Forbidden penta-peptides
- PMID: 17893362
- PMCID: PMC2204130
- DOI: 10.1110/ps.073067607
Forbidden penta-peptides
Abstract
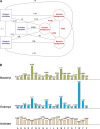
There are 3,200,000 amino acid sequences of length 5 (penta-peptides). Statistically, we expect to see a distribution of penta-peptides that is determined by the frequency of the participating amino acids. We show, however, that not only are there thousands of such penta-peptides that are absent from all known proteomes, but many of them are coded for multiple times in the non-coding genomic regions. This suggests a strong selection process that prevents these peptides from being expressed. We also show that the characteristics of these forbidden penta-peptides vary among different phylogenetic groups (e.g., eukaryotes, prokaryotes, and archaea). Our analysis provides the first steps toward understanding the "grammar" of the forbidden penta-peptides.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The origins of modern proteomes.Biochimie. 2007 Dec;89(12):1454-63. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2007.09.004. Epub 2007 Sep 15. Biochimie. 2007. PMID: 17949885
-
Proteomic signatures: amino acid and oligopeptide compositions differentiate among phyla.Proteins. 2004 Jan 1;54(1):20-40. doi: 10.1002/prot.10559. Proteins. 2004. PMID: 14705021
-
Estimation of phylogenetic inconsistencies in the three domains of life.Mol Biol Evol. 2008 Nov;25(11):2319-29. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msn176. Epub 2008 Aug 12. Mol Biol Evol. 2008. PMID: 18701430
-
Diversity and distribution of hemerythrin-like proteins in prokaryotes.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2008 Feb;279(2):131-45. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2007.01011.x. Epub 2007 Dec 12. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2008. PMID: 18081840 Review.
-
CRISPR--a widespread system that provides acquired resistance against phages in bacteria and archaea.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2008 Mar;6(3):181-6. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro1793. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18157154 Review.
Cited by
-
Predicting nucleosome binding motif set and analyzing their distributions around functional sites of human genes.Chromosome Res. 2012 Aug;20(6):685-98. doi: 10.1007/s10577-012-9305-0. Epub 2012 Jul 31. Chromosome Res. 2012. PMID: 22847645
-
Amino acid sequence repertoire of the bacterial proteome and the occurrence of untranslatable sequences.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Jun 28;113(26):7166-70. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1606518113. Epub 2016 Jun 15. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 27307442 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic DNA k-mer spectra: models and modalities.Genome Biol. 2009;10(10):R108. doi: 10.1186/gb-2009-10-10-r108. Epub 2009 Oct 8. Genome Biol. 2009. PMID: 19814784 Free PMC article.
-
Computational analysis of nascent peptides that induce ribosome stalling and their proteomic distribution in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.RNA. 2017 Jul;23(7):983-994. doi: 10.1261/rna.059188.116. Epub 2017 Mar 31. RNA. 2017. PMID: 28363900 Free PMC article.
-
The determinants of the rarity of nucleic and peptide short sequences in nature.NAR Genom Bioinform. 2024 Apr 4;6(2):lqae029. doi: 10.1093/nargab/lqae029. eCollection 2024 Jun. NAR Genom Bioinform. 2024. PMID: 38584871 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abe N. and Mamitsuka, H. 1997. Predicting protein secondary structure using stochastic tree grammars. J Mach Learn 29: 275–301.
-
- Alberts B., Johnson, A., Lewis, J., Raff, M., Roberts, K., and Walter, P. 2002. Molecular biology of the cell, 4th ed. Garland, New York.
-
- Benjamini Y. and Yekutieli, D. 2001. The control of the false discovery rate in multiple testing under dependency. Ann. Statist. 29: 1165–1188.
-
- Blaber M., Zhang, X.J., and Matthews, B.W. 1993. Structural basis of amino acid alpha helix propensity. Science 260: 1637–1640. - PubMed
-
- Bystroff C., Thorsson, V., and Baker, D. 2000. HMMSTR: A hidden Markov model for local sequence-structure correlations in proteins. J. Mol. Biol. 301: 173–190. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

