The rapid decrease in astrocyte-associated dystroglycan expression by focal cerebral ischemia is protease-dependent
- PMID: 18030304
- PMCID: PMC2588545
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.jcbfm.9600585
The rapid decrease in astrocyte-associated dystroglycan expression by focal cerebral ischemia is protease-dependent
Abstract
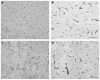
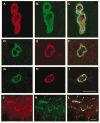
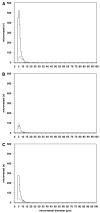
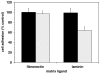
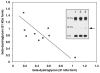
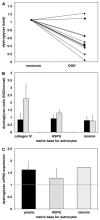
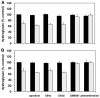
During focal cerebral ischemia, the detachment of astrocytes from the microvascular basal lamina is not completely explained by known integrin receptor expression changes. Here, the impact of experimental ischemia (oxygen-glucose deprivation (OGD)) on dystroglycan expression by murine endothelial cells and astrocytes grown on vascular matrix laminin, perlecan, or collagen and the impact of middle cerebral artery occlusion on alphabeta-dystroglycan within cerebral microvessels of the nonhuman primate were examined. Dystroglycan was expressed on all cerebral microvessels in cortical gray and white matter, and the striatum. Astrocyte adhesion to basal lamina proteins was managed in part by alpha-dystroglycan, while ischemia significantly reduced expression of dystroglycan both in vivo and in vitro. Furthermore, dystroglycan and integrin alpha6beta4 expressions on astrocyte end-feet decreased in parallel both in vivo and in vitro. The rapid loss of astrocyte dystroglycan during OGD appears protease-dependent, involving an matrix metalloproteinase-like activity. This may explain the rapid detachment of astrocytes from the microvascular basal lamina during ischemic injury, which could contribute to significant changes in microvascular integrity.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Disruption of dystroglycan-laminin interactions modulates water uptake by astrocytes.Brain Res. 2013 Mar 29;1503:89-96. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2013.01.049. Epub 2013 Feb 5. Brain Res. 2013. PMID: 23395731 Free PMC article.
-
Responses of endothelial cell and astrocyte matrix-integrin receptors to ischemia mimic those observed in the neurovascular unit.Stroke. 2008 Jan;39(1):191-7. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.107.486134. Epub 2007 Nov 21. Stroke. 2008. PMID: 18032737 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid disruption of an astrocyte interaction with the extracellular matrix mediated by integrin alpha 6 beta 4 during focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion.Stroke. 1997 Apr;28(4):858-65. doi: 10.1161/01.str.28.4.858. Stroke. 1997. PMID: 9099208
-
Integrin-matrix interactions in the cerebral microvasculature.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2006 Sep;26(9):1966-75. doi: 10.1161/01.ATV.0000232525.65682.a2. Epub 2006 Jun 15. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2006. PMID: 16778120 Review.
-
Vascular matrix adhesion and the blood-brain barrier.Biochem Soc Trans. 2006 Dec;34(Pt 6):1261-6. doi: 10.1042/BST0341261. Biochem Soc Trans. 2006. PMID: 17073798 Review.
Cited by
-
Cell-specific expression and function of laminin at the neurovascular unit.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2022 Nov;42(11):1979-1999. doi: 10.1177/0271678X221113027. Epub 2022 Jul 7. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2022. PMID: 35796497 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunohistochemical distribution of basement membrane proteins in the human inner ear from older subjects.Hear Res. 2009 Aug;254(1-2):1-14. doi: 10.1016/j.heares.2009.03.014. Epub 2009 Apr 5. Hear Res. 2009. PMID: 19348877 Free PMC article.
-
Disruption of dystroglycan-laminin interactions modulates water uptake by astrocytes.Brain Res. 2013 Mar 29;1503:89-96. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2013.01.049. Epub 2013 Feb 5. Brain Res. 2013. PMID: 23395731 Free PMC article.
-
In the hypoxic central nervous system, endothelial cell proliferation is followed by astrocyte activation, proliferation, and increased expression of the alpha 6 beta 4 integrin and dystroglycan.Glia. 2010 Aug;58(10):1157-67. doi: 10.1002/glia.20995. Glia. 2010. PMID: 20544851 Free PMC article.
-
The importance of laminin at the blood-brain barrier.Neural Regen Res. 2023 Dec;18(12):2557-2563. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.373677. Neural Regen Res. 2023. PMID: 37449589 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Andac Z, Sasaki T, Mann K, Brancaccio A, Deutzmann R, Timpl R. Analysis of heparin, alpha-dystroglycan and sulfatide binding to the G domain of the laminin alpha1 chain by site-directed mutagenesis. J Mol Biol. 1999;287:253–64. - PubMed
-
- Astrup J, Siesjö BK, Symon L. Thresholds in cerebral ischemia—the ischemic penumbra. Stroke. 1981;12:723–5. - PubMed
-
- Bragg AD, Amiry-Moghaddam M, Ottersen OP, Adams ME, Froehner SC. Assembly of a perivascular astrocyte protein scaffold at the mammalian blood–brain barrier is dependent on alpha-syntrophin. Glia. 2006;53:879–90. - PubMed
-
- Branston NM, Symon L, Crockard HA. Recovery of the cortical evoked response following middle cerebral artery occlusion in baboons: relation to local blood flow and PO2. Stroke. 1976;7:151–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

