Trypanosoma brucei RNA binding proteins p34 and p37 mediate NOPP44/46 cellular localization via the exportin 1 nuclear export pathway
- PMID: 17921352
- PMCID: PMC2168238
- DOI: 10.1128/EC.00176-07
Trypanosoma brucei RNA binding proteins p34 and p37 mediate NOPP44/46 cellular localization via the exportin 1 nuclear export pathway
Abstract
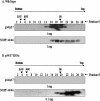
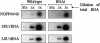
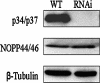
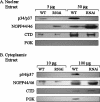
We have previously identified and characterized two novel nuclear RNA binding proteins, p34 and p37, which have been shown to interact with a family of nucleolar phosphoproteins, NOPP44/46, in Trypanosoma brucei. These proteins are nearly identical, the major difference being an 18-amino-acid insert in the N terminus of p37. In order to characterize the interaction between p34 and p37 and NOPP44/46, we have utilized an RNA interference (RNAi) cell line that specifically targets p34 and p37. Within these RNAi cells, we detected a disruption of a higher-molecular-weight complex containing NOPP44/46, as well as a dramatic increase in nuclear NOPP44/46 protein levels. We demonstrated that no change occurred in NOPP44/46 mRNA steady-state levels or stability, nor was there a change in cellular protein levels. These results led us to investigate whether p34 and p37 regulate NOPP44/46 cellular localization. Examination of the p34 and p37 amino acid sequences revealed a leucine-rich nuclear export signal, which interacts with the nuclear export factor exportin 1. Immune capture experiments demonstrated that p34, p37, and NOPP44/46 associate with exportin 1. When these experiments were performed with p34/p37 RNAi cells, NOPP44/46 no longer associated with exportin 1. Sequential immune capture experiments demonstrated that p34, p37, NOPP44/46, and exportin 1 exist in a common complex. Inhibiting exportin 1-mediated nuclear export led to an increase in nuclear NOPP44/46 proteins, indicating that they are exported from the nucleus via this pathway. Together, our results demonstrate that p34 and p37 regulate NOPP44/46 cellular localization by facilitating their association with exportin 1.
Figures

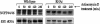


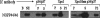

Similar articles
-
Assembly of the Trypanosoma brucei 60S ribosomal subunit nuclear export complex requires trypanosome-specific proteins P34 and P37.Eukaryot Cell. 2009 Jan;8(1):77-87. doi: 10.1128/EC.00234-08. Epub 2008 Aug 22. Eukaryot Cell. 2009. PMID: 18723605 Free PMC article.
-
Two families of RNA binding proteins from Trypanosoma brucei associate in a direct protein-protein interaction.Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2002 Jun;122(1):81-9. doi: 10.1016/s0166-6851(02)00076-2. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2002. PMID: 12076772
-
Two trypanosome-specific proteins are essential factors for 5S rRNA abundance and ribosomal assembly in Trypanosoma brucei.Eukaryot Cell. 2007 Oct;6(10):1766-72. doi: 10.1128/EC.00119-07. Epub 2007 Aug 22. Eukaryot Cell. 2007. PMID: 17715362 Free PMC article.
-
Exportin-mediated nuclear export of proteins and ribonucleoproteins.Results Probl Cell Differ. 2002;35:67-91. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-44603-3_4. Results Probl Cell Differ. 2002. PMID: 11791409 Review. No abstract available.
-
The STK38-XPO1 axis, a new actor in physiology and cancer.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 Mar;78(5):1943-1955. doi: 10.1007/s00018-020-03690-w. Epub 2020 Nov 3. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33145612 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Eukaryotic 5S rRNA biogenesis.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2011 Jul-Aug;2(4):523-33. doi: 10.1002/wrna.74. Epub 2011 Feb 25. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2011. PMID: 21957041 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Trypanosoma brucei life cycle switch TbPTP1 is structurally conserved and dephosphorylates the nucleolar protein NOPP44/46.J Biol Chem. 2010 Jul 16;285(29):22075-81. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.108860. Epub 2010 May 5. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20444707 Free PMC article.
-
The Cdc45·Mcm2-7·GINS protein complex in trypanosomes regulates DNA replication and interacts with two Orc1-like proteins in the origin recognition complex.J Biol Chem. 2011 Sep 16;286(37):32424-35. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.240143. Epub 2011 Jul 28. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21799014 Free PMC article.
-
Ribosome biogenesis in african trypanosomes requires conserved and trypanosome-specific factors.Eukaryot Cell. 2014 Jun;13(6):727-37. doi: 10.1128/EC.00307-13. Epub 2014 Apr 4. Eukaryot Cell. 2014. PMID: 24706018 Free PMC article.
-
A novel association between two trypanosome-specific factors and the conserved L5-5S rRNA complex.PLoS One. 2012;7(7):e41398. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0041398. Epub 2012 Jul 31. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22859981 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bassler, J., P. Grandi, O. Gadal, T. LeBmann, E. Petfalski, D. Tollervey, J. Lechner, and E. Hurt. 2001. Identification of a 60S preribosomal particle that is closely linked to nuclear export. Mol. Cell 8:517-529. - PubMed
-
- Bradford, M. M. 1976. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72:248-254. - PubMed
-
- Brown, T., and K. Mackey. 1997. Analysis of RNA by northern and slot blot hybridization, p. 4.9.1-4.9.16. In F. M. Ausubel, R. Brent, R. E. Kingston, D. D. Moore, J. G. Seidman, J. A. Smith, and K. Struhl (ed.), Current protocols in molecular biology. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York, NY.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

