A novel requirement for C. elegans Alix/ALX-1 in RME-1-mediated membrane transport
- PMID: 17997305
- PMCID: PMC2175126
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2007.10.045
A novel requirement for C. elegans Alix/ALX-1 in RME-1-mediated membrane transport
Abstract
Background: Alix/Bro1p family proteins have recently been identified as important components of multivesicular endosomes (MVEs) and are involved in the sorting of endocytosed integral membrane proteins, interacting with components of the ESCRT complex, the unconventional phospholipid LBPA, and other known endocytosis regulators. During infection, Alix can be co-opted by enveloped retroviruses, including HIV, providing an important function during virus budding from the plasma membrane. In addition, Alix is associated with the actin cytoskeleton and might regulate cytoskeletal dynamics.
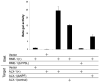
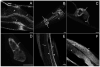
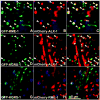
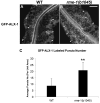
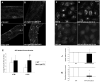
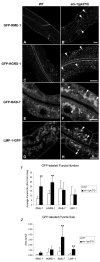
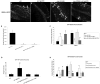
Results: Here we demonstrate a novel physical interaction between the only apparent Alix/Bro1p family protein in C. elegans, ALX-1, and a key regulator of receptor recycling from endosomes to the plasma membrane, called RME-1. The analysis of alx-1 mutants indicates that ALX-1 is required for the endocytic recycling of specific basolateral cargo in the C. elegans intestine, a pathway previously defined by the analysis of rme-1 mutants. The expression of truncated human Alix in HeLa cells disrupts the recycling of major histocompatibility complex class I, a known Ehd1/RME-1-dependent transport step, suggesting the phylogenetic conservation of this function. We show that the interaction of ALX-1 with RME-1 in C. elegans, mediated by RME-1/YPSL and ALX-1/NPF motifs, is required for this recycling process. In the C. elegans intestine, ALX-1 localizes to both recycling endosomes and MVEs, but the ALX-1/RME-1 interaction appears to be dispensable for ALX-1 function in MVEs and/or late endosomes.
Conclusions: This work provides the first demonstration of a requirement for an Alix/Bro1p family member in the endocytic recycling pathway in association with the recycling regulator RME-1.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regulation of endocytic recycling by C. elegans Rab35 and its regulator RME-4, a coated-pit protein.EMBO J. 2008 Apr 23;27(8):1183-96. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2008.54. Epub 2008 Mar 20. EMBO J. 2008. PMID: 18354496 Free PMC article.
-
SNX-3 mediates retromer-independent tubular endosomal recycling by opposing EEA-1-facilitated trafficking.PLoS Genet. 2021 Jun 3;17(6):e1009607. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1009607. eCollection 2021 Jun. PLoS Genet. 2021. PMID: 34081703 Free PMC article.
-
SNX-1 and RME-8 oppose the assembly of HGRS-1/ESCRT-0 degradative microdomains on endosomes.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Jan 17;114(3):E307-E316. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1612730114. Epub 2017 Jan 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28053230 Free PMC article.
-
ALIX and the multivesicular endosome: ALIX in Wonderland.Trends Cell Biol. 2014 Jan;24(1):19-25. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2013.10.009. Epub 2013 Nov 26. Trends Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 24287454 Review.
-
Mechanisms of EHD/RME-1 protein function in endocytic transport.Traffic. 2008 Dec;9(12):2043-52. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2008.00834.x. Epub 2008 Oct 14. Traffic. 2008. PMID: 18801062 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
C. elegans ciliated sensory neurons release extracellular vesicles that function in animal communication.Curr Biol. 2014 Mar 3;24(5):519-25. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2014.01.002. Epub 2014 Feb 13. Curr Biol. 2014. PMID: 24530063 Free PMC article.
-
Important relationships between Rab and MICAL proteins in endocytic trafficking.World J Biol Chem. 2010 Aug 26;1(8):254-64. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v1.i8.254. World J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 21537482 Free PMC article.
-
A CIE change in our understanding of endocytic mechanisms.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Dec 13;11:1334798. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1334798. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 38192364 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RTKN-1/Rhotekin shields endosome-associated F-actin from disassembly to ensure endocytic recycling.J Cell Biol. 2021 May 3;220(5):e202007149. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202007149. J Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 33844824 Free PMC article.
-
RAB-10-GTPase-mediated regulation of endosomal phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Aug 28;109(35):E2306-15. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1205278109. Epub 2012 Aug 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22869721 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nichols B. Caveosomes and endocytosis of lipid rafts. Journal of cell science. 2003;116:4707–4714. - PubMed
-
- Gesbert F, Sauvonnet N, Dautry-Varsat A. Clathrin-lndependent endocytosis and signalling of interleukin 2 receptors IL-2R endocytosis and signalling. Current topics in microbiology and immunology. 2004;286:119–148. - PubMed
-
- Mukherjee S, Ghosh RN, Maxfield FR. Endocytosis. Physiological reviews. 1997;77:759–803. - PubMed
-
- Maxfield FR, McGraw TE. Endocytic recycling. Nature reviews. 2004;5:121–132. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

