Different types of in vitro generated human monocyte-derived dendritic cells release exosomes with distinct phenotypes
- PMID: 17949417
- PMCID: PMC2433319
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2007.02714.x
Different types of in vitro generated human monocyte-derived dendritic cells release exosomes with distinct phenotypes
Abstract
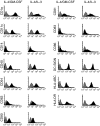
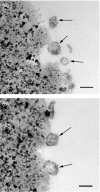
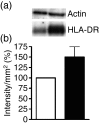
Human in vitro generated dendritic cells and the exosomes they release are potential tools for the modulation of immune responses. Here, we characterized differently generated monocyte-derived dendritic cells (MDDCs) and their exosomes. Culturing of peripheral CD14+ cells from the same individuals with either interleukin (IL)-4 and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) (conventional MDDCs) or alternatively with IL-4 and IL-3 generated immature MDDCs in 7 days. Fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) analysis showed that the IL-4/IL-3-generated MDDCs had significantly lower percentages of CD1a+, CD40+ and CD80+ cells and a higher percentage of CD86+ cells as compared with conventional MDDCs. In addition, IL-4/IL-3-generated MDDCs had significantly higher densities of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I [human leucocyte antigen (HLA)-ABC], MHC class II (HLA-DR), CD11c and the tetraspanin CD81 as compared with conventional MDDCs. In a comparison of their ability to stimulate CD8+ T cells, we found that the IL-4/IL-3 MDDCs were slightly more efficient than the conventional MDDCs at inducing interferon (IFN)-gamma release in response to viral peptides. Exosome morphology was confirmed by electron microscopy and exosome phenotypes were analysed by flow cytometry and western blot. In comparison to exosomes from conventional MDDCs, exosomes from IL-4/IL-3-generated MDDCs showed significantly stronger signals for HLA-ABC, HLA-DR, CD11c, CD63 and CD81. Thus, phenotypically the exosomes largely reflected their MDDCs of origin. When exosomes were loaded with viral peptides, both types of exosomes induced IFN-gamma release from CD8+ T cells. Our findings might have significance for the development of DC- and exosome-based therapies.
Figures
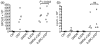

Similar articles
-
1-alpha,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 (1,25(OH)(2)D(3)) hampers the maturation of fully active immature dendritic cells from monocytes.Eur J Endocrinol. 2001 Sep;145(3):351-7. doi: 10.1530/eje.0.1450351. Eur J Endocrinol. 2001. PMID: 11517017
-
Direct exosome stimulation of peripheral human T cells detected by ELISPOT.Eur J Immunol. 2006 Jul;36(7):1772-81. doi: 10.1002/eji.200535615. Eur J Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16761310
-
Dendritic cells generated from CD34+ progenitor cells with flt3 ligand, c-kit ligand, GM-CSF, IL-4, and TNF-alpha are functional antigen-presenting cells resembling mature monocyte-derived dendritic cells.J Immunother. 2000 Jan;23(1):48-58. doi: 10.1097/00002371-200001000-00007. J Immunother. 2000. PMID: 10687137
-
Exosome: from internal vesicle of the multivesicular body to intercellular signaling device.J Cell Sci. 2000 Oct;113 Pt 19:3365-74. doi: 10.1242/jcs.113.19.3365. J Cell Sci. 2000. PMID: 10984428 Review.
-
Dendritic cells and routing cargo into exosomes.Immunol Cell Biol. 2018 May 24. doi: 10.1111/imcb.12170. Online ahead of print. Immunol Cell Biol. 2018. PMID: 29797348 Review.
Cited by
-
Intranasal administration of regulatory dendritic cells is useful for the induction of nasal mucosal tolerance in a mice model of allergic rhinitis.World Allergy Organ J. 2020 Aug 11;13(8):100447. doi: 10.1016/j.waojou.2020.100447. eCollection 2020 Aug. World Allergy Organ J. 2020. PMID: 32817781 Free PMC article.
-
Celastrol Downmodulates Alpha-Synuclein-Specific T Cell Responses by Mediating Antigen Trafficking in Dendritic Cells.Front Immunol. 2022 Mar 2;13:833515. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.833515. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35309340 Free PMC article.
-
Different In Vitro-Generated MUTZ-3-Derived Dendritic Cell Types Secrete Dexosomes with Distinct Phenotypes and Antigen Presentation Potencies.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 28;23(15):8362. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158362. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35955496 Free PMC article.
-
Altered microRNA expression profile in exosomes during osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells.PLoS One. 2014 Dec 11;9(12):e114627. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0114627. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25503309 Free PMC article.
-
Immature dendritic cell-derived exosomes: a promise subcellular vaccine for autoimmunity.Inflammation. 2013 Feb;36(1):232-40. doi: 10.1007/s10753-012-9539-1. Inflammation. 2013. PMID: 22956173 Review.
References
-
- Mellman I, Steinman RM. Dendritic cells: specialized and regulated antigen processing machines. Cell. 2001;106:255–8. - PubMed
-
- Liu YJ. Dendritic cell subsets and lineages, and their functions in innate and adaptive immunity. Cell. 2001;106:259–62. - PubMed
-
- Ebner S, Hofer S, Nguyen VA, Furhapter C, Herold M, Fritsch P, Heufler C, Romani N. A novel role for IL-3: human monocytes cultured in the presence of IL-3 and IL-4 differentiate into dendritic cells that produce less IL-12 and shift Th cell responses toward a Th2 cytokine pattern. J Immunol. 2002;168:6199–207. - PubMed
-
- Zitvogel L, Regnault A, Lozier A, et al. Eradication of established murine tumors using a novel cell-free vaccine: dendritic cell-derived exosomes. Nat Med. 1998;4:594–600. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

