The role of carcinine in signaling at the Drosophila photoreceptor synapse
- PMID: 18069895
- PMCID: PMC2134947
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.0030206
The role of carcinine in signaling at the Drosophila photoreceptor synapse
Abstract
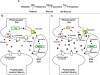
The Drosophila melanogaster photoreceptor cell has long served as a model system for researchers focusing on how animal sensory neurons receive information from their surroundings and translate this information into chemical and electrical messages. Electroretinograph (ERG) analysis of Drosophila mutants has helped to elucidate some of the genes involved in the visual transduction pathway downstream of the photoreceptor cell, and it is now clear that photoreceptor cell signaling is dependent upon the proper release and recycling of the neurotransmitter histamine. While the neurotransmitter transporters responsible for clearing histamine, and its metabolite carcinine, from the synaptic cleft have remained unknown, a strong candidate for a transporter of either substrate is the uncharacterized inebriated protein. The inebriated gene (ine) encodes a putative neurotransmitter transporter that has been localized to photoreceptor cells in Drosophila and mutations in ine result in an abnormal ERG phenotype in Drosophila. Loss-of-function mutations in ebony, a gene required for the synthesis of carcinine in Drosophila, suppress components of the mutant ine ERG phenotype, while loss-of-function mutations in tan, a gene necessary for the hydrolysis of carcinine in Drosophila, have no effect on the ERG phenotype in ine mutants. We also show that by feeding wild-type flies carcinine, we can duplicate components of mutant ine ERGs. Finally, we demonstrate that treatment with H(3) receptor agonists or inverse agonists rescue several components of the mutant ine ERG phenotype. Here, we provide pharmacological and genetic epistatic evidence that ine encodes a carcinine neurotransmitter transporter. We also speculate that the oscillations observed in mutant ine ERG traces are the result of the aberrant activity of a putative H(3) receptor.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests. The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The carcinine transporter CarT is required in Drosophila photoreceptor neurons to sustain histamine recycling.Elife. 2015 Dec 14;4:e10972. doi: 10.7554/eLife.10972. Elife. 2015. PMID: 26653853 Free PMC article.
-
tan and ebony genes regulate a novel pathway for transmitter metabolism at fly photoreceptor terminals.J Neurosci. 2002 Dec 15;22(24):10549-57. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-24-10549.2002. J Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 12486147 Free PMC article.
-
Long-distance mechanism of neurotransmitter recycling mediated by glial network facilitates visual function in Drosophila.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Feb 18;111(7):2812-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1323714111. Epub 2014 Feb 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 24550312 Free PMC article.
-
The dynamics of signaling at the histaminergic photoreceptor synapse of arthropods.Prog Neurobiol. 2007 Jul;82(4):202-27. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2007.03.006. Epub 2007 Apr 19. Prog Neurobiol. 2007. PMID: 17531368 Review.
-
Pigmentation and behavior: potential association through pleiotropic genes in Drosophila.Genes Genet Syst. 2013;88(3):165-74. doi: 10.1266/ggs.88.165. Genes Genet Syst. 2013. PMID: 24025245 Review.
Cited by
-
Two novel forms of ERG oscillation in Drosophila: age and activity dependence.J Neurogenet. 2018 Mar-Jun;32(2):118-126. doi: 10.1080/01677063.2018.1461866. Epub 2018 Apr 24. J Neurogenet. 2018. PMID: 29688104 Free PMC article.
-
Localization of a GABA transporter to glial cells in the developing and adult olfactory pathway of the moth Manduca sexta.J Comp Neurol. 2010 Mar 15;518(6):815-38. doi: 10.1002/cne.22244. J Comp Neurol. 2010. PMID: 20058309 Free PMC article.
-
Alternative tasks of Drosophila tan in neurotransmitter recycling versus cuticle sclerotization disclosed by kinetic properties.J Biol Chem. 2010 Jul 2;285(27):20740-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.120170. Epub 2010 May 3. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20439462 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of a homologue of a vertebrate non-visual opsin Opn3 in the insect photoreceptors.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2022 Oct 24;377(1862):20210274. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2021.0274. Epub 2022 Sep 5. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36058246 Free PMC article.
-
The carcinine transporter CarT is required in Drosophila photoreceptor neurons to sustain histamine recycling.Elife. 2015 Dec 14;4:e10972. doi: 10.7554/eLife.10972. Elife. 2015. PMID: 26653853 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Massoulie J, Sussman J, Bon S, Silman I. Structure and functions of acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase. Prog Brain Res. 1993;98:139–146. - PubMed
-
- Richardt A, Rybak J, Stortkuhl KF, Meinertzhagen IA, Hovemann BT. Ebony protein in the Drosophila nervous system: optic neuropile expression in glial cells. J Comp Neurol. 2002;452:93–102. - PubMed
-
- Arrang JM, Garbarg M, Schwartz JC. Autoinhibition of histamine synthesis mediated by presynaptic H3-receptors. Neuroscience. 1987;23:149–157. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

