Complex regulation of the TRPC3, 6 and 7 channel subfamily by diacylglycerol and phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate
- PMID: 17942152
- PMCID: PMC2465465
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ceca.2007.09.001
Complex regulation of the TRPC3, 6 and 7 channel subfamily by diacylglycerol and phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate
Abstract
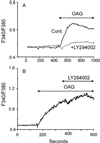
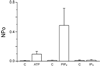
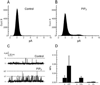
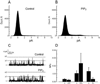
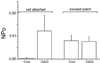
TRPC3, 6 and 7 channels constitute a subgroup of non-selective, calcium-permeable cation channels within the TRP superfamily that are activated by products of phospholipase C-mediated breakdown of phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate (PIP(2)). A number of ion channels, including other members of the TRP superfamily, are regulated directly by PIP(2). However, there is little information on the regulation of the TRPC channel subfamily by PIP(2). Pretreatment of TRPC7-expressing cells with a drug that blocks the synthesis of polyphosphoinositides inhibited the ability of the synthetic diacylglycerol, oleyl-acetyl glycerol, to activate TRPC7. In excised patches, TRPC7 channels were robustly activated by application of PIP(2) or ATP, but not by inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. Similar results were obtained with TRPC6 and TRPC3, although the effects of PIP(2) were somewhat less and with TRPC3 there was no significant effect of ATP. In the cell-attached configuration, TRPC7 channels could be activated by the synthetic diacylglycerol analog, oleyl-acetyl glycerol. However, this lipid mediator did not activate TRPC7 channels in excised patches. In addition, channel activation by PIP(2) in excised patches was significantly greater than that observed with oleyl-acetyl glycerol in the cell-attached configuration. These findings reveal complex regulation of TRPC channels by lipid mediators. The results also reveal for the first time direct activation by PIP(2) of members of the TRPC ion channel subfamily.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Complex functions of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate in regulation of TRPC5 cation channels.Pflugers Arch. 2009 Feb;457(4):757-69. doi: 10.1007/s00424-008-0550-1. Epub 2008 Jul 30. Pflugers Arch. 2009. PMID: 18665391 Free PMC article.
-
Ins(1,4,5)P3 interacts with PIP2 to regulate activation of TRPC6/C7 channels by diacylglycerol in native vascular myocytes.J Physiol. 2010 May 1;588(Pt 9):1419-33. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2009.185256. Epub 2010 Mar 8. J Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20211974 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelin-1 activates a Ca2+-permeable cation channel with TRPC3 and TRPC7 properties in rabbit coronary artery myocytes.J Physiol. 2007 May 1;580(Pt.3):755-64. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2006.126656. Epub 2007 Feb 15. J Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17303636 Free PMC article.
-
Signalling mechanisms for TRPC3 channels.Novartis Found Symp. 2004;258:123-33; discussion 133-9, 155-9, 263-6. Novartis Found Symp. 2004. PMID: 15104179 Review.
-
Transient receptor potential canonical 7: a diacylglycerol-activated non-selective cation channel.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2014;222:189-204. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-54215-2_8. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24756707 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The physiological function of store-operated calcium entry.Neurochem Res. 2011 Jul;36(7):1157-65. doi: 10.1007/s11064-010-0383-0. Epub 2011 Jan 14. Neurochem Res. 2011. PMID: 21234676 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Critical roles of Gi/o proteins and phospholipase C-δ1 in the activation of receptor-operated TRPC4 channels.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Jan 26;113(4):1092-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1522294113. Epub 2016 Jan 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 26755577 Free PMC article.
-
Canonical Transient Receptor Potential 6 Channel: A New Target of Reactive Oxygen Species in Renal Physiology and Pathology.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2016 Nov 1;25(13):732-748. doi: 10.1089/ars.2016.6661. Epub 2016 Mar 18. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2016. PMID: 26937558 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transient receptor potential channels in the vasculature.Physiol Rev. 2015 Apr;95(2):645-90. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00026.2014. Physiol Rev. 2015. PMID: 25834234 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of transient receptor potential channels by the phospholipase C pathway.Adv Biol Regul. 2013 Sep;53(3):341-55. doi: 10.1016/j.jbior.2013.07.004. Epub 2013 Jul 17. Adv Biol Regul. 2013. PMID: 23916247 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Clapham DE, Runnels LW, Strübing C. The TRP ion channel family. Nature Rev Neurosci. 2002;2:387–396. - PubMed
-
- Trebak M, Vazquez G, Bird GStJ, Putney JW., Jr The TRPC3/6/7 subfamily of cation channels. Cell Calcium. 2003;33:451–461. - PubMed
-
- Hardie RC. Regulation of trp channels via lipid second messengers. Ann Rev Physiol. 2003;65:735–759. - PubMed
-
- Dietrich A, Schnitzler M, Kalwa H, Storch U, Gudermann T. Functional characterization and physiological relevance of the TRPC3/6/7 subfamily of cation channels. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2005;371:257–265. - PubMed
-
- Trebak M, Bird GStJ, McKay RR, Birnbaumer L, Putney JW., Jr Signaling mechanism for receptor-activated TRPC3 channels. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:16244–16252. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

