The FGF14(F145S) mutation disrupts the interaction of FGF14 with voltage-gated Na+ channels and impairs neuronal excitability
- PMID: 17978045
- PMCID: PMC6673376
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2282-07.2007
The FGF14(F145S) mutation disrupts the interaction of FGF14 with voltage-gated Na+ channels and impairs neuronal excitability
Abstract
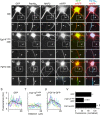
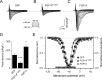
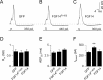
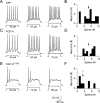
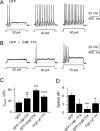
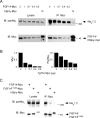
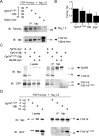
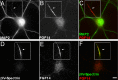
Fibroblast growth factor 14 (FGF14) belongs to the intracellular FGF homologous factor subfamily of FGF proteins (iFGFs) that are not secreted and do not activate tyrosine kinase receptors. The iFGFs, however, have been shown to interact with the pore-forming (alpha) subunits of voltage-gated Na+ (Na(v)) channels. The neurological phenotypes seen in Fgf14-/- mice and the identification of an FGF14 missense mutation (FGF14(F145S)) in a Dutch family presenting with cognitive impairment and spinocerebellar ataxia suggest links between FGF14 and neuronal functioning. Here, we demonstrate that the expression of FGF14(F145S) reduces Na(v) alpha subunit expression at the axon initial segment, attenuates Na(v) channel currents, and reduces the excitability of hippocampal neurons. In addition, and in contrast with wild-type FGF14, FGF14(F145S) does not interact directly with Na(v) channel alpha subunits. Rather, FGF14(F145S) associates with wild-type FGF14 and disrupts the interaction between wild-type FGF14 and Na(v) alpha subunits, suggesting that the mutant FGF14(F145S) protein acts as a dominant negative, interfering with the interaction between wild-type FGF14 and Na(v) channel alpha subunits and altering neuronal excitability.
Figures
Similar articles
-
FGF14 N-terminal splice variants differentially modulate Nav1.2 and Nav1.6-encoded sodium channels.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2009 Oct;42(2):90-101. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2009.05.007. Epub 2009 May 22. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19465131 Free PMC article.
-
Fibroblast growth factor 14 is an intracellular modulator of voltage-gated sodium channels.J Physiol. 2005 Nov 15;569(Pt 1):179-93. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2005.097220. Epub 2005 Sep 15. J Physiol. 2005. PMID: 16166153 Free PMC article.
-
CK2 activity is required for the interaction of FGF14 with voltage-gated sodium channels and neuronal excitability.FASEB J. 2016 Jun;30(6):2171-86. doi: 10.1096/fj.201500161. Epub 2016 Feb 25. FASEB J. 2016. PMID: 26917740 Free PMC article.
-
In Vivo Expression of an SCA27A-linked FGF14 Mutation Results in Haploinsufficiency and Impaired Firing of Cerebellar Purkinje Neurons.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Oct 25:2024.10.25.620253. doi: 10.1101/2024.10.25.620253. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39484407 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Voltage-gated sodium channel-associated proteins and alternative mechanisms of inactivation and block.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012 Apr;69(7):1067-76. doi: 10.1007/s00018-011-0832-1. Epub 2011 Sep 27. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012. PMID: 21947499 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
FGF14 regulates presynaptic Ca2+ channels and synaptic transmission.Cell Rep. 2013 Jul 11;4(1):66-75. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2013.06.012. Epub 2013 Jul 3. Cell Rep. 2013. PMID: 23831029 Free PMC article.
-
Nav1.3 and FGF14 are primary determinants of the TTX-sensitive sodium current in mouse adrenal chromaffin cells.J Gen Physiol. 2021 Apr 5;153(4):e202012785. doi: 10.1085/jgp.202012785. J Gen Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33651884 Free PMC article.
-
TNFR1 signaling converging on FGF14 controls neuronal hyperactivity and sickness behavior in experimental cerebral malaria.J Neuroinflammation. 2023 Dec 19;20(1):306. doi: 10.1186/s12974-023-02992-7. J Neuroinflammation. 2023. PMID: 38115011 Free PMC article.
-
Acetazolamide-Responsive Episodic Ataxia Linked to Novel Splice Site Variant in FGF14 Gene.Cerebellum. 2019 Jun;18(3):649-653. doi: 10.1007/s12311-018-0997-3. Cerebellum. 2019. PMID: 30607796
-
Channelrhodopsin-2 localised to the axon initial segment.PLoS One. 2010 Oct 29;5(10):e13761. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0013761. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 21048938 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bechtold DA, Smith KJ. Sodium-mediated axonal degeneration in inflammatory demyelinating disease. J Neurol Sci. 2005;233:27–35. - PubMed
-
- Catterall WA. From ionic currents to molecular mechanisms: the structure and function of voltage-gated sodium channels. Neuron. 2000;26:13–25. - PubMed
-
- Catterall WA, Goldin AL, Waxman SG. International Union of Pharmacology. XLVII. Nomenclature and structure-function relationships of voltage-gated sodium channels. Pharmacol Rev. 2005;57:397–409. - PubMed
-
- Clark B, Hausser M. Neural coding: hybrid analog and digital signalling in axons. Curr Biol. 2006;16:R585–R588. - PubMed
-
- Clark BA, Monsivais P, Branco T, London M, Hausser M. The site of action potential initiation in cerebellar Purkinje neurons. Nat Neurosci. 2005;8:137–139. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
