Clinical and serological features of patients with autoantibodies to GW/P bodies
- PMID: 17870671
- PMCID: PMC2147044
- DOI: 10.1016/j.clim.2007.07.016
Clinical and serological features of patients with autoantibodies to GW/P bodies
Abstract
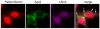
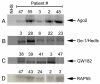
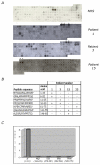
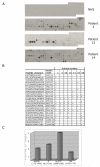
GW bodies (GWBs) are unique cytoplasmic structures involved in messenger RNA (mRNA) processing and RNA interference (RNAi). GWBs contain mRNA, components of the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC), microRNA (miRNA), Argonaute proteins, the Ge-1/Hedls protein and other enzymes involving mRNA degradation. The objective of this study was to identify the target GWB autoantigens reactive with 55 sera from patients with anti-GWB autoantibodies and to identify clinical features associated with these antibodies. Analysis by addressable laser bead immunoassay (ALBIA) and immunoprecipitation of recombinant proteins indicated that autoantibodies in this cohort of anti-GWB sera were directed against Ge-1/Hedls (58%), GW182 (40%) and Ago2 (16%). GWB autoantibodies targeted epitopes that included the N-terminus of Ago2 and the nuclear localization signal (NLS) containing region of Ge-1/Hedls. Clinical data were available on 42 patients of which 39 were female and the mean age was 61 years. The most common clinical presentations were neurological symptoms (i.e. ataxia, motor and sensory neuropathy) (33%), Sjögren's syndrome (SjS) (31%) and the remainder had a variety of other diagnoses that included systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC). Moreover, 44% of patients with anti-GWB antibodies had reactivity to Ro52. These studies indicate that Ge-1 is a common target of anti-GWB sera and the majority of patients in a GWB cohort had SjS and neurological disease.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Autoantibodies to GW bodies and other autoantigens in primary biliary cirrhosis.Clin Exp Immunol. 2011 Feb;163(2):147-56. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2010.04288.x. Epub 2010 Nov 22. Clin Exp Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21091667 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical and serological associations of autoantibodies to GW bodies and a novel cytoplasmic autoantigen GW182.J Mol Med (Berl). 2003 Dec;81(12):811-8. doi: 10.1007/s00109-003-0495-y. Epub 2003 Nov 4. J Mol Med (Berl). 2003. PMID: 14598044
-
Autoantibodies to mRNA processing pathways (glycine and tryptophan-rich bodies antibodies): prevalence and clinical utility in a South Australian cohort.Pathology. 2019 Dec;51(7):723-726. doi: 10.1016/j.pathol.2019.07.008. Epub 2019 Oct 17. Pathology. 2019. PMID: 31630877
-
Autoantibodies and their target antigens in Sjögren's syndrome.Neth J Med. 1992 Apr;40(3-4):140-7. Neth J Med. 1992. PMID: 1603204 Review.
-
Sjögren's syndrome: autoantibodies to cellular antigens. Clinical and molecular aspects.Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2000 Sep;123(1):46-57. doi: 10.1159/000024423. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2000. PMID: 11014971 Review.
Cited by
-
Establishment of international autoantibody reference standards for the detection of autoantibodies directed against PML bodies, GW bodies, and NuMA protein.Clin Chem Lab Med. 2020 Aug 10;59(1):197-207. doi: 10.1515/cclm-2020-0981. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2020. PMID: 32776893 Free PMC article.
-
Mammalian stress granules and P bodies at a glance.J Cell Sci. 2020 Sep 1;133(16):jcs242487. doi: 10.1242/jcs.242487. J Cell Sci. 2020. PMID: 32873715 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The miR-17 ∼ 92 Cluster: A Key Player in the Control of Inflammation during Rheumatoid Arthritis.Front Immunol. 2013 Mar 19;4:70. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2013.00070. eCollection 2013. Front Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23516027 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-146a in autoimmunity and innate immune responses.Ann Rheum Dis. 2013 Apr;72 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):ii90-5. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-202203. Epub 2012 Dec 19. Ann Rheum Dis. 2013. PMID: 23253933 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systematic Analysis of Differential Expression Profile in Rheumatoid Arthritis Chondrocytes Using Next-Generation Sequencing and Bioinformatics Approaches.Int J Med Sci. 2018 Jul 13;15(11):1129-1142. doi: 10.7150/ijms.27056. eCollection 2018. Int J Med Sci. 2018. PMID: 30123050 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fritzler MJ, Wiik A. Autoantibody Assays, Testing, and Standardization. In: Rose NR, Mackay IR, editors. The Autoimmune Diseases. Elsevier Academic Press; Syndey: 2006. pp. 1011–1022.
-
- Lerner MR, Boyle JA, Hardin JA, Steitz JA. Two novel classes of small ribonucleoproteins detected by antibodies associated with lupus erythematosus. Science. 1981;211:400–402. - PubMed
-
- Padgett RA, Mount SM, Steitz JA, Sharp PA. Splicing of messenger RNA precursors is inhibited by antisera to small nuclear ribonucleoprotein. Cell. 1983;35:101–107. - PubMed
-
- Craft J. Antibodies to snRNPs in systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheum Dis Clin N A. 1992;18:311–335. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

