Differential regulation of iron chelator-induced IL-8 synthesis via MAP kinase and NF-kappaB in immortalized and malignant oral keratinocytes
- PMID: 17850672
- PMCID: PMC2078595
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-7-176
Differential regulation of iron chelator-induced IL-8 synthesis via MAP kinase and NF-kappaB in immortalized and malignant oral keratinocytes
Abstract
Background: Interleukin-8 (IL-8) is a cytokine that plays an important role in tumor progression in a variety of cancer types; however, its regulation is not well understood in oral cancer cells. In the present study, we examined the expression and mechanism of IL-8 in which it is involved by treating immortalized (IHOK) and malignant human oral keratinocytes (HN12) cells with deferoxamine (DFO).
Methods: IL-8 production was measured by an enzyme-linked immunoabsorbent assay and reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) analysis. Electrophoretic mobility shift assays was used to determine NF-kappaB binding activity. Phosphorylation and degradation of the I-kappaB were analyized by Western blot.
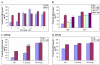
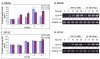
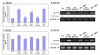
Results: IHOK cells incubated with DFO showed increased expression of IL-8 mRNA, as well as higher release of the IL-8 protein. The up-regulation of DFO-induced IL-8 expression was higher in IHOK cells than in HN12 cells and was concentration-dependent. DFO acted additively with IL-1beta to strongly up-regulate IL-8 in IHOK cells but not in HN12 cells. Accordingly, selective p38 and ERK1/2 inhibitors for both kinases abolished DFO-induced IL-8 expression in both IHOK and HN12 cells. Furthermore, DFO induced the degradation and phosphorylation of IkappaB, and activation of NF-kappaB. The IL-8 inducing effects of DFO were mediated by a nitric oxide donor (S-nitrosoglutathione), and by pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate, an inhibitor of NF-kappaB, as well as by wortmannin, which inhibits the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-dependent activation of NAD(P)H oxidase.
Conclusion: This results demonstrate that DFO-induced IL-8 acts via multiple signaling pathways in immortalized and malignant oral keratinocytes, and that the control of IL-8 may be an important target for immunotheraphy against human oral premalignant lesions.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Iron chelator differentially activates macrophage inflammatory protein-3alpha/CCL20 in immortalized and malignant human oral keratinocytes.Arch Oral Biol. 2008 Sep;53(9):801-9. doi: 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2008.01.015. Epub 2008 Mar 7. Arch Oral Biol. 2008. PMID: 18328460
-
Iron chelator-induced growth arrest and cytochrome c-dependent apoptosis in immortalized and malignant oral keratinocytes.J Oral Pathol Med. 2006 Apr;35(4):218-26. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0714.2006.00415.x. J Oral Pathol Med. 2006. PMID: 16519769
-
Transcriptional regulation of IL-8 by iron chelator in human epithelial cells is independent from NF-kappaB but involves ERK1/2- and p38 kinase-dependent activation of AP-1.J Cell Biochem. 2007 Dec 15;102(6):1442-57. doi: 10.1002/jcb.21367. J Cell Biochem. 2007. PMID: 17471497
-
p38 and ERK MAP kinase mediates iron chelator-induced apoptosis and -suppressed differentiation of immortalized and malignant human oral keratinocytes.Life Sci. 2006 Sep 5;79(15):1419-27. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2006.04.011. Epub 2006 Apr 26. Life Sci. 2006. PMID: 16697418
-
Involvement of mitogen-activated protein kinases and nuclear factor-kappa B activation in nitric oxide-induced interleukin-8 expression in human pulp cells.Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2008 May;105(5):654-60. doi: 10.1016/j.tripleo.2007.11.011. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2008. PMID: 18442745
Cited by
-
Mucus increases cell iron uptake to impact the release of pro-inflammatory mediators after particle exposure.Sci Rep. 2023 Mar 9;13(1):3925. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-30335-2. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36894564 Free PMC article.
-
Air pollutants disrupt iron homeostasis to impact oxidant generation, biological effects, and tissue injury.Free Radic Biol Med. 2020 May 1;151:38-55. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2020.02.007. Epub 2020 Feb 21. Free Radic Biol Med. 2020. PMID: 32092410 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cigarette Smoke Particle-Induced Lung Injury and Iron Homeostasis.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2022 Jan 12;17:117-140. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S337354. eCollection 2022. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2022. PMID: 35046648 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quartz Disrupts Iron Homeostasis in Alveolar Macrophages To Impact a Pro-Inflammatory Effect.Chem Res Toxicol. 2019 Sep 16;32(9):1737-1747. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrestox.8b00301. Epub 2019 Aug 26. Chem Res Toxicol. 2019. PMID: 31407890 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro Lung Epithelial Cell Model Reveals Novel Roles for Pseudomonas aeruginosa Siderophores.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Oct 16:2023.01.26.525796. doi: 10.1101/2023.01.26.525796. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Microbiol Spectr. 2024 Mar 5;12(3):e0369323. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.03693-23. PMID: 36747656 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Licciardello JT, Spitz MR, Hong WK. Multiple primary cancer in patients with cancer of the head and neck : Second cancer of the head and neck, esophagus, and lung. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1989;17:467–476. - PubMed
-
- Silverman S, Jr, Bahl S. Oral lichen planus update: clinical characteristics, treatment responses, and malignant transformation. Am J Dent. 1997;10:259–263. - PubMed
-
- McCann J. Texas center studies research alternative treatments. J Natl Inst. 1997;89:1485–1486. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

