Calpain 1 and 2 are required for RNA replication of echovirus 1
- PMID: 18032503
- PMCID: PMC2224425
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01375-07
Calpain 1 and 2 are required for RNA replication of echovirus 1
Abstract
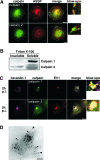
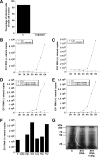
Calpains are calcium-dependent cysteine proteases that degrade cytoskeletal and cytoplasmic proteins. We have studied the role of calpains in the life cycle of human echovirus 1 (EV1). The calpain inhibitors, including calpeptin, calpain inhibitor 1, and calpain inhibitor 2 as well as calpain 1 and calpain 2 short interfering RNAs, completely blocked EV1 infection in the host cells. The effect of the inhibitors was not specific for EV1, because they also inhibited infection by other picornaviruses, namely, human parechovirus 1 and coxsackievirus B3. The importance of the calpains in EV1 infection also was supported by the fact that EV1 increased calpain activity 3 h postinfection. Confocal microscopy and immunoelectron microscopy showed that the EV1/caveolin-1-positive vesicles also contain calpain 1 and 2. Our results indicate that calpains are not required for virus entry but that they are important at a later stage of infection. Calpain inhibitors blocked the production of EV1 particles after microinjection of EV1 RNA into the cells, and they effectively inhibited the synthesis of viral RNA in the host cells. Thus, both calpain 1 and calpain 2 are essential for the replication of EV1 RNA.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Internalization of echovirus 1 in caveolae.J Virol. 2002 Feb;76(4):1856-65. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.4.1856-1865.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 11799180 Free PMC article.
-
Echovirus 1 endocytosis into caveosomes requires lipid rafts, dynamin II, and signaling events.Mol Biol Cell. 2004 Nov;15(11):4911-25. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e04-01-0070. Epub 2004 Sep 8. Mol Biol Cell. 2004. PMID: 15356270 Free PMC article.
-
Coxsackievirus B3-induced calpain activation facilitates the progeny virus replication via a likely mechanism related with both autophagy enhancement and apoptosis inhibition in the early phase of infection: an in vitro study in H9c2 cells.Virus Res. 2014 Jan 22;179:177-86. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2013.10.014. Epub 2013 Oct 28. Virus Res. 2014. PMID: 24177271
-
Coxsackievirus B RNA replication: lessons from poliovirus.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2008;323:89-121. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-75546-3_5. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18357767 Review.
-
Calpains: intact and active?Bioessays. 1997 Nov;19(11):1011-8. doi: 10.1002/bies.950191111. Bioessays. 1997. PMID: 9394623 Review.
Cited by
-
Dual roles of calpain in facilitating Coxsackievirus B3 replication and prompting inflammation in acute myocarditis.Int J Cardiol. 2016 Oct 15;221:1123-31. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2016.07.121. Epub 2016 Jul 9. Int J Cardiol. 2016. PMID: 27472894 Free PMC article.
-
Coxsackievirus A9 infects cells via nonacidic multivesicular bodies.J Virol. 2014 May;88(9):5138-51. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03275-13. Epub 2014 Feb 26. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24574401 Free PMC article.
-
CD163ΔSRCR5 MARC-145 Cells Resist PRRSV-2 Infection via Inhibiting Virus Uncoating, Which Requires the Interaction of CD163 With Calpain 1.Front Microbiol. 2020 Jan 13;10:3115. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.03115. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32038556 Free PMC article.
-
Permeability changes of integrin-containing multivesicular structures triggered by picornavirus entry.PLoS One. 2014 Oct 9;9(10):e108948. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0108948. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25299706 Free PMC article.
-
Infectious Entry Pathway of Enterovirus B Species.Viruses. 2015 Dec 7;7(12):6387-99. doi: 10.3390/v7122945. Viruses. 2015. PMID: 26690201 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Arthur, J. S., and C. Crawford. 1996. Investigation of the interaction of m-calpain with phospholipids: calpain-phospholipid interactions. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1293201-206. - PubMed
-
- Auvinen, P., M. J. Mäkelä, M. Roivainen, M. Kallajoki, R. Vainionpää, and T. Hyypiä. 1993. Mapping of antigenic sites of coxsackievirus B3 by synthetic peptides. APMIS 101517-528. - PubMed
-
- Bergelson, J. M., M. P. Shepley, B. M. Chan, M. E. Hemler, and R. W. Finberg. 1992. Identification of the integrin VLA-2 as a receptor for echovirus 1. Science 2551718-1720. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

