Co-expression of adjacent genes in yeast cannot be simply attributed to shared regulatory system
- PMID: 17910772
- PMCID: PMC2045684
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-8-352
Co-expression of adjacent genes in yeast cannot be simply attributed to shared regulatory system
Abstract
Background: Adjacent gene pairs in the yeast genome have a tendency to express concurrently. Sharing of regulatory elements within the intergenic region of those adjacent gene pairs was often considered the major mechanism responsible for such co-expression. However, it is still in debate to what extent that common transcription factors (TFs) contribute to the co-expression of adjacent genes. In order to resolve the evolutionary aspect of this issue, we investigated the conservation of adjacent pairs in five yeast species. By using the information for TF binding sites in promoter regions available from the MYBS database http://cg1.iis.sinica.edu.tw/~mybs/, the ratios of TF-sharing pairs among all the adjacent pairs in yeast genomes were analyzed. The levels of co-expression in different adjacent patterns were also compared.
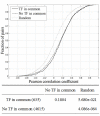
Results: Our analyses showed that the proportion of adjacent pairs conserved in five yeast species is relatively low compared to that in the mammalian lineage. The proportion was also low for adjacent gene pairs with shared TFs. Particularly, the statistical analysis suggested that co-expression of adjacent gene pairs was not noticeably associated with the sharing of TFs in these pairs. We further proposed a case of the PAC (polymerase A and C) and RRPE (rRNA processing element) motifs which co-regulate divergent/bidirectional pairs, and found that the shared TFs were not significantly relevant to co-expression of divergent promoters among adjacent genes.
Conclusion: Our findings suggested that the commonly shared cis-regulatory system does not solely contribute to the co-expression of adjacent gene pairs in yeast genome. Therefore we believe that during evolution yeasts have developed a sophisticated regulatory system that integrates both TF-based and non-TF based mechanisms(s) for concurrent regulation of neighboring genes in response to various environmental changes.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Genome-wide analysis of the cis-regulatory modules of divergent gene pairs in yeast.Genomics. 2010 Dec;96(6):352-61. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2010.08.008. Epub 2010 Sep 6. Genomics. 2010. PMID: 20826206
-
Genome-wide co-occurrence of promoter elements reveals a cis-regulatory cassette of rRNA transcription motifs in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Genome Res. 2002 Nov;12(11):1723-31. doi: 10.1101/gr.301202. Genome Res. 2002. PMID: 12421759 Free PMC article.
-
Inferring condition-specific modulation of transcription factor activity in yeast through regulon-based analysis of genomewide expression.PLoS One. 2008 Sep 3;3(9):e3112. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0003112. PLoS One. 2008. PMID: 18769540 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping yeast transcriptional networks.Genetics. 2013 Sep;195(1):9-36. doi: 10.1534/genetics.113.153262. Genetics. 2013. PMID: 24018767 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The N.C.Yeastract and CommunityYeastract databases to study gene and genomic transcription regulation in non-conventional yeasts.FEMS Yeast Res. 2021 Sep 11;21(6):foab045. doi: 10.1093/femsyr/foab045. FEMS Yeast Res. 2021. PMID: 34427650 Review.
Cited by
-
A low-temperature-responsive element involved in the regulation of the Arabidopsis thaliana At1g71850/At1g71860 divergent gene pair.Plant Cell Rep. 2016 Aug;35(8):1757-67. doi: 10.1007/s00299-016-1994-y. Epub 2016 May 23. Plant Cell Rep. 2016. PMID: 27215439
-
Genome-wide analysis of the effect of histone modifications on the coexpression of neighboring genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.BMC Genomics. 2010 Oct 9;11:550. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-11-550. BMC Genomics. 2010. PMID: 20932330 Free PMC article.
-
Histone modifications facilitate the coexpression of bidirectional promoters in rice.BMC Genomics. 2016 Sep 30;17(1):768. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-3125-0. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27716056 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear colocalization of transcription factor target genes strengthens coregulation in yeast.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Jan;40(1):27-36. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr689. Epub 2011 Aug 31. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 21880591 Free PMC article.
-
Co-expression of neighboring genes in the zebrafish (Danio rerio) genome.Int J Mol Sci. 2009 Aug 21;10(8):3658-3670. doi: 10.3390/ijms10083658. Int J Mol Sci. 2009. PMID: 20111688 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

