ApoE4 disrupts sterol and sphingolipid metabolism in Alzheimer's but not normal brain
- PMID: 17888544
- PMCID: PMC2758772
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2007.07.024
ApoE4 disrupts sterol and sphingolipid metabolism in Alzheimer's but not normal brain
Abstract
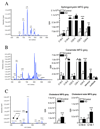
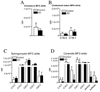
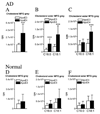
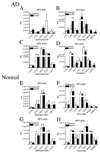
The epsilon 4 allele of ApoE is associated with an earlier onset and faster progression of Alzheimer's disease in patients with the familial form of this neurodegenerative condition. Although ApoE4 has been repeatedly associated with altered sphingomyelin and cholesterol levels in tissue culture and rodent models, there has not been a direct quantification of sphingomyelin or sterol levels in the brains of patients with different forms of ApoE. We measured the sphingolipid and sterol content of human brain tissues and found no evidence of perturbed sterol or sphingolipid biochemistry in the brains of individuals expressing ApoE4 who did not have a preexisting neurodegenerative condition. Nevertheless, ApoE4 was associated with gross abnormalities in the sterol and sphingolipid content of numerous brain regions in patients with Alzheimer's disease. The findings suggest that ApoE4 may not by itself alter sterol or sphingolipid metabolism in the brain under normal conditions, but that other neuropathologic changes of Alzheimer's are required to unmask the effect of ApoE4, and to perturb sterol and sphingolipid biochemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure statement. The authors have no actual or potential conflicts of interest related to this manuscript.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dysregulation of sphingolipid and sterol metabolism by ApoE4 in HIV dementia.Neurology. 2004 Aug 24;63(4):626-30. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000134662.19883.06. Neurology. 2004. PMID: 15326233
-
FTY720 decreases ceramides levels in the brain and prevents memory impairments in a mouse model of familial Alzheimer's disease expressing APOE4.Biomed Pharmacother. 2022 Aug;152:113240. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113240. Epub 2022 Jun 9. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022. PMID: 35689862
-
Intraneuronal amyloid-beta plays a role in mediating the synergistic pathological effects of apoE4 and environmental stimulation.J Neurochem. 2007 Nov;103(3):1031-40. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2007.04810.x. Epub 2007 Jul 31. J Neurochem. 2007. PMID: 17666042
-
Abeta-independent roles of apolipoprotein E4 in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease.Trends Mol Med. 2010 Jun;16(6):287-94. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2010.04.004. Epub 2010 May 27. Trends Mol Med. 2010. PMID: 20537952 Review.
-
ApoE4 May be a Promising Target for Treatment of Coronary Heart Disease and Alzheimer's Disease.Curr Drug Targets. 2018;19(9):1038-1044. doi: 10.2174/1389450119666180406112050. Curr Drug Targets. 2018. PMID: 29623835 Review.
Cited by
-
Circulating sphingolipids in relation to cognitive decline and incident dementia: The Cardiovascular Health Study.Alzheimers Dement (Amst). 2024 Aug 8;16(3):e12623. doi: 10.1002/dad2.12623. eCollection 2024 Jul-Sep. Alzheimers Dement (Amst). 2024. PMID: 39130802 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of Vitamin E and Other Fat-Soluble Vitamins on Alzheimer´s Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Oct 26;17(11):1785. doi: 10.3390/ijms17111785. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27792188 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An apolipoprotein E4 fragment can promote intracellular accumulation of amyloid peptide beta 42.J Neurochem. 2010 Nov;115(4):873-84. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2010.06756.x. J Neurochem. 2010. PMID: 20412390 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondria, cholesterol and amyloid beta peptide: a dangerous trio in Alzheimer disease.J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2009 Oct;41(5):417-23. doi: 10.1007/s10863-009-9242-6. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2009. PMID: 19784764 Review.
-
Mitochondrial cholesterol loading exacerbates amyloid beta peptide-induced inflammation and neurotoxicity.J Neurosci. 2009 May 20;29(20):6394-405. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4909-08.2009. J Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19458211 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bodovitz S, Klein WL. Cholesterol modulates alpha-secretase cleavage of amyloid precursor protein. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:4436–4440. - PubMed
-
- Bohnet K, Pillot T, Visvikis S, Sabolovic N, Siest G. Apolipoprotein (apo) E genotype and apoE concentration determine binding of normal very low density lipoproteins to HepG2 cell surface receptors. J Lipid Res. 1996;37:1316–1324. - PubMed
-
- Brown CM, Wright E, Colton CA, Sullivan PM, Laskowitz DT, Vitek MP. Apolipoprotein E isoform mediated regulation of nitric oxide release. Free Radic Biol Med. 2002;32:1071–1075. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AG023471-02/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG023471-03/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG023471/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG05146/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG024984/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG023471/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 MH075673/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005146/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AG034849/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG023471-05/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH077542/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- AG24984/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH077542-01A2/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG023471-04/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG023471-01/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH077542-02/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

