The surprising kinetics of the T cell response to live antigenic cells
- PMID: 17911583
- PMCID: PMC2776090
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.179.8.4988
The surprising kinetics of the T cell response to live antigenic cells
Abstract
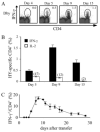
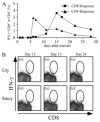
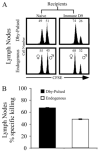
Cooperation between CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cells is required for the proper development of primary effector and memory CD8(+) T cells following immunization with noninflammatory immunogens. In this study, we characterized murine CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cell responses to male-specific minor histocompatibility (HY) Ags following injection of live male cells into females of the same strain. Male cells are rejected 10-12 days after transfer, coinciding with the expansion and effector function of CD8(+) CTLs to two H-2D(b)-restricted epitopes. Although anti-HY CD4(+) T cell responses are readily detectable day 5 posttransfer, CD8(+) responses are undetectable until day 10. The early CD4(+) response is not dependent on direct presentation of Ag by donor male cells, but depends on presentation of the male cells by recipient APC. The CD4(+) T cell response is required for the priming of CD8(+) T cell effector responses and rejection of HY-incompatible cells. Unexpectedly, HY-specific CD4(+) T cells are also capable of efficiently lysing target cells in vivo. The delay in the CD8(+) T cell response can be largely abrogated by depleting T cells from the male inoculum, and donor male CD8(+) T cells in particular suppress host anti-HY CD8(+) responses. These data demonstrate dramatic differences in host T cell responses to noninflammatory Ags compared with responses to pathogens. We explain the delayed CD8(+) response by proposing that there is a balance between cross-presentation of Ag by helper cell-licensed dendritic cells, on the one hand, and veto suppression by live male lymphocytes on the other.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflict of interest.
Figures

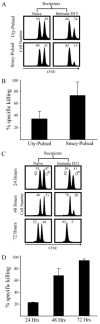
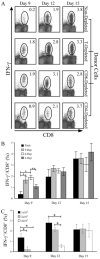
 ), or 4 × 107 (□) male UbC-GFP splenocytes and host T cell responses were measured at days 9, 12, and 15. Numbers represent the combined CD8+ T cell responses to Uty246–254 and Smcy738–746 measured by intracellular IFN-γ production. Error bars, SEM (n = 4 mice for each group) and are representative of two independent experiments. Statistically significant differences using Student's t test are indicated with * (p ≤ 0.02).
), or 4 × 107 (□) male UbC-GFP splenocytes and host T cell responses were measured at days 9, 12, and 15. Numbers represent the combined CD8+ T cell responses to Uty246–254 and Smcy738–746 measured by intracellular IFN-γ production. Error bars, SEM (n = 4 mice for each group) and are representative of two independent experiments. Statistically significant differences using Student's t test are indicated with * (p ≤ 0.02).Similar articles
-
Isolation of human CD4/CD8 double-positive, graft-versus-host disease-protective, minor histocompatibility antigen-specific regulatory T cells and of a novel HLA-DR7-restricted HY-specific CD4 clone.J Immunol. 2013 Jan 1;190(1):184-94. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1201163. Epub 2012 Dec 7. J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23225889
-
Glycoprotein 96 can chaperone both MHC class I- and class II-restricted epitopes for in vivo presentation, but selectively primes CD8+ T cell effector function.J Immunol. 2004 May 15;172(10):6087-92. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.172.10.6087. J Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15128793 Free PMC article.
-
The male minor transplantation antigen preferentially activates recipient CD4+ T cells through the indirect presentation pathway in vivo.J Immunol. 2003 Dec 15;171(12):6510-8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.171.12.6510. J Immunol. 2003. PMID: 14662851
-
Dissection of cytotoxic and helper T cell responses.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2005 Dec;62(23):2695-710. doi: 10.1007/s00018-005-5266-1. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2005. PMID: 16231088 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Timing of T Cell Priming and Cycling.Front Immunol. 2015 Nov 5;6:563. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2015.00563. eCollection 2015. Front Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26594213 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
KDEL receptor 1 regulates T-cell homeostasis via PP1 that is a key phosphatase for ISR.Nat Commun. 2015 Jun 17;6:7474. doi: 10.1038/ncomms8474. Nat Commun. 2015. PMID: 26081938 Free PMC article.
-
Intrinsic transgene immunogenicity gears CD8(+) T-cell priming after rAAV-mediated muscle gene transfer.Mol Ther. 2015 Apr;23(4):697-706. doi: 10.1038/mt.2014.235. Epub 2014 Dec 10. Mol Ther. 2015. PMID: 25492560 Free PMC article.
-
Splenocytes seed bone marrow of myeloablated mice: implication for atherosclerosis.PLoS One. 2015 Jun 3;10(6):e0125961. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0125961. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26038819 Free PMC article.
-
Blockade of gammac signals in combination with donor-specific transfusion induces cardiac allograft acceptance in murine models.J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2010 Aug;30(4):421-4. doi: 10.1007/s11596-010-0442-4. Epub 2010 Aug 17. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2010. PMID: 20714863
-
Cutting Edge: Roles for Batf3-Dependent APCs in the Rejection of Minor Histocompatibility Antigen-Mismatched Grafts.J Immunol. 2015 Jul 1;195(1):46-50. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1500669. Epub 2015 Jun 1. J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26034174 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Williams MA, Bevan MJ. Effector and memory CTL differentiation. Annu Rev Immunol. 2007;25:171–192. - PubMed
-
- Kaech SM, Wherry EJ, Ahmed R. Effector and memory T-cell differentiation: implications for vaccine development. Nat Rev Immunol. 2002;2:251–262. - PubMed
-
- Homann D, Teyton L, Oldstone MB. Differential regulation of antiviral T-cell immunity results in stable CD8+ but declining CD4+ T-cell memory. Nat Med. 2001;7:913–919. - PubMed
-
- Seder RA, Ahmed R. Similarities and differences in CD4+ and CD8+ effector and memory T cell generation. Nat Immunol. 2003;4:835–842. - PubMed
-
- Buller RM, Holmes KL, Hugin A, Frederickson TN, Morse HC., III Induction of cytotoxic T-cell responses in vivo in the absence of CD4 helper cells. Nature. 1987;328:77–79. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

