The redox sensor TXNL1 plays a regulatory role in fluid phase endocytosis
- PMID: 17987124
- PMCID: PMC2043495
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0001144
The redox sensor TXNL1 plays a regulatory role in fluid phase endocytosis
Abstract
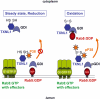
Background: Small GTPases of the Rab family can cycle between a GTP- and a GDP-bound state and also between membrane and cytosol. The latter cycle is mediated by the Guanine Nucleotide Dissociation Inhibitor GDI, which can selectively extract GDP-bound Rab proteins from donor membranes, and then reload them on target membranes. In previous studies, we found that capture of the small GTPase Rab5, a key regulator of endocytic membrane traffic, by GDI is stimulated by oxidative stress via p38MAPK, resulting in increased fluid phase endocytosis.
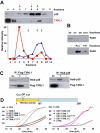
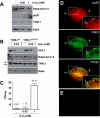
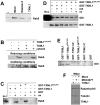
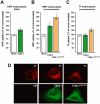
Methodology/principal findings: When purifying the GDI stimulating activity we found that that it copurified with a high MW protein complex, which included p38MAPK. Here we report the identification and characterization of another component of this complex as the thioredoxin-like protein TXNL1. Our observations indicate that TXNL1 play a selective role in the regulation of fluid phase endocytosis, by controlling GDI capacity to capture Rab5.
Conclusions/significance: Oxidants, which are known to cause cellular damage, can also trigger signaling pathways, in particular via members of the thioredoxin family. We propose that TXNL1 acts as an effector of oxidants or a redox sensor by converting redox changes into changes of GDI capacity to capture Rab5, which in turn modulates fluid phase endocytosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Capture of the small GTPase Rab5 by GDI: regulation by p38 MAP kinase.Methods Enzymol. 2005;403:367-81. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(05)03032-6. Methods Enzymol. 2005. PMID: 16473603
-
The stress-induced MAP kinase p38 regulates endocytic trafficking via the GDI:Rab5 complex.Mol Cell. 2001 Feb;7(2):421-32. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(01)00189-7. Mol Cell. 2001. PMID: 11239470
-
Recognition and stabilization of geranylgeranylated human Rab5 by the GDP Dissociation Inhibitor (GDI).Small GTPases. 2019 May;10(3):227-242. doi: 10.1080/21541248.2017.1371268. Epub 2017 Oct 25. Small GTPases. 2019. PMID: 29065764 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular control of Rab activity by GEFs, GAPs and GDI.Small GTPases. 2018 Mar 4;9(1-2):5-21. doi: 10.1080/21541248.2016.1276999. Epub 2017 Feb 1. Small GTPases. 2018. PMID: 28055292 Free PMC article. Review.
-
GDIs: central regulatory molecules in Rho GTPase activation.Trends Cell Biol. 2005 Jul;15(7):356-63. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2005.05.001. Trends Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15921909 Review.
Cited by
-
Thioredoxin-related protein 32 (TRP32) specifically reduces oxidized phosphatase of regenerating liver (PRL).J Biol Chem. 2013 Mar 8;288(10):7263-70. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.418004. Epub 2013 Jan 28. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23362275 Free PMC article.
-
TXNL1-XRCC1 pathway regulates cisplatin-induced cell death and contributes to resistance in human gastric cancer.Cell Death Dis. 2014 Feb 13;5(2):e1055. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2014.27. Cell Death Dis. 2014. PMID: 24525731 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of in ovo electroporation on endogenous gene expression: genome-wide analysis.Neural Dev. 2011 Apr 28;6:17. doi: 10.1186/1749-8104-6-17. Neural Dev. 2011. PMID: 21527010 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism-based proteomic screening identifies targets of thioredoxin-like proteins.J Biol Chem. 2015 Feb 27;290(9):5685-95. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.597245. Epub 2015 Jan 5. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25561728 Free PMC article.
-
Biodegradable and Dual-Responsive Polypeptide-Shelled Cyclodextrin-Containers for Intracellular Delivery of Membrane-Impermeable Cargo.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021 Sep;8(18):e2100694. doi: 10.1002/advs.202100694. Epub 2021 Jul 18. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021. PMID: 34278745 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Conner SD, Schmid SL. Regulated portals of entry into the cell. Nature. 2003;422:37–44. - PubMed
-
- Kirkham M, Parton RG. Clathrin-independent endocytosis: new insights into caveolae and non-caveolar lipid raft carriers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005;1746:349–363. - PubMed
-
- Gruenberg J. The endocytic pathway: a mosaic of domains. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology. 2001;2:721–730. - PubMed
-
- Di Fiore PP, De Camilli P. Endocytosis and signaling. an inseparable partnership. Cell. 2001;106:1–4. - PubMed
-
- Pelkmans L, Fava E, Grabner H, Hannus M, Habermann B, et al. Genome-wide analysis of human kinases in clathrin- and caveolae/raft-mediated endocytosis. Nature. 2005;436:78–86. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

