Induction of interleukin-6 in human retinal epithelial cells by an attenuated Herpes simplex virus vector requires viral replication and NFkappaB activation
- PMID: 18061164
- PMCID: PMC2279187
- DOI: 10.1016/j.exer.2007.10.008
Induction of interleukin-6 in human retinal epithelial cells by an attenuated Herpes simplex virus vector requires viral replication and NFkappaB activation
Abstract
Gene delivery has potential for treating ocular disease and a number of delivery systems have been tested in animal models. However, several viral vectors have been shown to trigger undesirable transient inflammatory responses in the eye. Previously, it was shown that an attenuated Herpes simplex virus vector (hrR3) transduced numerous cell types in the anterior and posterior segments of monkey eyes, but this was accompanied by inflammation. In the retina, retinal pigment epithelial cells were the predominant cell type transduced by hrR3. IL-6 is an important pro-inflammatory cytokine and may play a role in the response to the hrR3 vector. Infection of human ARPE-19 cells with hrR3 resulted in increased IL-6 expression and secretion 3-4h post-infection. In the presence of acyclovir (70 microM) or in cells infected with UV-inactivated hrR3, IL-6 was not up-regulated indicating viral replication was required. Expression of the HSV-1 alpha and beta genes may be necessary but was not sufficient for NF-kappaB activation and IL-6 up-regulation. The translocation of NF-kappaB into the nucleus also occurred between 3 and 4h post-infection, coincident with increased IL-6 expression. Inhibition of NF-kappaB translocation by an Adenovirus vector expressing a dominant negative IkappaB (AdIkappaBam) inhibited IL-6 up-regulation, indicating that NF-kappaB plays a role in increasing IL-6 expression in APRE-19 cells. The hrR3 virus lacks viral ribonucleotide reductase (RR) activity, thus RR is not required for NF-kappaB activation or IL-6 up-regulation in ARPE-19 cells.
Figures
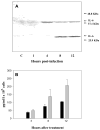
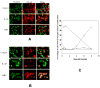

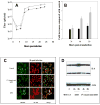
 , hrR3. (C). hrR3 or UV-inactivated hrR3 induction of NF-κB p65 nuclear translocation in ARPE-19 cells. ARPE-19 cells were seeded in 4-well chamber slides the day before experiment. On the day of experiment, cells were infected with hrR3 or UV-inactivated hrR3 and eight hours later they were immunostained for NF-κB p65. Hoescht stained images were pseudocolored green to facilitate image merger. All images were originally taken at a magnification of 40x. (D). Immunoblot analysis of hrR3 or UV-inactivated hrR3 induced IL-6 expression in ARPE-19 cells. The ARPE-19 cells were grown to confluence and the cells were infected with hrR3 or UV-inactivated hrR3 at a MOI of 1 (the titer for UV-inactivated hrR3 was the titer prior to UV-irradiation). At 8 h post-infection cell lysates were subjected to western blotting with polyclonal rabbit anti-human IL-6. The blot was the stripped and re-probed with actin antibody as a loading control. Signals were detected using ECL system and the signal intensities were determined using Scion Image 4.0.3.2 (Scion Corp., Frederick, MD).
, hrR3. (C). hrR3 or UV-inactivated hrR3 induction of NF-κB p65 nuclear translocation in ARPE-19 cells. ARPE-19 cells were seeded in 4-well chamber slides the day before experiment. On the day of experiment, cells were infected with hrR3 or UV-inactivated hrR3 and eight hours later they were immunostained for NF-κB p65. Hoescht stained images were pseudocolored green to facilitate image merger. All images were originally taken at a magnification of 40x. (D). Immunoblot analysis of hrR3 or UV-inactivated hrR3 induced IL-6 expression in ARPE-19 cells. The ARPE-19 cells were grown to confluence and the cells were infected with hrR3 or UV-inactivated hrR3 at a MOI of 1 (the titer for UV-inactivated hrR3 was the titer prior to UV-irradiation). At 8 h post-infection cell lysates were subjected to western blotting with polyclonal rabbit anti-human IL-6. The blot was the stripped and re-probed with actin antibody as a loading control. Signals were detected using ECL system and the signal intensities were determined using Scion Image 4.0.3.2 (Scion Corp., Frederick, MD).Similar articles
-
Primate neural retina upregulates IL-6 and IL-10 in response to a herpes simplex vector suggesting the presence of a pro-/anti-inflammatory axis.Exp Eye Res. 2016 Jul;148:12-23. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2016.05.003. Epub 2016 May 8. Exp Eye Res. 2016. PMID: 27170050 Free PMC article.
-
Resveratrol suppresses nuclear factor-kappaB in herpes simplex virus infected cells.Antiviral Res. 2006 Dec;72(3):242-51. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2006.06.011. Epub 2006 Jul 14. Antiviral Res. 2006. PMID: 16876885
-
Herpes simplex virus mediated gene transfer to primate ocular tissues.Exp Eye Res. 1999 Oct;69(4):385-95. doi: 10.1006/exer.1999.0711. Exp Eye Res. 1999. PMID: 10504272
-
Induction of cytokine expression by herpes simplex virus in human monocyte-derived macrophages and dendritic cells is dependent on virus replication and is counteracted by ICP27 targeting NF-kappaB and IRF-3.J Gen Virol. 2006 May;87(Pt 5):1099-1108. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.81541-0. J Gen Virol. 2006. PMID: 16603509
-
[Battle with herpes for 37 years].Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2015 Mar;119(3):145-66; discussion 167. Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2015. PMID: 25854108 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Toll-like receptors 4, 5, 6 and 7 are constitutively expressed in non-human primate retinal neurons.J Neuroimmunol. 2018 Sep 15;322:26-35. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2018.06.007. Epub 2018 Jun 11. J Neuroimmunol. 2018. PMID: 29954626 Free PMC article.
-
Oligonucleotides designed to inhibit TLR9 block Herpes simplex virus type 1 infection at multiple steps.Antiviral Res. 2014 Sep;109:83-96. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2014.06.015. Epub 2014 Jul 1. Antiviral Res. 2014. PMID: 24995383 Free PMC article.
-
Signalling pathways involved in ribonuclease-7 expression.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2011 Jun;68(11):1941-52. doi: 10.1007/s00018-010-0540-2. Epub 2010 Oct 22. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2011. PMID: 20967562 Free PMC article.
-
Primate neural retina upregulates IL-6 and IL-10 in response to a herpes simplex vector suggesting the presence of a pro-/anti-inflammatory axis.Exp Eye Res. 2016 Jul;148:12-23. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2016.05.003. Epub 2016 May 8. Exp Eye Res. 2016. PMID: 27170050 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amici C, Belardo G, Rossi A, Santoro MG. Activation of I kappa b kinase by herpes simplex virus type 1. A novel target for anti-herpetic therapy. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:28759–28766. - PubMed
-
- Amici C, Rossi A, Costanzo A, Ciafre S, Marinari B, Balsamo M, Levrero M, Santoro MG. Herpes simplex virus disrupts NF-kappaB regulation by blocking its recruitment on the IkappaBalpha promoter and directing the factor on viral genes. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:7110–7117. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

