ATM-NF-kappaB connection as a target for tumor radiosensitization
- PMID: 17979628
- PMCID: PMC4156318
- DOI: 10.2174/156800907780809769
ATM-NF-kappaB connection as a target for tumor radiosensitization
Abstract
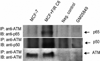
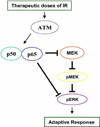
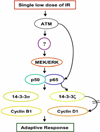
Ionizing radiation (IR) plays a key role in both areas of carcinogenesis and anticancer radiotherapy. The ATM (ataxia-telangiectasia mutated) protein, a sensor to IR and other DNA-damaging agents, activates a wide variety of effectors involved in multiple signaling pathways, cell cycle checkpoints, DNA repair and apoptosis. Accumulated evidence also indicates that the transcription factor NF-kappaB (nuclear factor-kappaB) plays a critical role in cellular protection against a variety of genotoxic agents including IR, and inhibition of NF-kappaB leads to radiosensitization in radioresistant cancer cells. NF-kappaB was found to be defective in cells from patients with A-T (ataxia-telangiectasia) who are highly sensitive to DNA damage induced by IR and UV lights. Cells derived from A-T individuals are hypersensitive to killing by IR. Both ATM and NF-kappaB deficiencies result in increased sensitivity to DNA double strand breaks. Therefore, identification of the molecular linkage between the kinase ATM and NF-kappaB signaling in tumor response to therapeutic IR will lead to a better understanding of cellular response to IR, and will promise novel molecular targets for therapy-associated tumor resistance. This review article focuses on recent findings related to the relationship between ATM and NF-kappaB in response to IR. Also, the association of ATM with the NF-kappaB subunit p65 in adaptive radiation response, recently observed in our lab, is also discussed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Persistence of unrepaired DNA double strand breaks caused by inhibition of ATM does not lead to radio-sensitisation in the absence of NF-κB activation.DNA Repair (Amst). 2011 Feb 7;10(2):235-44. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2010.11.005. Epub 2010 Dec 8. DNA Repair (Amst). 2011. PMID: 21144805
-
Induction of MET by ionizing radiation and its role in radioresistance and invasive growth of cancer.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2011 Apr 20;103(8):645-61. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djr093. Epub 2011 Apr 4. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2011. PMID: 21464397
-
Nuclear initiated NF-κB signaling: NEMO and ATM take center stage.Cell Res. 2011 Jan;21(1):116-30. doi: 10.1038/cr.2010.179. Epub 2010 Dec 28. Cell Res. 2011. PMID: 21187855 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ionizing radiation can induce GSK-3beta phosphorylation and NF-kappaB transcriptional transactivation in ATM-deficient fibroblasts.Cell Signal. 2008 Apr;20(4):602-12. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2007.10.022. Epub 2007 Nov 6. Cell Signal. 2008. PMID: 18243662
-
ATMINistrating ATM signalling: regulation of ATM by ATMIN.Cell Cycle. 2008 Nov 15;7(22):3483-6. doi: 10.4161/cc.7.22.7044. Epub 2008 Nov 18. Cell Cycle. 2008. PMID: 19001856 Review.
Cited by
-
Exosomes impact survival to radiation exposure in cell line models of nervous system cancer.Oncotarget. 2018 Nov 16;9(90):36083-36101. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.26300. eCollection 2018 Nov 16. Oncotarget. 2018. PMID: 30546829 Free PMC article.
-
Sensitization of tumor cells to cancer therapy by molecularly targeted inhibition of the inhibitor of nuclear factor κB kinase.Transl Cancer Res. 2012 Aug;1(2):100-108. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2218-676X.2012.05.04. Transl Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22953243 Free PMC article.
-
Coactivation of ATM/ERK/NF-kappaB in the low-dose radiation-induced radioadaptive response in human skin keratinocytes.Free Radic Biol Med. 2009 Jun 1;46(11):1543-50. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2009.03.012. Epub 2009 Mar 24. Free Radic Biol Med. 2009. PMID: 19324081 Free PMC article.
-
Disruption of microtubules sensitizes the DNA damage-induced apoptosis through inhibiting nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) DNA-binding activity.J Korean Med Sci. 2010 Nov;25(11):1574-81. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2010.25.11.1574. Epub 2010 Oct 26. J Korean Med Sci. 2010. PMID: 21060745 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-oxidative stress response genes: bioinformatic analysis of their expression and relevance in multiple cancers.Oncotarget. 2013 Dec;4(12):2577-90. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.1658. Oncotarget. 2013. PMID: 24342878 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shao R, Karunagaran D, Zhou BP, Li K, Lo SS, Deng J, Chiao P, Hung MC. Inhibition of nuclear factor-kappaB activity is involved in ElA-mediated sensitization of radiation-induced apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 1997;272(52):32739–32742. - PubMed
-
- Kato T, Duffey DC, Ondrey FG, Dong G, Chen Z, Cook JA, Mitchell JB, Van Waes C. Cisplatin and radiation sensitivity in human head and neck squamous carcinomas are independently modulated by glutathione and transcription factor NF-kappaB. Head Neck. 2000;22(8):748–759. - PubMed
-
- Yang JP, Hori M, Takahashi N, Kawabe T, Kato H, Okamoto T. NF-kappaB subunit p65 binds to 53BP2 and inhibits cell death induced by 53BP2. Oncogene. 1999;18(37):5177–5186. - PubMed
-
- Herscher LL, Cook JA, Pacelli R, Pass HI, Russo A, Mitchell JB. Principles of chemoradiation: theoretical and practical considerations. Oncology. 1999;13(10 Suppl 5):11–22. - PubMed
-
- Tang G, Mmemoto Y, Dibling B, Purcell HN, Li Z, Karin M, Lin A. Inhibition of JNK activation through NF-kappaB target genes. Nature. 2001;414(6861):313–317. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

