The transcriptional cycle of HIV-1 in real-time and live cells
- PMID: 17954611
- PMCID: PMC2064765
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200706018
The transcriptional cycle of HIV-1 in real-time and live cells
Abstract
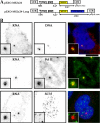
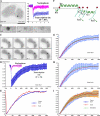
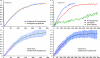
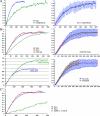
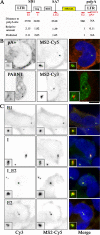
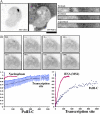
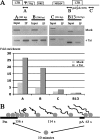
RNA polymerase II (RNAPII) is a fundamental enzyme, but few studies have analyzed its activity in living cells. Using human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) type 1 reporters, we study real-time messenger RNA (mRNA) biogenesis by photobleaching nascent RNAs and RNAPII at specific transcription sites. Through modeling, the use of mutant polymerases, drugs, and quantitative in situ hybridization, we investigate the kinetics of the HIV-1 transcription cycle. Initiation appears efficient because most polymerases demonstrate stable gene association. We calculate an elongation rate of approximately 1.9 kb/min, and, surprisingly, polymerases remain at transcription sites 2.5 min longer than nascent RNAs. With a total polymerase residency time estimated at 333 s, 114 are assigned to elongation, and 63 are assigned to 3'-end processing and/or transcript release. However, mRNAs were released seconds after polyadenylation onset, and analysis of polymerase density by chromatin immunoprecipitation suggests that they pause or lose processivity after passing the polyA site. The strengths and limitations of this kinetic approach to analyze mRNA biogenesis in living cells are discussed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Fast transcription rates of RNA polymerase II in human cells.EMBO Rep. 2011 Dec 1;12(12):1280-5. doi: 10.1038/embor.2011.196. EMBO Rep. 2011. PMID: 22015688 Free PMC article.
-
Measuring the kinetics of mRNA transcription in single living cells.J Vis Exp. 2011 Aug 25;(54):e2898. doi: 10.3791/2898. J Vis Exp. 2011. PMID: 21904295 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo dynamics of RNA polymerase II transcription.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2007 Sep;14(9):796-806. doi: 10.1038/nsmb1280. Epub 2007 Aug 5. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17676063 Free PMC article.
-
Real-time imaging of the HIV-1 transcription cycle in single living cells.Methods. 2011 Jan;53(1):62-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2010.06.015. Epub 2010 Jun 25. Methods. 2011. PMID: 20600934 Review.
-
Measuring transcription dynamics in living cells using a photobleaching approach.Methods. 2017 May 1;120:58-64. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2017.04.007. Epub 2017 Apr 21. Methods. 2017. PMID: 28434903 Review.
Cited by
-
FISH-quant: automatic counting of transcripts in 3D FISH images.Nat Methods. 2013 Apr;10(4):277-8. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2406. Nat Methods. 2013. PMID: 23538861 No abstract available.
-
Complex dynamics of transcription regulation.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Jul;1819(7):657-66. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2012.03.004. Epub 2012 Mar 28. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 22484099 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Three-dimensional architecture of tick-borne encephalitis virus replication sites and trafficking of the replicated RNA.J Virol. 2013 Jun;87(11):6469-81. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03456-12. Epub 2013 Apr 3. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 23552408 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the HIV-1 RNA associated proteome identifies Matrin 3 as a nuclear cofactor of Rev function.Retrovirology. 2011 Jul 20;8:60. doi: 10.1186/1742-4690-8-60. Retrovirology. 2011. PMID: 21771346 Free PMC article.
-
Kinetic Modeling of Virus Growth in Cells.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2018 Mar 28;82(2):e00066-17. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00066-17. Print 2018 Jun. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2018. PMID: 29592895 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ashe, M., P. Griffin, W. James, and N. Proudfoot. 1995. Poly(A) site selection in the HIV-1 provirus: inhibition of promoter-proximal polyadenylation by the downstream major splice donor site. Genes Dev. 9:3008–3025. - PubMed
-
- Batsche, E., M. Yaniv, and C. Muchardt. 2006. The human SWI/SNF subunit Brm is a regulator of alternative splicing. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 13:22–29. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

