The receptor tyrosine kinase EphA2 promotes mammary adenocarcinoma tumorigenesis and metastatic progression in mice by amplifying ErbB2 signaling
- PMID: 18079969
- PMCID: PMC2129239
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI33154
The receptor tyrosine kinase EphA2 promotes mammary adenocarcinoma tumorigenesis and metastatic progression in mice by amplifying ErbB2 signaling
Abstract
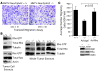
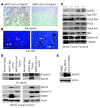
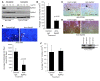
Overexpression of the receptor tyrosine kinase EPH receptor A2 (EphA2) is commonly observed in aggressive breast cancer and correlates with a poor prognosis. However, while EphA2 has been reported to enhance tumorigenesis, proliferation, and MAPK activation in several model systems, other studies suggest that EphA2 activation diminishes these processes and inhibits the activity of MAPK upon ligand stimulation. In this study, we eliminated EphA2 expression in 2 transgenic mouse models of mammary carcinoma. EphA2 deficiency impaired tumor initiation and metastatic progression in mice overexpressing ErbB2 (also known as Neu) in the mammary epithelium (MMTV-Neu mice), but not in mice overexpressing the polyomavirus middle T antigen in mammary epithelium (MMTV-PyV-mT mice). Histologic and ex vivo analyses of MMTV-Neu mouse mammary epithelium indicated that EphA2 enhanced tumor proliferation and motility. Biochemical analyses revealed that EphA2 formed a complex with ErbB2 in human and murine breast carcinoma cells, resulting in enhanced activation of Ras-MAPK signaling and RhoA GTPase. Additionally, MMTV-Neu, but not MMTV-PyV-mT, tumors were sensitive to therapeutic inhibition of EphA2. These data suggest that EphA2 cooperates with ErbB2 to promote tumor progression in mice and may provide a novel therapeutic target for ErbB2-dependent tumors in humans. Moreover, EphA2 function in tumor progression appeared to depend on oncogene context, an important consideration for the application of therapies targeting EphA2.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Sustained trophism of the mammary gland is sufficient to accelerate and synchronize development of ErbB2/Neu-induced tumors.Oncogene. 2006 Jun 1;25(23):3325-34. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1209365. Epub 2006 Jan 23. Oncogene. 2006. PMID: 16434967 Free PMC article.
-
P190B RhoGAP has pro-tumorigenic functions during MMTV-Neu mammary tumorigenesis and metastasis.Breast Cancer Res. 2010;12(5):R73. doi: 10.1186/bcr2643. Epub 2010 Sep 22. Breast Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20860838 Free PMC article.
-
ErbB2/Neu-induced, cyclin D1-dependent transformation is accelerated in p27-haploinsufficient mammary epithelial cells but impaired in p27-null cells.Mol Cell Biol. 2002 Apr;22(7):2204-19. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.7.2204-2219.2002. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 11884607 Free PMC article.
-
Tyrosine kinase signalling in breast cancer: tyrosine kinase-mediated signal transduction in transgenic mouse models of human breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res. 2000;2(3):211-6. doi: 10.1186/bcr56. Epub 2000 Apr 12. Breast Cancer Res. 2000. PMID: 11250712 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Noncanonical TGF-β signaling during mammary tumorigenesis.J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2011 Jun;16(2):127-46. doi: 10.1007/s10911-011-9207-3. Epub 2011 Mar 31. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2011. PMID: 21448580 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Delivery of chemo-sensitizing siRNAs to HER2+-breast cancer cells using RNA aptamers.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Jul;40(13):6319-37. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks294. Epub 2012 Mar 30. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22467215 Free PMC article.
-
Ras functional proximity proteomics establishes mTORC2 as new direct ras effector.Oncotarget. 2019 Aug 27;10(50):5126-5135. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.27025. eCollection 2019 Aug 27. Oncotarget. 2019. PMID: 31497244 Free PMC article.
-
The expansion of targetable biomarkers for CAR T cell therapy.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018 Jul 21;37(1):163. doi: 10.1186/s13046-018-0817-0. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 30031396 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Eph receptors in breast cancer: roles in tumor promotion and tumor suppression.Breast Cancer Res. 2008;10(6):217. doi: 10.1186/bcr2207. Epub 2008 Dec 22. Breast Cancer Res. 2008. PMID: 19144211 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Elevated Slit2 Activity Impairs VEGF-Induced Angiogenesis and Tumor Neovascularization in EphA2-Deficient Endothelium.Mol Cancer Res. 2015 Mar;13(3):524-37. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-14-0142. Epub 2014 Dec 12. Mol Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 25504371 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hanahan D., Weinberg R.A. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell. 2000;100:57–70. - PubMed
-
- Hahn W.C., Weinberg R.A. Rules for making human tumor cells. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002;347:1593–1603. - PubMed
-
- Vogelstein B., Kinzler K.W. Cancer genes and the pathways they control. Nat. Med. 2004;10:789–799. - PubMed
-
- Blume-Jensen P., Hunter T. Oncogenic kinase signalling. Nature. 2001;411:355–365. - PubMed
-
- Brantley-Sieders D.M., Chen J. Eph receptor tyrosine kinases in angiogenesis: from development to disease. Angiogenesis. 2004;7:17–28. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

