spleen is regulated by positive growth signals through the lymphotoxin (LT)-beta receptor; however, the countering inhibitory signals that achieve homeostatic control are unresolved. Mice deficient in LTalpha, LTbeta, LTbetaR, and the NFkappaB inducing kinase show a specific loss of CD8- DC subsets. In contrast, the CD8alpha- DC subsets were overpopulated in mice deficient in the herpesvirus entry mediator (HVEM) or B and T lymphocyte attenuator (BTLA). HVEM- and BTLA-deficient DC subsets displayed a specific growth advantage in repopulating the spleen in competitive replacement bone marrow chimeric mice. Expression of HVEM and BTLA were required in DC and in the surrounding microenvironment, although DC expression of LTbetaR was necessary to maintain homeostasis. Moreover, enforced activation of the LTbetaR with an agonist Ab drove expansion of CD8alpha- DC subsets, overriding regulation by the HVEM-BTLA pathway. These results indicate the HVEM-BTLA pathway provides an inhibitory checkpoint for DC homeostasis in lymphoid tissue. Together, the LTbetaR and HVEM-BTLA pathways form an integrated signaling network regulating DC homeostasis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Targeting lymphocyte activation through the lymphotoxin and LIGHT pathways.Immunol Rev. 2008 Jun;223:186-201. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2008.00629.x. Immunol Rev. 2008. PMID: 18613837 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The TNF receptor and Ig superfamily members form an integrated signaling circuit controlling dendritic cell homeostasis.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2008 Jun-Aug;19(3-4):277-84. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2008.04.013. Epub 2008 Jun 3. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2008. PMID: 18511331 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The signaling networks of the herpesvirus entry mediator (TNFRSF14) in immune regulation.Immunol Rev. 2011 Nov;244(1):169-87. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2011.01064.x. Immunol Rev. 2011. PMID: 22017438 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The CD160, BTLA, LIGHT/HVEM pathway: a bidirectional switch regulating T-cell activation.Immunol Rev. 2009 May;229(1):244-58. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2009.00783.x. Immunol Rev. 2009. PMID: 19426226 Review.
-
Regulatory T cell expression of herpesvirus entry mediator suppresses the function of B and T lymphocyte attenuator-positive effector T cells.J Immunol. 2008 May 15;180(10):6649-55. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.180.10.6649. J Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18453584
Cited by
-
Fine-tuning of dendritic cell biology by the TNF superfamily.Nat Rev Immunol. 2012 Apr 10;12(5):339-51. doi: 10.1038/nri3193. Nat Rev Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22487654 Review.
-
Immunomodulatory Properties of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors-More than Boosting T-Cell Responses?Cancers (Basel). 2022 Mar 28;14(7):1710. doi: 10.3390/cancers14071710. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35406483 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting lymphocyte activation through the lymphotoxin and LIGHT pathways.Immunol Rev. 2008 Jun;223:186-201. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2008.00629.x. Immunol Rev. 2008. PMID: 18613837 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LTβR signaling in dendritic cells induces a type I IFN response that is required for optimal clonal expansion of CD8+ T cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Feb 1;108(5):2046-51. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1014188108. Epub 2011 Jan 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21245292 Free PMC article.
-
The benefits of clustering in TNF receptor superfamily signaling.Front Immunol. 2023 Aug 17;14:1225704. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1225704. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37662920 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Banchereau J, Briere F, Caux C, Davoust J, Lebecque S, Liu YJ, Pulendran B, Palucka K. Immunobiology of dendritic cells. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2000;18:767–811. - PubMed
-
- Vremec D, Pooley J, Hochrein H, Wu L, Shortman K. CD4 and CD8 expression by dendritic cell subtypes in mouse thymus and spleen. J. Immunol. 2000;164:2978–2986. - PubMed
-
- Leenen PJ, Radosevic K, Voerman JS, Salomon B, van Rooijen N, Klatzmann D, van Ewijk W. Heterogeneity of mouse spleen dendritic cells: in vivo phagocytic activity, expression of macrophage markers, and subpopulation turnover. J. Immunol. 1998;160:2166–2173. - PubMed
-
- Maldonado-Lopez R, Moser M. Dendritic cell subsets and the regulation of Th1/Th2 responses. Semin. Immunol. 2001;13:275–282. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- AI06789/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI067890-01A2/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI067890/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- CA69381/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- AI33068/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI048073/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA069381-120001/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- AI48073/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA069381/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI033068-07/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI033068/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI033068/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI048073-07/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

