Use of docking peptides to design modular substrates with high efficiency for mitogen-activated protein kinase extracellular signal-regulated kinase
- PMID: 17918909
- PMCID: PMC2597387
- DOI: 10.1021/cb700158q
Use of docking peptides to design modular substrates with high efficiency for mitogen-activated protein kinase extracellular signal-regulated kinase
Abstract
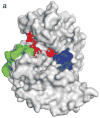
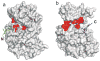
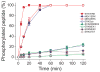
The mitogen-activated protein kinase extracellular regulated kinase (ERK) plays a key role in the regulation of cellular proliferation. Mutations in the ERK cascade occur in 30% of malignant tumors. Thus understanding how the kinase identifies its cognate substrates as well as monitoring the activity of ERK is central to cancer research and therapeutic development. ERK binds to its protein targets, both downstream substrates and upstream activators, via a binding site distinct from the catalytic site of ERK. The substrate sequences that bind, or dock, to these sites on ERK influence the efficiency of phosphorylation. For this reason, simple peptide substrates containing only phosphorylation sequences typically possess low efficiencies for ERK. Appending short docking peptides derived from full-length protein substrates and activators of ERK to a phosphorylation sequence increased the affinity of ERK for the phosphorylation sequence by as much as 200-fold while only slightly diminishing the maximal velocity of the reaction. The efficiency of the phosphorylation reaction was increased by up to 150-fold, while the specificity of the substrate for ERK was preserved. Simple modular peptide substrates, which can be easily tailored to possess high phosphorylation efficiencies, will enhance our understanding of the regulation of ERK and provide a tool for the development of new kinase assays.
Figures

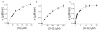
Similar articles
-
Effect of the DEF motif on phosphorylation of peptide substrates by ERK.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009 Sep 18;387(2):414-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.07.049. Epub 2009 Jul 15. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009. PMID: 19615338 Free PMC article.
-
Docking sites on mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) kinases, MAPK phosphatases and the Elk-1 transcription factor compete for MAPK binding and are crucial for enzymic activity.Biochem J. 2003 Mar 15;370(Pt 3):1077-85. doi: 10.1042/BJ20021806. Biochem J. 2003. PMID: 12529172 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple docking sites on substrate proteins form a modular system that mediates recognition by ERK MAP kinase.Genes Dev. 1999 Jan 15;13(2):163-75. Genes Dev. 1999. PMID: 9925641 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear export of the stress-activated protein kinase p38 mediated by its substrate MAPKAP kinase-2.Curr Biol. 1998 Sep 24;8(19):1049-57. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(98)70442-7. Curr Biol. 1998. PMID: 9768359 Review.
-
Atypical mitogen-activated protein kinases: structure, regulation and functions.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007 Aug;1773(8):1376-87. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2006.11.001. Epub 2006 Nov 7. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007. PMID: 17161475 Review.
Cited by
-
The Relationship between Effective Molarity and Affinity Governs Rate Enhancements in Tethered Kinase-Substrate Reactions.Biochemistry. 2020 Jun 16;59(23):2182-2193. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.0c00205. Epub 2020 Jun 1. Biochemistry. 2020. PMID: 32433869 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic discovery of linear binding motifs targeting an ancient protein interaction surface on MAP kinases.Mol Syst Biol. 2015 Nov 3;11(11):837. doi: 10.15252/msb.20156269. Mol Syst Biol. 2015. PMID: 26538579 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular-Regulated Kinases: Signaling From Ras to ERK Substrates to Control Biological Outcomes.Adv Cancer Res. 2018;138:99-142. doi: 10.1016/bs.acr.2018.02.004. Epub 2018 Mar 2. Adv Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 29551131 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quantification of a Pharmacodynamic ERK End Point in Melanoma Cell Lysates: Toward Personalized Precision Medicine.ACS Med Chem Lett. 2014 Oct 17;6(1):47-52. doi: 10.1021/ml500198b. eCollection 2015 Jan 8. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2014. PMID: 25589929 Free PMC article.
-
Examining docking interactions on ERK2 with modular peptide substrates.Biochemistry. 2011 Nov 8;50(44):9500-10. doi: 10.1021/bi201103b. Epub 2011 Oct 18. Biochemistry. 2011. PMID: 21955038 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cobb MH. MAP kinase pathways. Progress in Biophysics and Molecular Biology. 1999;71:479–500. - PubMed
-
- Lewis TS, Shapiro PS, Ahn NG. Signal transduction through MAP kinase cascades. Adv Cancer Res. 1998;74:49–139. - PubMed
-
- Bradham C, McClay DR. p38 MAPK in development and cancer. Cell Cycle. 2006;5:8. - PubMed
-
- Kaminska B. MAPK signalling pathways as molecular targets for anti-inflammatory therapy--from molecular mechanisms to therapeutic benefits. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Proteins & Proteomics. 2005;1754:253–262. - PubMed
-
- Manning AM, Davis RJ. Targeting JNK for therapeutic benefit: from junk to gold? Nature Reviews Drug Discovery. 2003;2:554–565. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

