Computational design of antibody-affinity improvement beyond in vivo maturation
- PMID: 17891135
- PMCID: PMC2803018
- DOI: 10.1038/nbt1336
Computational design of antibody-affinity improvement beyond in vivo maturation
Abstract
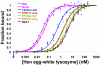
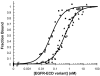
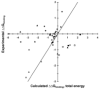
Antibodies are used extensively in diagnostics and as therapeutic agents. Achieving high-affinity binding is important for expanding detection limits, extending dissociation half-times, decreasing drug dosages and increasing drug efficacy. However, antibody-affinity maturation in vivo often fails to produce antibody drugs of the targeted potency, making further affinity maturation in vitro by directed evolution or computational design necessary. Here we present an iterative computational design procedure that focuses on electrostatic binding contributions and single mutants. By combining multiple designed mutations, a tenfold affinity improvement to 52 pM was engineered into the anti-epidermal growth factor receptor drug cetuximab (Erbitux), and a 140-fold improvement in affinity to 30 pM was obtained for the anti-lysozyme model antibody D44.1. The generality of the methods was further demonstrated through identification of known affinity-enhancing mutations in the therapeutic antibody bevacizumab (Avastin) and the model anti-fluorescein antibody 4-4-20. These results demonstrate computational capabilities for enhancing and accelerating the development of protein reagents and therapeutics.
Figures






Comment in
-
No free energy lunch.Nat Biotechnol. 2007 Oct;25(10):1109-10. doi: 10.1038/nbt1007-1109. Nat Biotechnol. 2007. PMID: 17921992 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Antibody Affinity Maturation by Computational Design.Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1827:15-34. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-8648-4_2. Methods Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 30196490
-
Affinity improvement of a therapeutic antibody by structure-based computational design: generation of electrostatic interactions in the transition state stabilizes the antibody-antigen complex.PLoS One. 2014 Jan 27;9(1):e87099. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0087099. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24475232 Free PMC article.
-
OptMAVEn--a new framework for the de novo design of antibody variable region models targeting specific antigen epitopes.PLoS One. 2014 Aug 25;9(8):e105954. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0105954. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25153121 Free PMC article.
-
Trends in therapeutic antibody affinity maturation: From in-vitro towards next-generation sequencing approaches.Immunol Lett. 2019 Aug;212:106-113. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2019.06.009. Epub 2019 Jun 24. Immunol Lett. 2019. PMID: 31247224 Review.
-
Computational design of antibodies.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2018 Aug;51:156-162. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2018.04.007. Epub 2018 May 20. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2018. PMID: 29791878 Review.
Cited by
-
Protein electrostatics: From computational and structural analysis to discovery of functional fingerprints and biotechnological design.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2020 Jun 30;18:1774-1789. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2020.06.029. eCollection 2020. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2020. PMID: 32695270 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Optimizing Antibody-Antigen Binding Affinities with the ADAPT Platform.Methods Mol Biol. 2023;2552:361-374. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-2609-2_20. Methods Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 36346603
-
Redesigning HVEM Interface for Selective Binding to LIGHT, BTLA, and CD160.Structure. 2020 Nov 3;28(11):1197-1205.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2020.07.013. Epub 2020 Aug 13. Structure. 2020. PMID: 32795404 Free PMC article.
-
Next generation of multispecific antibody engineering.Antib Ther. 2023 Dec 8;7(1):37-52. doi: 10.1093/abt/tbad027. eCollection 2024 Jan. Antib Ther. 2023. PMID: 38235376 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MoFvAb: Modeling the Fv region of antibodies.MAbs. 2015;7(5):838-52. doi: 10.1080/19420862.2015.1068492. MAbs. 2015. PMID: 26176812 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dahiyat BI, Mayo SL. De novo protein design: Fully automated sequence selection. Science. 1997;278:82–87. - PubMed
-
- Kuhlman B, et al. Design of a novel globular protein fold with atomic-level accuracy. Science. 2003;302:1364–1368. - PubMed
-
- Reina J, et al. Computer-aided design of a PDZ domain to recognize new target sequences. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2002;9:621–627. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

