Mycobacterium tuberculosis 6-kDa early secreted antigenic target (ESAT-6) protein downregulates lipopolysaccharide induced c-myc expression by modulating the extracellular signal regulated kinases 1/2
- PMID: 17915024
- PMCID: PMC2082026
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2172-8-24
Mycobacterium tuberculosis 6-kDa early secreted antigenic target (ESAT-6) protein downregulates lipopolysaccharide induced c-myc expression by modulating the extracellular signal regulated kinases 1/2
Abstract
Background: Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) causes death of 2-3 million people every year. The persistence of the pathogenic mycobacteria inside the macrophage occurs through modulation of host cell signaling which allows them, unlike the other non-pathogenic species, to survive inside the host. The secretory proteins of M. tuberculosis have gained attention in recent years both as vaccine candidates and diagnostic tools; they target the immune system and trigger a putatively protective response; however, they may also be involved in the clinical symptoms of the disease.
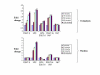
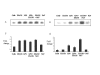
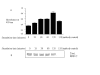
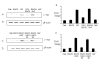
Results: Our studies showed that RD-1-encoded secretory protein ESAT-6 is involved in modulation of the mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase-signaling pathway inside the macrophage. ESAT-6 induced phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1/2 (ERK1/2) in the cytoplasm but not in the nucleus, which normally is the case for MAP kinases. ESAT-6 also antagonized LPS-induced ERK1/2 phosphorylation in the nucleus. Stimulation of cells by ESAT-6 along with sodium orthovanadate (a tyrosine phosphatase inhibitor) restored phosphorylation of ERK1/2 in the nucleus, suggesting active dephosphorylation of ERK1/2 by some putative phosphatase(s) in the nucleus. Further, ESAT-6 was found to down regulate the expression of LPS-inducible gene c-myc in an ERK1/2-dependent manner.
Conclusion: This study showed the effect of secretory proteins of M. tuberculosis in the modulation of macrophage signaling pathways particularly ERK1/2 MAP kinase pathway. This modulation appears to be achieved by limiting the ERK1/2 activation in the nucleus which ultimately affects the macrophage gene expression. This could be a mechanism by which secretory proteins of Mtb might modulate gene expression inside the macrophages.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Early Secreted Antigenic Target of 6 kDa of Mycobacterium tuberculosis Stimulates Macrophage Chemoattractant Protein-1 Production by Macrophages and Its Regulation by p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases and Interleukin-4.Scand J Immunol. 2016 Jul;84(1):39-48. doi: 10.1111/sji.12447. Scand J Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27154637
-
Mycobacterium tuberculosis secretory proteins CFP-10, ESAT-6 and the CFP10:ESAT6 complex inhibit lipopolysaccharide-induced NF-kappaB transactivation by downregulation of reactive oxidative species (ROS) production.Immunol Cell Biol. 2008 Jan;86(1):98-106. doi: 10.1038/sj.icb.7100117. Epub 2007 Oct 2. Immunol Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 17909563
-
The involvement of NADPH oxidase-mediated ROS in cytokine secretion from macrophages induced by Mycobacterium tuberculosis ESAT-6.Inflammation. 2014 Jun;37(3):880-92. doi: 10.1007/s10753-013-9808-7. Inflammation. 2014. PMID: 24408010
-
Nuclear export of the stress-activated protein kinase p38 mediated by its substrate MAPKAP kinase-2.Curr Biol. 1998 Sep 24;8(19):1049-57. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(98)70442-7. Curr Biol. 1998. PMID: 9768359 Review.
-
Immune regulatory activities of early secreted antigenic target of 6-kD protein of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and implications for tuberculosis vaccine design.Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2011 Dec;91 Suppl 1:S114-8. doi: 10.1016/j.tube.2011.10.020. Epub 2011 Dec 9. Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2011. PMID: 22169731 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Antitumor efficacy of viable tumor vaccine modified by heterogenetic ESAT-6 antigen and cytokine IL-21 in melanomatous mouse.Immunol Res. 2012 Jun;52(3):240-9. doi: 10.1007/s12026-012-8332-4. Immunol Res. 2012. PMID: 22477528
-
Mycobacterium tuberculosis-Secreted Protein, ESAT-6, Inhibits Lipopolysaccharide-Induced MMP-9 Expression and Inflammation Through NF-κB and MAPK Signaling in RAW 264.7 Macrophage Cells.Inflammation. 2020 Feb;43(1):54-65. doi: 10.1007/s10753-019-01087-x. Inflammation. 2020. PMID: 31720987
-
Mycobacterium tuberculosis secretory proteins downregulate T cell activation by interfering with proximal and downstream T cell signalling events.BMC Immunol. 2015 Nov 9;16:67. doi: 10.1186/s12865-015-0128-6. BMC Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26552486 Free PMC article.
-
Relative and Quantitative Phosphoproteome Analysis of Macrophages in Response to Infection by Virulent and Avirulent Mycobacteria Reveals a Distinct Role of the Cytosolic RNA Sensor RIG-I in Mycobacterium tuberculosis Pathogenesis.J Proteome Res. 2020 Jun 5;19(6):2316-2336. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.9b00895. Epub 2020 May 14. J Proteome Res. 2020. PMID: 32407090 Free PMC article.
-
ESAT-6 inhibits production of IFN-gamma by Mycobacterium tuberculosis-responsive human T cells.J Immunol. 2009 Mar 15;182(6):3668-77. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0803579. J Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19265145 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Malik Z, Iyer SS, Kusner DJ. Mycobacterium tuberculosis phagosomes exhibit altered calmodulin-dependent signal transduction: contribution to inhibition of phagosome-lysosome fusion and intracellular survival in human macrophages. J Immunol. 2001;166:3392–3401. - PubMed
-
- Malik ZA, Thompson CR, Hashimi S, Porter B, Iyer SS, Kusner DJ. Cutting edge: Mycobacterium tuberculosis blocks Ca2+ signaling and phagosome maturation in human macrophages via specific inhibition of sphingosine kinase. J Immunol. 2003;170:2811–2815. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

