Filamin repeat segments required for photosensory signalling in Dictyostelium discoideum
- PMID: 17997829
- PMCID: PMC2211301
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2121-8-48
Filamin repeat segments required for photosensory signalling in Dictyostelium discoideum
Abstract
Background: Filamin is an actin binding protein which is ubiquitous in eukaryotes and its basic structure is well conserved - an N-terminal actin binding domain followed by a series of repeated segments which vary in number in different organisms. D. discoideum is a well established model organism for the study of signalling pathways and the actin cytoskeleton and as such makes an excellent organism in which to study filamin. Ddfilamin plays a putative role as a scaffolding protein in a photosensory signalling pathway and this role is thought to be mediated by the unusual repeat segments in the rod domain.
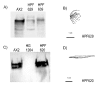
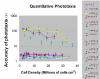
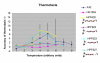
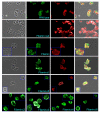
Results: To study the role of filamin in phototaxis, a filamin null mutant, HG1264, was transformed with constructs each of which expressed wild type filamin or a mutant filamin with a deletion of one of the repeat segments. Transformants expressing the full length filamin to wild type levels completely rescued the phototaxis defect in HG1264, however if filamin was expressed at lower than wild type levels the phototaxis defect was not restored. The transformants lacking any one of the repeat segments 2-6 retained defective phototaxis and thermotaxis phenotypes, whereas transformants expressing filaminDelta1 exhibited a range of partial complementation of the phototaxis phenotype which was related to expression levels. Immunofluorescence microscopy showed that filamin lacking any of the repeat segments still localised to the same actin rich areas as wild type filamin. Ddfilamin interacts with RasD and IP experiments demonstrated that this interaction did not rely upon any single repeat segment or the actin binding domain.
Conclusion: This paper demonstrates that wild type levels of filamin expression are essential for the formation of functional photosensory signalling complexes and that each of the repeat segments 2-6 are essential for filamins role in phototaxis. By contrast, repeat segment 1 is not essential provided the mutated filamin lacking repeat segment 1 is expressed at a high enough level. The defects in photo/thermosensory signal transduction caused by the absence of the repeats are due neither to mislocalisation of filamin nor to the loss of RasD recruitment to the previously described photosensory signalling complex.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Cell type-specific filamin complex regulation by a novel class of HECT ubiquitin ligase is required for normal cell motility and patterning.Development. 2011 Apr;138(8):1583-93. doi: 10.1242/dev.063800. Epub 2011 Mar 9. Development. 2011. PMID: 21389049 Free PMC article.
-
A phototaxis signalling complex in Dictyostelium discoideum.Eur J Cell Biol. 2006 Sep;85(9-10):1099-106. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2006.04.005. Epub 2006 Jun 2. Eur J Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16735078
-
Filamin-regulated F-actin assembly is essential for morphogenesis and controls phototaxis in Dictyostelium.J Biol Chem. 2007 Jan 19;282(3):1948-55. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M610262200. Epub 2006 Nov 22. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17121815
-
Structural portrait of filamin interaction mechanisms.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2010 Nov;11(7):639-50. doi: 10.2174/138920310794109111. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2010. PMID: 20887254 Review.
-
Filamins: promiscuous organizers of the cytoskeleton.Trends Biochem Sci. 2006 Jul;31(7):411-9. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2006.05.006. Epub 2006 Jun 16. Trends Biochem Sci. 2006. PMID: 16781869 Review.
Cited by
-
Cell type-specific filamin complex regulation by a novel class of HECT ubiquitin ligase is required for normal cell motility and patterning.Development. 2011 Apr;138(8):1583-93. doi: 10.1242/dev.063800. Epub 2011 Mar 9. Development. 2011. PMID: 21389049 Free PMC article.
-
The Parkinson's disease-associated protein DJ-1 plays a positive nonmitochondrial role in endocytosis in Dictyostelium cells.Dis Model Mech. 2017 Oct 1;10(10):1261-1271. doi: 10.1242/dmm.028084. Epub 2017 Aug 17. Dis Model Mech. 2017. PMID: 28819044 Free PMC article.
-
FLN-1/filamin is required for maintenance of actin and exit of fertilized oocytes from the spermatheca in C. elegans.Dev Biol. 2010 Nov 15;347(2):247-57. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2010.08.005. Epub 2010 Aug 10. Dev Biol. 2010. PMID: 20707996 Free PMC article.
-
The filamins: organizers of cell structure and function.Cell Adh Migr. 2011 Mar-Apr;5(2):160-9. doi: 10.4161/cam.5.2.14401. Epub 2011 Mar 1. Cell Adh Migr. 2011. PMID: 21169733 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitochondrial HTRA2 Plays a Positive, Protective Role in Dictyostelium discoideum but Is Cytotoxic When Overexpressed.Genes (Basel). 2018 Jul 16;9(7):355. doi: 10.3390/genes9070355. Genes (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30013019 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Van Troys M, Vandekeerckhove J, Ampe C. Structural modules in actin-binding proteins: towards a new classification. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta. 1999;1448:323–348. - PubMed
-
- Noegel AA, Rapp S, Lottspeich F, Schleicher M, Stewart M. The Dictyostelium gelation factor shares a putative actin binding site with alpha-actinins and dystrophin and also has a rod domain containing six 100-residue motifs that appear to have a cross-beta conformation. J Cell Biol. 1989;109:607–618. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.2.607. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

